Wishing to become a Network Engineer? Want to get familiar with the top Network Engineer skills required to excel in IT? Leave all of your worries at bay and read this blog till the end to understand the skills better.
What are the fundamental roles of a Network Engineer?
The fundamental roles of a Network Engineer are as follows-
- Strategizing and designing network infrastructure.
- Setting up routers, switches, firewalls, and other network equipment.
- Deploying and integrating network hardware and software.
- Establishing and managing connectivity among devices and servers.
- Regularly updating security components.
- Diagnosing and resolving network issues.
Note: Read Network Engineer Roles and Responsibilities in Detail
Why are Network Engineers crucial in today's digital landscape?
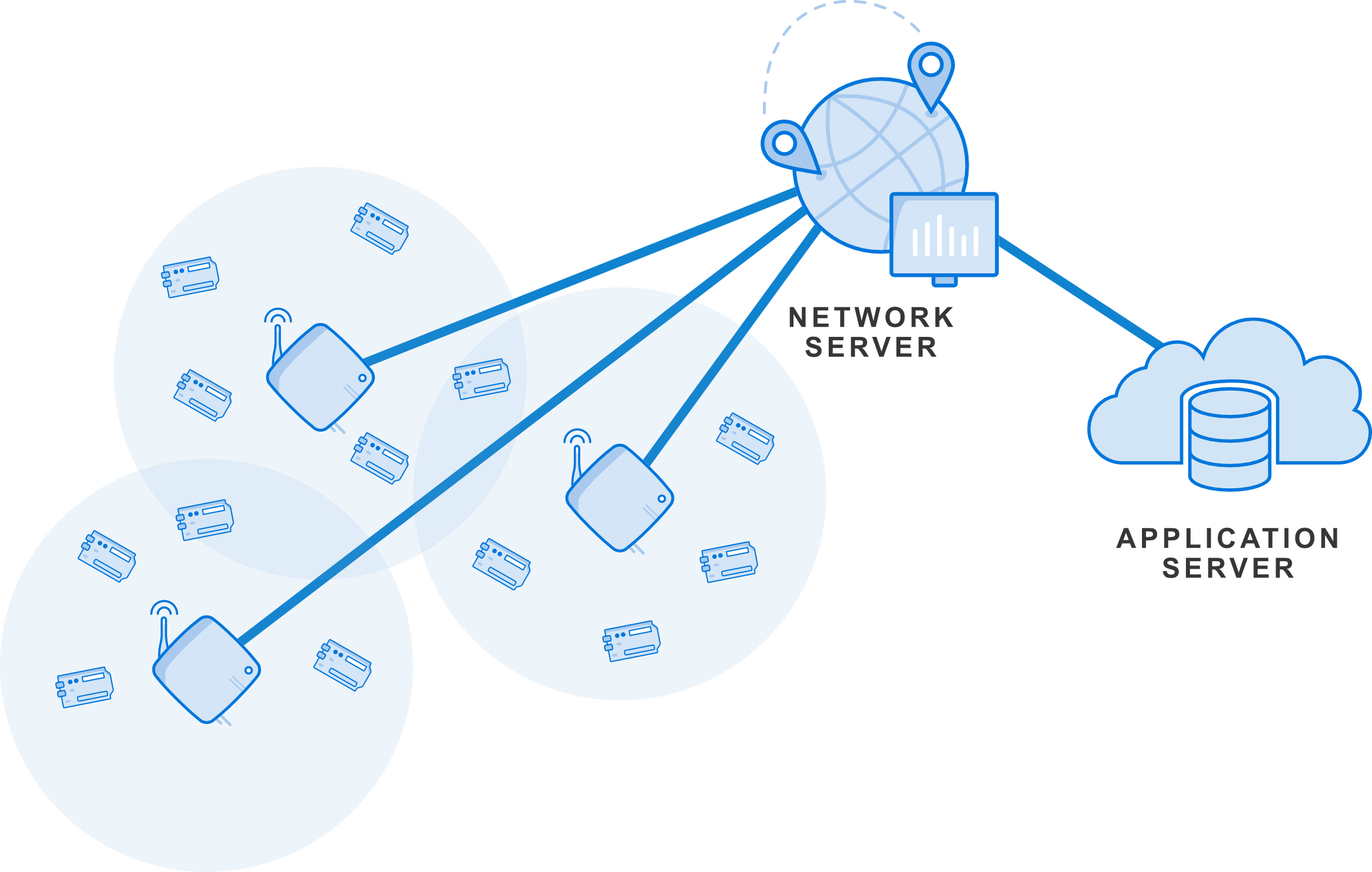
Network Engineers are crucial in today’s digital landscape since they design, implement, and maintain complex network infrastructure. Due to the rapid expansion of technology and the increasing reliance on interconnected systems, network engineers ensure seamless communication and data exchange by optimizing network performance, troubleshooting issues, and bolstering security measures to defend against cyber threats. Undoubtedly, Network Engineers serve as the backbone of connectivity, facilitating the flow of information critical for businesses, institutions, and individuals alike.
