
Do you want to explore the different types of Networks? Look no further! Computer Networks, often described as a connection between two or more computer devices established to share data and information back and forth, are an integral part of technology differentiated based on connection modes (wired or wireless) and the requirement of the network channel. Since the networks, hence established to connect multiple devices altogether are used to share hardware and software data and resources, the need for computer networks is already clear.
In this blog, let us get familiar with the different types of networks and their features to understand them better. Therefore, keep reading the blog till the end to know the computer network types in detail directly from the experts.
What is a Computer Network?
.jpg)
A computer network is just like the internet that connects everything globally. In layman’s terms, a computer network refers to the connection between two or more computer devices used to share resources and data. It is like a web of connections, depending upon the requirement of the channel sometimes wireless and at times wired.
Explain the different types of Network?

The different types of Networks are as follows-
- Local Area Network (LAN)
- Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)
- Wide Area Network (WAN)
- Personal Area Network (PAN)
What is a Local Area Network (LAN)?
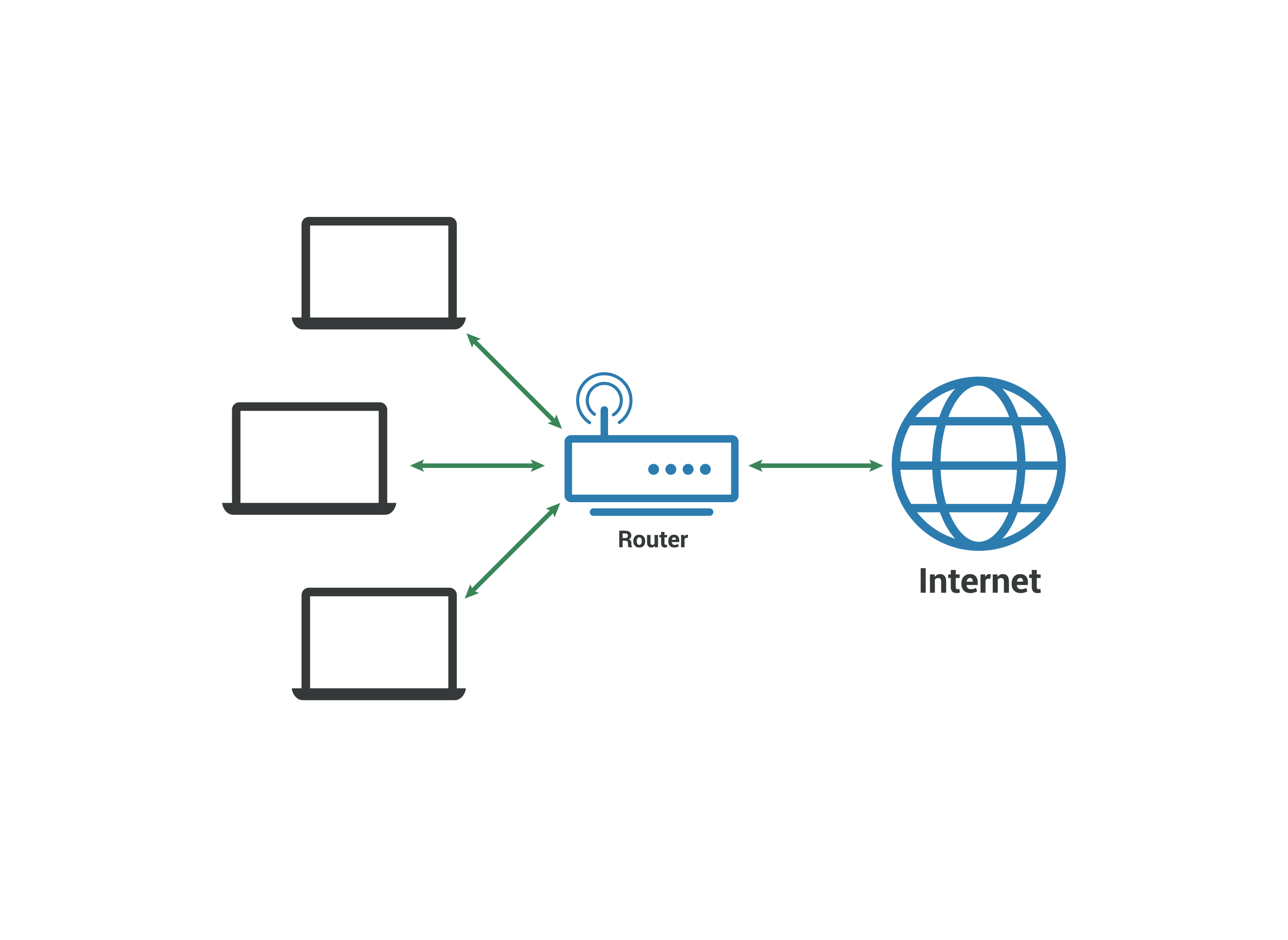
The Local Area Network (LAN) refers to the kind of network that connects digital devices within a limited geographic area, i.e., a building. The devices get connected using the cables and wires for data transmission. The devices in the LAN network get connected using multiple protocols to exchange data and services.
