Are you in search of an explanation about what is LAN (local area network) and how it operates? Perplexed by all the technical lingo surrounding this tech? Then look no more. In this blog, we will cover whatever you need to be aware of regarding Local Area Networks: from their fundamental components right through to networking principles for wired connections.
We will delve deep into the technology, explain its benefits to you personally, and offer some handy advice on getting the very best out of your local area set-up! So come with us as we probe further into the realm of LANs – broadening our knowledge base around such exciting tech!
Understanding the Concept of What is LAN and Its Basics
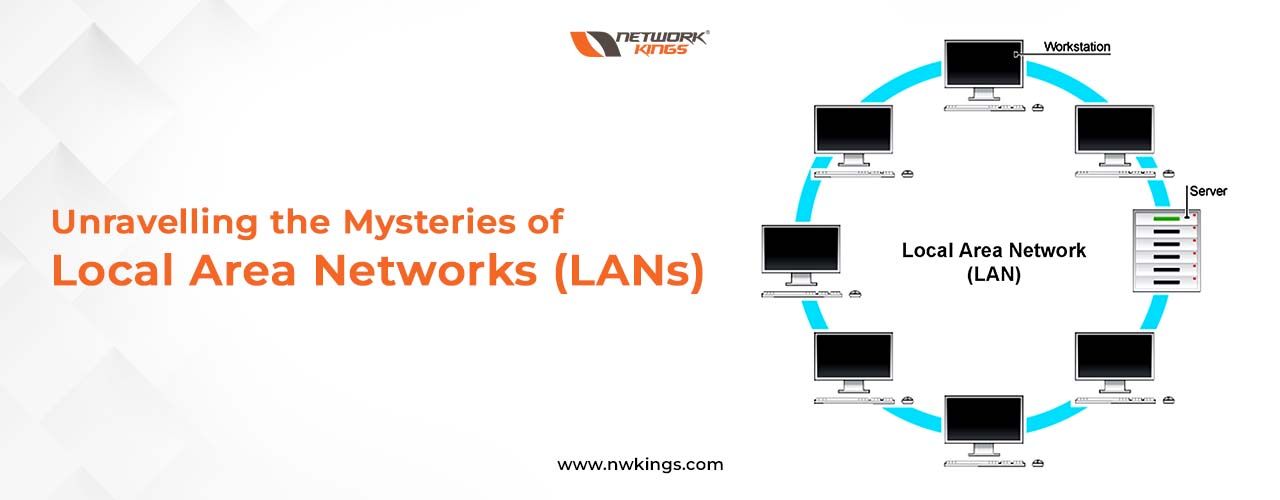
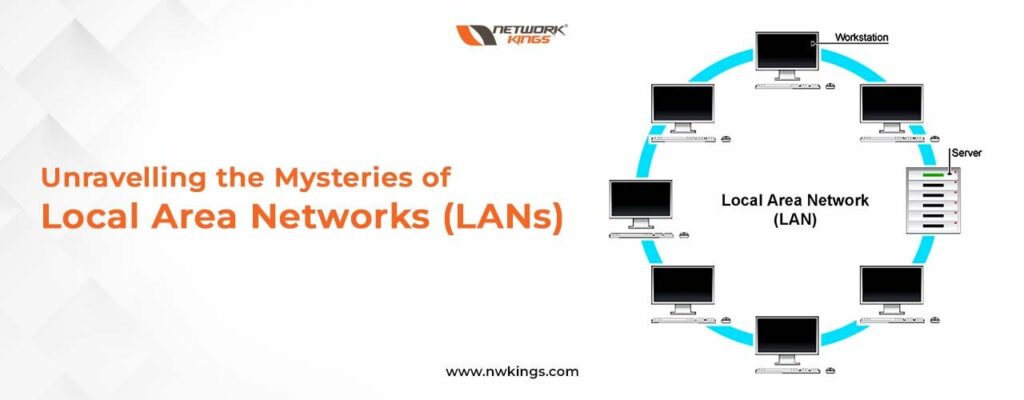
Today, a local area network (LAN) is now an essential part of our present-day lives; providing us with the ability to communicate and share data within a localized space. Understanding the fundamentals of LANs as well as their overall concept is paramount for anybody intending to set up or use one that already exists. On a basic level, establishing your own LAN requires at least two computers linked together through some form of physical medium – be it cables or wireless technology- so they can interact with each other utilizing applications and protocols specific to this purpose.