What are the top Network Engineer skills required to excel in IT?
The top Network Engineer skills required to excel in IT are as follows-
Network Fundamentals
What are the basic principles of networking?
The basic principles of networking are routers, switches, and wireless access points since they help in seamless communication between diverse devices.
How do network topologies function?
Network topologies provide insight into the network by visualizing the physical connection of devices and the data flow within the network.
What are the OSI and TCP/IP models?
OSI model refers to the Open System Interconnection model. It enables diverse communication systems to communicate via standard protocols.
TCP/IP models refer to Transmission Control Protocol and Internet Protocol. These are used to interconnect network devices.
Network Protocols
What are the common network protocols?
There are mainly three types of network protocols, namely-
> Network Communication Protocol: NCPs determine the rules and formats to transfer data across the networks. A few NCPs are as follows-
- Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol (HTTP)
- Transmission Control Protocol (TCP)
- Internet Protocol (IP)
- User Datagram Protocol (UDP)
- File Transfer Protocol (FTP)
> Network Security Protocol: NSPs ensure secure data transmission over the network connections. A few NSPs are as follows-
- Secure File Transfer Protocol (SFTP)
- Hyper-Text Transfer Protocol Secure (HTTPS)
- Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
> Network Management Protocol: NMPs ensure quick troubleshooting across the network. A few NMPs are as follows-
- Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)
- Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP)
How do protocols like TCP, UDP, and ICMP function within a network?
TCP is a reliable protocol but has a slow speed and is more complex than UDP.
UDP is fast and simple, but less reliable and more prone to errors than TCP.
ICMP is used for network management and troubleshooting.
What are the differences between IPv4 and IPv6?
IPv4 uses 32-bit addresses, while IPv6 uses 128-bit addresses, allowing for vastly more unique addresses in IPv6.
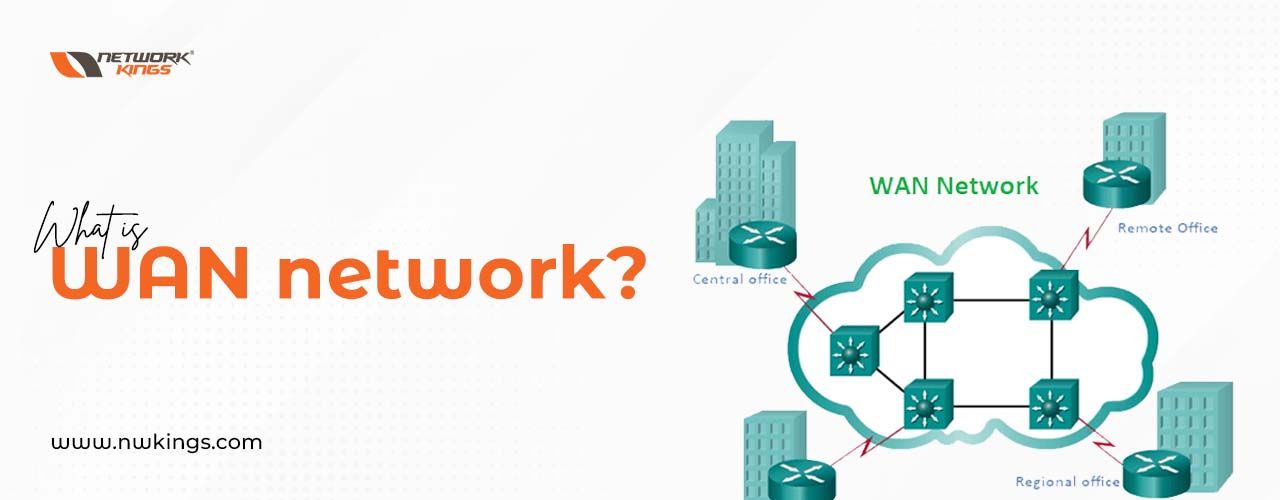
Routing and Switching
What is the role of routers and switches in a network?
Routers determine the best path for data to travel between networks, while switches direct data within a single network.
How do routing protocols such as OSPF, BGP, and EIGRP operate?
BGP is a networking protocol that exchanges routing data among autonomous systems.
OSPF is a link-state routing protocol to find the optimum path between the source and the destination router.
EIGRP is a distance-vector protocol for automating routing configuration and decisions on a network.