What are the attributes of LAN?
The key attributes of LAN (Local Area Network) are as follows-
- LANs are designed to cover a short geographical area for information and data transmission.
- LANs enable fast communication and data transmission with the networks.
- LANs are owned by private entities.
- LANs are reliable and easy to maintain.
- LANs provide low latency by increasing the speed of data exchange.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of LAN?
The advantages of LAN (Local Area Network) are as follows-
- LAN prevents duplication of data and information shared on a network.
- LAN offers high-speed data transfer.
- LAN enhances data security by implementing centralized access controls.
- LAN networks are easy to monitor and maintain.
- LANs facilitate quick and direct communication between devices.
The disadvantages of LAN (Local Area Network) are as follows-
- LAN covers a limited geographical area.
- The cost of setting up LAN infrastructure is high.
- Multiple users on the LAN can lead to network congestion and reduce performance.
- Complex LAN setup can lead to inefficiency of network usage.
- LANs relying on wired connections are vulnerable to physical damage.
What is a Metropolitan Area Network (MAN)?

The Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) refers to the kind of network that connects digital devices within a larger geographic area than a Local Area Network (LAN) but smaller than a Wide Area Network (WAN), i.e., a city or a region. MANs provide high-speed connectivity and efficient data transmission between local networks. MANs are connected using wires, i.e., data cables.
What are the attributes of MAN?
The key attributes of MAN (Wide Area Network) are as follows-
- MANs cover a larger geographic area than Local Area Networks (LANs) but smaller than Wide Area Networks (WANs).
- MANs provide high-speed data transmission within the metropolitan area.
- MANs use various communication technologies, including fibre optics, Ethernet, and wireless connections.
- MANs are scalable networks.
- MANs offer a cost-effective solution for organizations.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of MAN?
The advantages of MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) are as follows-
- MANs provide efficient and high-speed connectivity.
- MANs provide moderate latency for effective data transfer.
- MANs ensure network reliability.
- MANs comprise fibre optics and wireless connections.
- MANs provide flexibility to meet connectivity requirements.
The disadvantages of MAN (Metropolitan Area Network) are as follows-
- MANs cover a limited geographical area.
- Designing and implementing a MAN is complex.
- MANs are susceptible to security concerns.
- Managing and maintaining a MAN involves dealing with diverse technologies.
- MANs add complexity to network management and operations.
What is a Wide Area Network (WAN)?