The main aim of creating a LAN is usually to let users work together on documents, share facilities such as printers and scanners, and access the internet from various devices without extra cabling. This makes it more user-friendly than having several single network connections all over the system. Plus, LANs can be employed for transmitting confidential data securely inside a limited area – since they commonly need authentication before getting any shared asset or service. Crafting up a LAN is pretty straightforward if you just get your head around its fundamentals! What could be easier?
Firstly, you will need two or more computers with an operating system installed. You can connect them using physical cables such as Ethernet wires, or wirelessly; through Wi-Fi connections and Bluetooth. Depending on your set-up, you may also require routers and hubs – these divide the traffic between different parts of a LAN network (local area network) or route it beyond that particular boundary. Lastly for everything to work correctly the configuration must match what’s needed; like setting up IP addresses DHCP servers which will allocate unique local IPs for every connected device automatically!
Evolution and History of Local Area Networks

When it comes to connecting computers, the local area network or LAN has become one of the most common means available today. Although its form and function have come a long way since being first introduced in the late 1970s. Initially, just two PCs connected by a single cable could be regarded as LAN; however, with advancing technology more complex networks can be set up nowadays – what wonders we can achieve!
In the 1980s, Ethernet cables were developed and this revolutionised data transfer within a LAN. Speeds increased dramatically compared to previously available options – leading to the development of hubs and switches which are now indispensable components of modern networks. Moreover, today’s local area networks (LANs) can even boast wireless connections making them more efficient while also user-friendly. Who would have thought that connecting devices could be made so fast AND convenient?!
Wi-Fi routers have had a major impact on how people can link up to their local area networks so they don’t need to fret about all the tangled cable around their house or workplace. Furthermore, plenty of businesses now use Virtual Local Area Networks (VLANs) as an additional layer of security for delicate information that must be kept safe from potential dangers outside. To put it in a nutshell, LANs have grown tremendously since they first began and keep changing with technological advances.
The advantages are numerous; enhanced safety measures against cyber threats along with increased ease when obtaining shared resources on various gadgets; which makes them essential components of any business or home network system these days. What’s more, using them is undoubtedly one way you can stay ahead in today’s digital world – but do you know enough to make sure your data remains secure?
Fundamental Components that Make up a LAN

It is key to get a grasp of what exactly LAN is, so it is important to identify its main components. This can help us realise how those parts work together and maximise our Local Area Network usage. Let us begin by looking into two principal elements that make up a LAN: machines and network interface cards (NIC). Computers are used for running programs, remember data – this is where all your labour comes in place!
The Network Interface Card (NIC) is what binds them together, using either wires or Wi-Fi. This enables devices to send and receive data through a shared medium – think of it as the digital equivalent of a telephone line. Depending on your own needs for speediness versus cost, you might opt for cables made out of copper or fibre optics. Copper’s cheaper but slower whereas fibres are pricier but faster; if neither appeal then wireless signals can also be used instead so everything doesn’t have to be physically connected up at once.
Are you looking to get more out of your connection? Switches are here to help! They act like an active hub, allowing multiple computers to communicate without interfering with each other. It essentially means that different users can access the same services simultaneously – and speeds vary depending on requirements. So if one user needs a faster connection than another; they will be able to accommodate both seamlessly.
Finally, there are routers which act as a go-between for your network and the wider world. They oversee traffic coming in from other networks while allowing communications within your network to pass through freely without external disturbances or security breaches. Routers also boast additional features such as firewalls, failover prevention and virtual private networking (VPN) capabilities – making them an absolute must when it comes to any secure home or corporate setup.
These four components collectively constitute the bedrock of any local area network setup; working together seamlessly so that users get reliable connections capable of managing even massive volumes of data with no chance of collapse under pressure! When planning on setting up a personal/business network then take into account these crucial bits – computers, NIC cards cabling and routers – they will be fundamental in getting you connected quickly but most importantly securely!