What are VLANs, and how do they enhance network efficiency?
VLANs manage network traffic by dividing the network into different broadcast domains. This ensures broadcast traffic is only sent to devices in the same VLAN, reducing unnecessary load and refining overall network performance. Enhanced security.
Network Security
What are the fundamental principles of network security?
The fundamental principles of network security are as follows-
- Defense in Depth
- Least Privilege
- Principle of Least Astonishment
- Separation of Duties
- Access Control
- Secure Configuration
- Confidentiality
- Integrity
- Availability
- Authentication and Authorization
What are common security threats?
The most common security threats are as follows-
- Malware
- Phishing
- DDoS Attacks (Distributed Denial of Service)
- Ransomware
- Insider Threats
- Man-in-the-Middle Attacks
- SQL Injection
- Cross-Site Scripting (XSS)
- Zero-Day Exploits
- Social Engineering
Network Automation
What is network automation?
Network automation refers to the process of automating the configuration, management, and operation of network devices and infrastructure. It involves using software tools and scripts to streamline repetitive tasks, improve efficiency, and enhance network reliability. Network automation enables faster deployment, better scalability, and more agile responses to changing network requirements.
How can automation streamline network configuration, management, and troubleshooting?
Automation can streamline network configuration, management, and troubleshooting. A few of the features are as follows-
- Automation can deploy network configurations across multiple devices, reducing the time and effort required for manual setup.
- Automated processes ensure uniformity in network configurations.
- Automation scales easily to manage large and complex networks.
- Automated monitoring and diagnostic tools can quickly identify and rectify network issues.
- By automating routine tasks, network engineers can focus on strategic planning, innovation, and addressing more complex challenges.
Network Troubleshooting
What are common network problems?
The common network problems are listed as follows-
- Connectivity Issues
- Slow Network Performance
- Packet Loss
- Network Congestion
- DNS Resolution Problems
- IP Address Conflicts
- Security Breaches
- Hardware Failures
- Configuration Errors
- Routing Issues
Performance Monitoring and Optimization
How can network performance be monitored effectively?
Network performance can be monitored effectively using the given measures-
- Network Monitoring Tools
- Performance Metrics Tracking
- Bandwidth Utilization Monitoring
- Packet Analysis
- SNMP (Simple Network Management Protocol)
- Flow Monitoring (NetFlow, sFlow)
- Latency Monitoring
- End-to-End Testing
- Real-time Alerts and Notifications
- Historical Data Analysis
How can network engineers optimize performance?
Network Engineers can optimize performance using the given measures-
- Traffic Prioritization
- Quality of Service (QoS) Configuration
- Load Balancing
- Traffic Shaping
- Network Segmentation
- Optimization of Routing Protocols
- Protocol Optimization
- Bandwidth Management