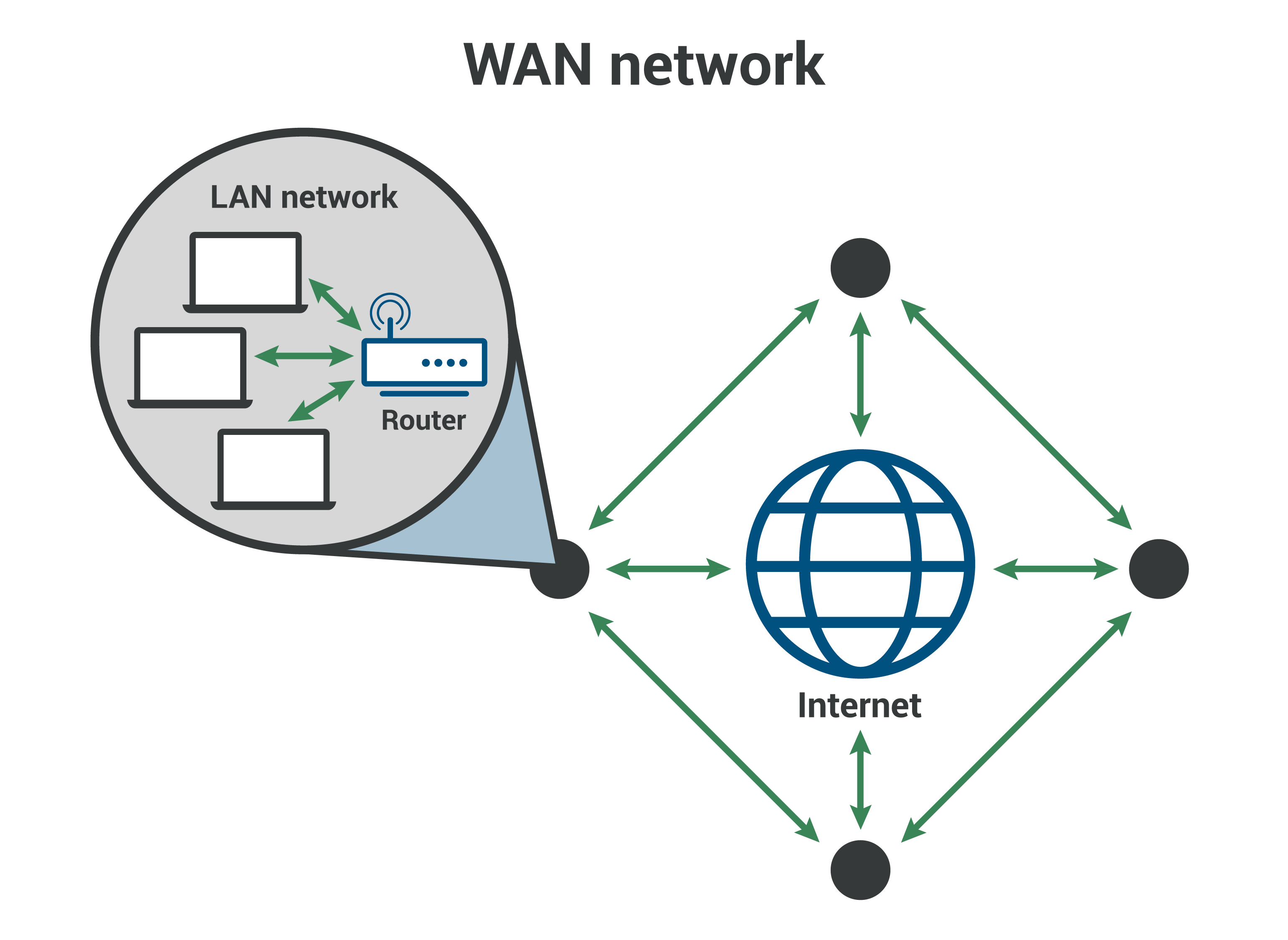
The Wide Area Network (WAN) refers to the kind of network that connects digital devices within a large geographical area, i.e., different cities, states, countries, or continents. WAN uses wireless connections to enable long-distance data transmission. A WAN network is a combination of multiple MAN and LANs.
What are the attributes of WAN?
The key attributes of WAN (Wide Area Network) are as follows-
- WANs are designed to cover a large geographical area for information and data transmission.
- WANs interconnect multiple LANs and individual devices.
- WANs provide higher latency by affecting the speed of data exchange.
- It becomes complex to address WAN connectivity issues.
- WANs enable global connectivity.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of WAN?
The advantages of WAN (Wide Area Network) are as follows-
- WAN covers a large geographical area.
- Data can be shared among widely dispersed locations.
- WANs offer flexibility in designing network architectures.
- WANs allow remote users to access applications and services globally.
- WANs support effective collaboration and communication.
The disadvantages of WAN (Wide Area Network) are as follows-
- Setting up and maintaining WAN infrastructure is very high.
- Managing diverse technologies and addressing connectivity issues in WAN is more complex.
- WANs pose security challenges.
- Longer distances and the use of diverse technologies contribute to higher latency.
- WANs may experience bandwidth limitations, affecting the speed and efficiency of data transmission.
What is the difference between LAN, MAN, and WAN?