Importance of LAN in the World of Technology
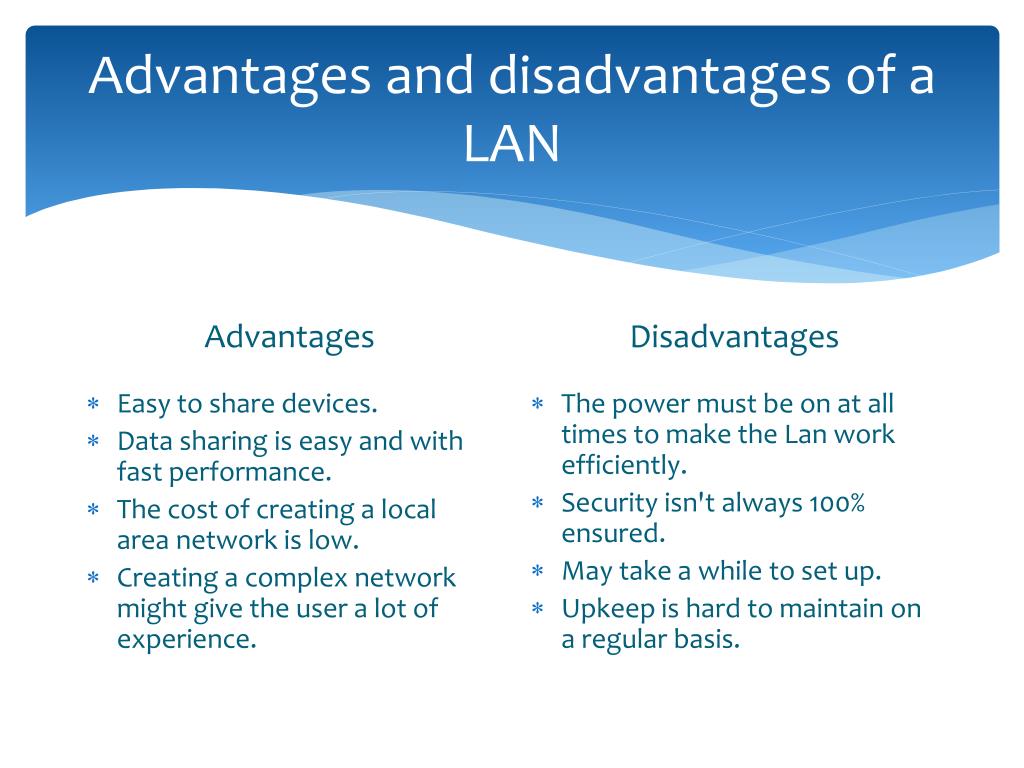
The Local Area Network (LAN) is integral to current technology. It enables devices within a given geographic area, such as offices and homes, to share data and resources by connecting them with cables or wireless routers. Every device has its IP address so they can communicate without needing an external source. This provides tight security from the outside world while allowing safe remote access to networks through the LAN connection – how convenient!
When it comes to its applications, LAN can be utilised for a multitude of purposes – from sharing data and transferring files to hosting gaming networks, streaming videos over the internet as well and using VoIP systems. Furthermore, this type of connection is widely employed by businesses due to enhanced security and trustworthiness compared with other network connections like Wi-Fi or cell phone networks. What’s more commercial enterprises frequently depend on secure LAN links for highly important activities such as client relationship management (CRM), enterprise resource planning (ERP) or supply chain management (SCM).
Besides being used in businesses, Local Area Networks (LANs) are very useful for educational institutions. Schools require reliable and secure internet access to equip their students with the knowledge they need for studying. Moreover, schools heavily rely on online sources like course material libraries and virtual classrooms to boost learning results too. Without strong networks along with dependable LAN connections, these wouldn’t be accessible all of the time which could affect the education quality given by such organisations.
As technology advances so does our reliance upon Local Area Networking become more extensive each day offering us tremendous advantages that make life smoother than ever before! It makes you wonder what else we can do if such technologies continue developing at this rate.
How does a LAN Function and Operate?