- Network Performance Tuning
- Capacity Planning
Cloud and Virtualization
What is the role of cloud computing in modern networking?
The role of cloud computing in modern networking is as follows-
- Scalability
- Flexibility
- Cost Reduction
- Disaster Recovery
- Virtualization
Continuous Learning and Adaptability
What are effective strategies for adapting to changes in network technology?
The effective strategies for adapting to changes in network technology are as follows-
- Continuous Learning and Skill Development
- Agile Network Design and Implementation
- Regular Technology Assessments and Updates
- Collaboration with Industry Peers and Experts
- Flexible Network Architecture Design
Recap of Essential Skills for Network Engineers
The top Network Engineer skills required are mentioned as follows-
- Network Fundamentals
- Network Protocols
- Routing & Switching
- Network Security
- Network Automation
- Network Troubleshooting
- Performance Monitoring & Optimization
- Cloud & Virtualization
- Continuous Learning & Adaptability
How to Become a Network Engineer? - Roadmap
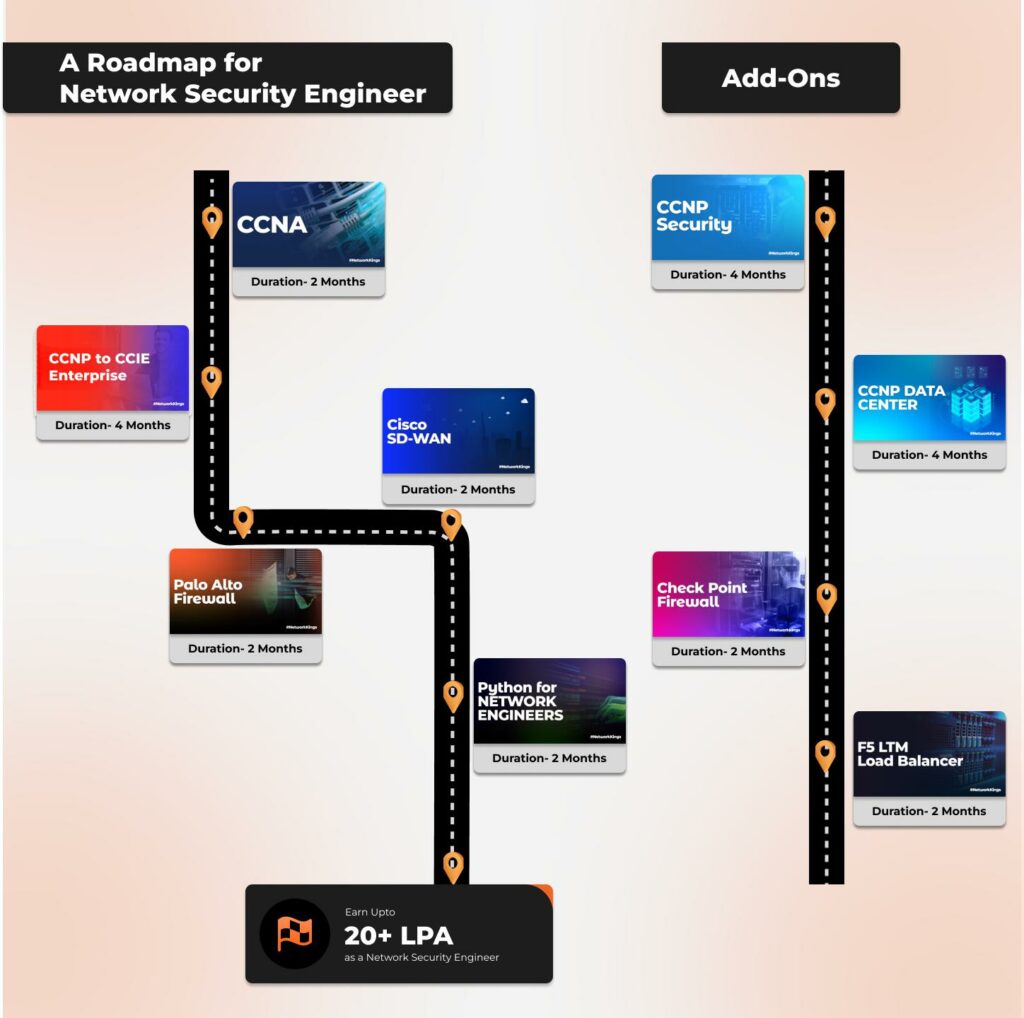
To become a Network Engineer, you must follow the Network Kings’ created roadmap-
Enroll in the Network Kings Network Engineer Master Program, where you will learn CCNA, CCNP Enterprise, and Palo Alto Firewall courses in detail.
You can also enroll on our All Access Pass comprising 50+ IT Networking, Cloud, Cybersecurity, and DevOps courses to master the network security roadmap in depth.
The perks of choosing Network Kings as your learning partner are as follows-
- Live sessions that are recorded for future reference.
- Career guidance to ensure successful professional trajectories.
- Live training sessions for real-time learning experiences.
- Receipt of a completion certificate to officially validate acquired skills.
- Flexible learning options to accommodate individual schedules.
- Training led by industry experts to guarantee relevant and up-to-date knowledge.
What are the salary aspects for a Network Engineer?
The salary aspects for a Network Engineer in different countries are mentioned as follows-
- United States – USD 80,000 to USD 120,000 per year
- Canada – CAD 70,000 to CAD 110,000 per year
- United Kingdom – GBP 45,000 to GBP 70,000 per year
- Germany – EUR 50,000 to EUR 80,000 per year
- France – EUR 45,000 to EUR 70,000 per year
- Spain – EUR 35,000 to EUR 55,000 per year
- Italy – EUR 40,000 to EUR 65,000 per year
- Australia – AUD 90,000 to AUD 130,000 per year
- New Zealand – NZD 80,000 to NZD 120,000 per year
- United Arab Emirates – AED 150,000 to AED 200,000 per year
- Singapore – SGD 80,000 to SGD 120,000 per year
- India – INR 600,000 to INR 1,200,000 per year
- China – CNY 200,000 to CNY 400,000 per year
- Brazil – BRL 100,000 to BRL 150,000 per year
- South Africa – ZAR 400,000 to ZAR 600,000 per year
Wrapping Up!
The top Network Engineer skills required to land a highly-paying job in the industry can be learnt at Network Kings. Therefore, enroll today to begin framing your dream career. Feel free to reach us regarding any of your queries.
Happy Learning!









.jpg)











/Complete-Guide-to-%E2%80%93-2.png)