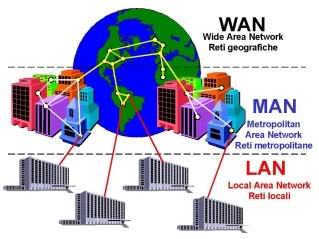
The differences between LAN, MAN, and WAN are as follows-
DIFFERENCE | LAN | MAN | WAN |
Full Form | LAN stands for Local Area Network. | MAN stands for Metropolitan Area Network. | WAN stands for Wide Area Network. |
Geographic Coverage | Covers a small geographic area, such as a single building, campus, or a group of nearby buildings. | Spans a larger geographic area, typically covering a city or a large campus. | Encompasses a wide geographic area, connecting devices across cities, countries, or continents. |
Size of Network | Generally smaller in scale, connecting devices within a localized area. | Moderately larger than LANs, connecting multiple LANs within a metropolitan area. | Largest in scale, connecting devices across extensive geographic distances. |
Data Transfer Rates | Offers high-speed data transfer within the local network. | Provides moderate to high-speed data transfer rates within the metropolitan area. | Typically has lower data transfer rates compared to LANs and MANs due to longer distances. |
Technologies Used | Uses technologies like Ethernet and Wi-Fi for data transmission within a confined area. | Utilizes diverse technologies, including fibre optics and wireless connections, for efficient data transfer within a city. | Involves various technologies such as leased lines, satellite links, and public or private networks for long-distance communication. |
Latency | Typically has low latency, ensuring quick data transmission within the local area. | Offers moderate latency, balancing the need for high-speed connectivity and longer distances. | Generally has higher latency due to extended geographical coverage. |
Use Cases | Used for local resource sharing, intranets, and connecting devices within a single organization. | Suitable for connecting multiple branches or campuses of an organization within a city. | Ideal for connecting geographically dispersed offices, branches, or data centers on a global scale. |
Cost | Generally has lower setup and maintenance costs compared to MANs and WANs. | Costs are moderate, falling between LANs and WANs. | Involves higher setup and maintenance costs, especially for long-distance connectivity. |
Reliability | Generally more reliable due to the limited geographical area and fewer points of failure. | Moderately reliable, with redundancy options available to enhance network stability. | Faces potential reliability challenges due to longer distances and a higher number of potential points of failure. |
Expansion Ease | Relatively easy to expand within the same physical location. | Scalable to accommodate additional locations within the metropolitan area. | Can be expanded globally but involves complex scaling due to diverse international infrastructures. |
Security Consideration | Easier to implement and maintain security measures within the confined local area. | Requires robust security measures, considering the larger coverage area and potential external threats. | Presents greater security challenges due to long-distance connections and diverse network infrastructures. |
Cost Per User | Generally has a lower cost per user, making it cost-effective for smaller groups. | Moderate cost per user, suitable for medium-sized organizations within a city. | Higher cost per user, especially for global networks, due to extensive infrastructure requirements. |
Impact of Network Congestion | Minimal impact from network congestion due to the localized nature of the network. | Moderate impact, depending on the size of the metropolitan area and the level of congestion. | More susceptible to congestion issues, potentially leading to delays in data transmission. |
Internet Access Points | Typically has a single internet access point for the entire local network. | Multiple access points may be distributed across the metropolitan area for efficient internet connectivity. | Involves various internet access points globally, providing widespread internet connectivity. |
What are the similarities between the different types of Computer Networks?
The similarities between the different types of computer networks are as follows-
- Data Transmission: All three types of networks involve the transmission of data between connected devices, facilitating communication and resource sharing.
- Networking Devices: Common networking devices, such as routers, switches, and hubs, are utilized in LANs, WANs, and MANs to manage data traffic, regulate communication, and ensure connectivity.
- Communication Protocols: LANs, WANs, and MANs rely on standardized communication protocols, such as TCP/IP (Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol), to enable devices to communicate with each other.
- Connectivity Technologies: Various connectivity technologies, both wired (e.g., Ethernet) and wireless (e.g., Wi-Fi), are employed in LANs, WANs, and MANs to establish communication links between devices.
- Resource Sharing: The concept of resource sharing is fundamental across all three types of networks, allowing connected devices to share files, printers, and other network resources.
- Centralized Management: Networks typically involve centralized management to coordinate and optimize data traffic, ensure security, and facilitate efficient resource sharing, regardless of their size or coverage area.
- Security Measures: LANs, WANs, and MANs implement security measures, including firewalls, encryption, and authentication protocols, to protect against unauthorized access and security threats.
- Topology Configurations: Similar network topologies, such as star, bus, ring, or mesh configurations, can be employed in LANs, WANs, and MANs based on specific requirements and design considerations.