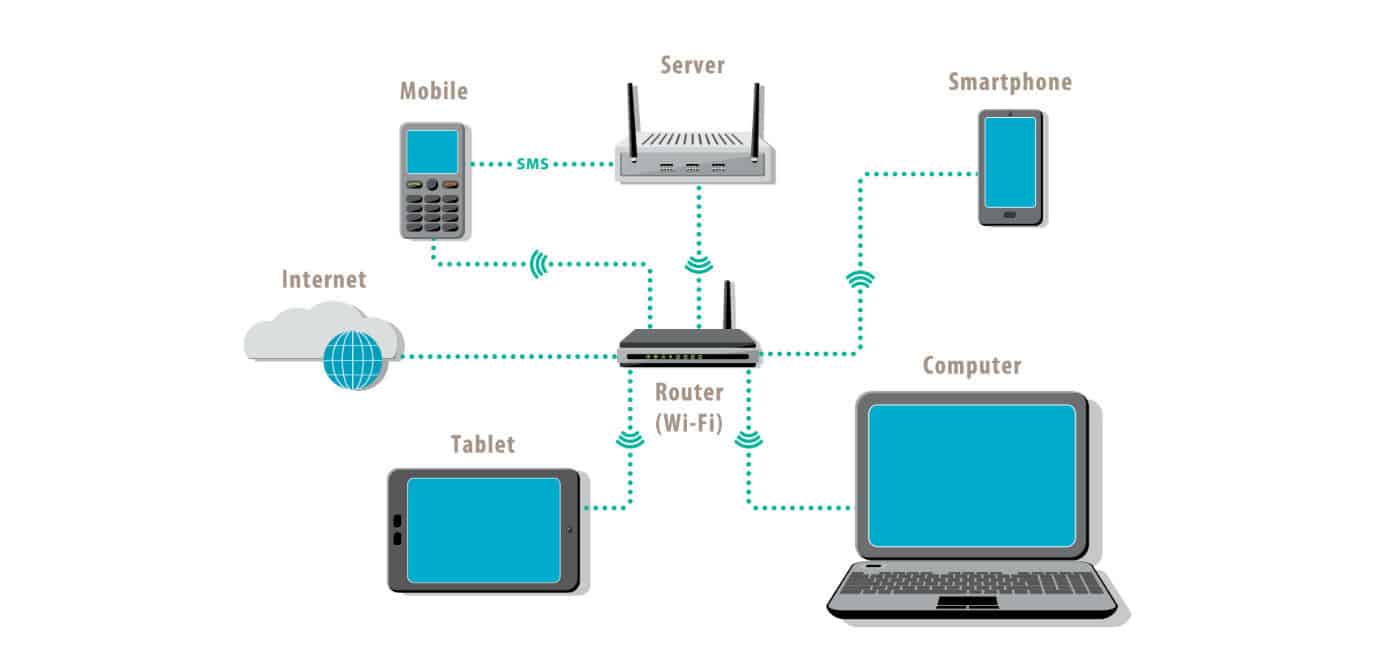
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a type of computer network that links up computers and devices within the same vicinity, such as an office building or school. The network infrastructure allows users on the LAN to share resources like files, printers etc. A LAN generally consists of two or more computers linked together using either wired or wireless technology.
To comprehend how a LAN operates, it is important to examine its components first. The key constituents of a LAN are its hardware, software and communications mediums.
Hardware components on a Local Area Network (LAN) can range from network interface cards (NICs), switches and routers to operating systems, communication protocols and firewall programs. Establishing a connection between devices involves connecting them using one of the available communication mediums such as twisted-pair wiring or optical fibre cables – linking all these parts up.
When users want to communicate on their LAN they must create this link so that it joins their device with other computers connected to the network; how do I ensure my hardware is talking directly?
They need to get their NIC settings in order if they want data to be transmitted between two devices that are on the same LAN. Once connected, users can then share information between their gadgets by using various protocols such as Transport Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). How quickly data travels or gets received over a Local Area Network mainly depends upon the amount of traffic it has at any one time.
When the roads get too busy for the local infrastructure to cope with, performance difficulties may occur such as poor connection speeds or losing packets because of a blockage in the network. Generally speaking though, neighbourhood networks are usually quicker than wide-area ones like the internet when it comes to transferring data owing to less latency and fewer bandwidth limitations.
It is also worth remembering that safe access management needs must be considered when you have a LAN; firewalls can be used to regulate entry from unauthorised users by deciding what kind of info is allowed across that particular segment – say no more file sharing etc..
Distinct features of Wired Connections in LAN

When it comes to setting up a Local Area Network (LAN), wired connections prove themselves as the most reliable and stable option. Ethernet cables are used for this purpose, providing superb bandwidth and low latency when transferring data from one device to another. This system generally contains computers, servers, printers and routers – all linked together via the same cable. It has these distinct features of wired connection which make it stand out amongst other varieties! What advantages does having a LAN provide?
The initial trait is the speed at which data can be transferred over the network. As cables give more direct ways for transferring data, they usually provide speeds that are much higher than what you would get from wireless solutions such as Wi-Fi or Bluetooth. What’s more, wired networks often necessitate fewer additional components like extenders or range boosters to maintain proper signal power with wireless networks. And because these cords don’t require any supplementary authentication protocols to create a connection between two points on a network, it is typically quicker to establish them too.
The next attribute is their safety benefits when compared with wireless ones. Because wired links often don’t transmit data through radio waves as Wi-Fi does, they typically offer better security from possible cyber threats or interference from external forces like hackers or harmful code sent on unprotected networks. Moreover, wires also reduce the chances of accidental disconnection since there is no need for authentication key exchange between two points every time an update needs to be made or a device moved somewhere else in your home/office building.
Moreover, the third separate feature is their lower energy consumption than wireless options such as Bluetooth and WiFi gadgets. This not only helps diminish utility bills for businesses but it likewise assists in lessening power waste due to reduced demand for electricity over long periods without any bad effects on performance quality or trustworthiness – leaving you feeling assured that what is used works just fine! So why bother changing?
The role of networking in LAN and its basics

When it comes to local area networks (LANs), networking is an essential part. Essentially, a LAN connects computers in just one small zone – either a single room, office block or campus. The idea of networking has been around since machines first gained popularity back in the 1950s and now it has become an integral element of most LAN systems. Networking allows multiple PCs to communicate with each other over diverse mediums such as Ethernet cables or Wi-Fi and exchange resources like printers and files. So you can see how vital this technology is!
When it comes to setting up a LAN for the first time, you will need to configure your network hardware such as routers and switches to create that all-important backbone of yours. Firewalls and DHCP servers are also key components – these are responsible for assigning IP addresses and making sure any unwelcome traffic stays off your network. With this setup, users on one computer can easily access files or resources from another without having to physically move between machines – streamlining collaborative work or communication significantly. Doesn’t this sound wonderful?
Now that you have all the components, it is time to get started connecting devices on the network. You can do this through various methods such as WiFi or ethernet cable connections. Network security is a priority when setting up a LAN – without proper protection in place malicious actors might be able to gain access and cause great damage by stealing sensitive data or corrupting systems.
To make sure your network stays safe, install antivirus software on every single computer connected to the network and keep their operating system patches updated at all times. Additionally, set up an efficient firewall system which will only permit certain traffic while keeping unauthorised sources away from outside networks.
LAN vs other network types: A comparison

When we talk about performance, LANs are the way to go. They use hardware that is specially designed for local networking needs giving them a huge advantage in terms of both speed and security compared to other types like wide area networks (WANs). A Local Area Network or LAN lets you connect multiple computers as well as other devices within the same vicinity – be it at home, for businesses, educational institutions, healthcare centres etc. This makes them extremely fast when communicating with each other plus they offer flexibility and connectivity to all users present in that space. How cool is that?
The architecture of the network also contributes to performance; most LANs use switched Ethernet architectures which route data packets from one device on the network to another a lot more efficiently than general router-based protocols used by WANs. This implies that data is sent quicker between clients on a LAN compared with those connected to a WAN. Safety and security is yet another eloquent advantage of using an efficient LAN system instead of other possibilities such as Wi-Fi networks or WANS – something that can make all the difference for some businesses!
When it comes to internet access, you may want to consider a local area network (LAN). All traffic on such networks passes through secure hardware components on the switch – this prevents unauthorised people from accessing your data without having to rely entirely upon software solutions like firewalls and encryption protocols. Many employers opt for LANs when setting up their employee’s laptops so that sensitive information remains within the organisation’s internal network.
But what are the benefits of using a Local Area Network? For sure there is an advantage with regards to speed and security over wireless or wide area networks. If these factors are important considerations then investing in a LAN should be seriously considered as one potential solution suitable for fulfilling business needs.
Real-world Examples and Applications of LAN
A Local Area Network (LAN) is a sort of computer network that enables two or more users to interact and share knowledge. With LAN, multiple computers are linked together via cables or wireless connections so information can be transmitted among them. This technology has various practical uses in real life such as networks employed by offices, universities, and homes.
For example, an office environment might use the LAN to connect staff PCs, enable the sharing of databases and files across the team members’ systems, and make available services like printing out documents electronically or browsing websites. How productive would teams be without this kind of access?
Some companies also utilise LANs to allow for the usage of internal communication tools such as emails and instant messaging. It is commonly used to give access to public resources including the internet too. Universities particularly depend on these networks when providing computing provisions to their students; they could divide them into sections that are allocated for different departments or student residences. This includes printers and other shared assets which pupils require whilst using computers during classes or research assignments – pretty useful stuff!
Similarly, home LANs are becoming an increasingly popular way for families to access online content such as streaming video services without having to shell out on costly broadband contracts with internet service providers. This can save money while still offering the same degree of convenience.
Further applications of LAN technology can be discovered in industrial settings where it is used for monitoring operations on production lines and also granting employees secure points of access so they can get their hands on essential data from anywhere within the premises (instead of relying heavily upon clunky VPNs). It may even be utilised in medical environments where patient records need to be shared between staff members promptly and seamlessly without compromising privacy or integrity.
The range of uses for LAN technology certainly indicates its importance when providing dependable networking solutions now and into the future; its versatility implies that it will probably stay a vital component of local computer networks wherever these types of systems exist across our planet!
Prospects and Advancements in LAN Technology

The local area network (LAN) tech is seriously shifting up a gear and offering more exciting opportunities than ever before. One of the most obvious advances in LAN tech has been the explosion of wireless technologies, which let devices link to each other or go online without needing any cables at all. This makes it much easier for people working with various business applications – as well as those simply wanting to surf the web from anywhere! What’s not to love about that?
Recently, there has been a rise in faster and more reliable connections such as Broadband. This makes it easier for companies to stay connected even when they are travelling or working from home. To save money on traditional phone lines and physical offices, many businesses have also adopted new technologies like VoIP services and cloud computing. Not only is this cost-effective but it has revolutionised the way these organisations can work – providing increased speed over long distances which was previously inconceivable!
The future for Local Area Network technologies is looking even more positive due to the ongoing research into new standards and protocols. Fibre optic cables, for instance, are gaining traction as they offer high speeds without a hefty price tag. Moreover, software-defined networking (SDN) has allowed organisations to configure their networks with far greater flexibility than before.
On top of that 5G wireless technology will be widely accessible shortly; it could significantly change how we access information online by providing faster speeds across spacious areas. All in all LAN’s perspective looks very encouraging – businesses around the world stand to benefit from cost savings plus productivity gains along with improved customer satisfaction!
Wrapping Up!
In conclusion, LANs are a vital part of modern computing and have been around since the 1970s in some form. They offer quick, safe and dependable ways for computers to be connected. For homes or smaller businesses that need their data transferred quickly from device to device, LAN is an ideal solution. With all the new technology advances we have seen in recent times wireless connections have become increasingly popular – however, wired remain faster and more reliable generally speaking.
To truly understand what’s going on with networking today it’s key you get your head round the basics of Local Area Networks first!
Are you on the lookout for an exhilarating career in network engineering? Then get signed up for our Master’s Program right away! Our intensive course is designed to guide you through all the stages of turning into a completely qualified network engineer, arming you with the skills and understanding necessary to put your expertise into practice. We know that networking can be daunting but fear not – we have an incredible team of experts who are seasoned professionals equipped with years’ worth of information and experience within this industry.
With their backing, you will become capable of constructing a robust understanding of all aspects concerning contemporary computer networks – extending from essential principles, protocols, infrastructure and topology to superior topics such as traffic control, routing protocols and MPLS VPNs.
You will get hands-on practice with actual case studies provided by prominent specialists globally. When you have accomplished this degree of aptitude we will assist in your job search by offering network engineering career exhortation along with access to our continuously developing database for networking positions.
Sign up for our Network Engineer Master Program now and commence that rewarding future!
Are you keen to give your career an upgrade? Look no further than our Network Engineer Master Program – it is the perfect choice for a prosperous future. This program has been designed with thoroughness in mind, giving you all the essential abilities and knowledge required to become quite the expert network engineer. With us, there will be no gap between theory and implementation; we have experienced faculty that will help guide you through every step of honing those cutting-edge principles, tools and techniques needed in this field.
Plus, by getting practical experience via real-life scenarios during your time here at the highest level network engineering work environment – would not want any surprises popping up later on down the line right? So don’t hang around – sign yourself up today! Starting as soon as now is only going to benefit you more so why wait until tomorrow?!
Happy Learning!