- Scalability: The ability to scale the network to accommodate additional devices or locations is a common consideration in LANs, WANs, and MANs to support changing organizational needs and growth.
- OSI Model Layers: LANs, WANs, and MANs adhere to the OSI (Open Systems Interconnection) model, which defines seven layers, including the Physical and Data Link layers, ensuring a standardized approach to data transmission and network architecture.
How to set up the Networks?
Setting Up a LAN:
For a Local Area Network (LAN), use Ethernet as the foundation, connecting computers and servers, either with cables or wirelessly through WiFi. WiFi Access Points (WAPs) help with wireless connections, allowing devices to link up. Servers are usually connected using cables, ensuring a stable connection.
Setting Up a MAN:
A Metropolitan Area Network (MAN) brings together multiple LANs using fibre optics. It works like an internet service provider for a city. MANs can also use wireless connections like microwave or infrared lasers. These networks are often owned by a big organization, mainly serving cities to provide high-speed connections.
Setting Up a WAN:
A Wide Area Network (WAN) connects computers and users in different areas. It combines two or more LANs or MANs. Computers in a WAN are linked using public networks like phone lines, satellites, or leased lines (which can be costly). Routers are used at each end of a leased line to extend the network across locations.
How do these Networks function?
LAN (Local Area Network)
A local area network (LAN) is like a group of computers and other devices that talk to each other using cables or Wi-Fi in a small area. Usually, there is a main computer (server) that stores shared information and programs for all the other computers in that area.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
Imagine several LANs connected using special cables and Wi-Fi in a bigger area, like a city. This is called a metropolitan area network (MAN). It connects to important points in the city’s network and the internet, helping different LANs share information quickly.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
For even larger connections, there is a wide area network (WAN). It’s like connecting one point to another using things like traditional phone lines or modems. Companies that provide this service can be local phone companies or long-distance operators.
What are the characteristics of LAN, MAN, and WAN?
The characteristics of LAN, MAN, and WAN are as follows-
LAN (Local Area Network)
- LANs cover a small geographic area.
- LANs provide high-speed data transfer.
- LANs experience low error rates in data transmission.
- LANs are known for their reliability.
- LANs are relatively easy to install and manage.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- MANs cover a larger geographic area.
- MANs interconnect multiple LANs within a metropolitan area.
- MANs offer higher data transfer rates compared to LANs.
- Setting up and maintaining MANs involves higher costs compared to LANs.
- MANs may use a combination of wired and wireless technologies.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- WANs cover a large geographic area.
- WANs may have lower data transfer rates compared to LANs and MANs.
- Setting up and maintaining WANs involves higher costs.
- WANs may experience higher latency in data transmission.
- WANs face increased security challenges.
What are the benefits of different computer network types - LAN, MAN, and WAN?
The benefits of different computer network types – LAN, MAN, and WAN are as follows-
LAN (Local Area Network)
- LANs allow efficient sharing of resources among connected devices.
- LANs provide high-speed data transfer rates.
- LANs enhance communication within an organization.
- LANs are easily scalable.
- LANs are relatively easy to maintain.
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- MANs interconnect multiple LANs.
- MANs offer high-speed connectivity.
- MANs provide increased bandwidth.
- MANs offer a cost-efficient solution for organizations.
- MANs are flexible and scalable.
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- WANs support a wide range of communication services.
- WANs enhance business continuity by enabling data backup.
- WANs facilitate resource sharing among organizations.
- WANs provide sufficient bandwidth for remote sites.
- WANs can be designed with redundancy to ensure reliable connectivity and minimize downtime.
What are the disadvantages of LAN, MAN, and WAN?
The disadvantages of LAN, MAN, and WAN are as follows-
LAN (Local Area Network)
- Limited Geographic Range
- High Initial Setup Costs
- Security Concerns
- Limited Scalability
- Dependency on a Centralized Server
- Potential for Network Congestion
- Maintenance Complexity
- Limited Coverage for Remote Users
MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- Costly Infrastructure
- Complex Design and Implementation
- Security Challenges
- Dependency on External Service Providers
- Data Transfer Speeds
- Limited Flexibility
- Potential for Network Congestion
- Not Ideal for Global Connectivity
WAN (Wide Area Network)
- Complex Network Infrastructure
- Latency Issues
- Security Concerns
- Dependence on External Service Providers
- Bandwidth Limitations
- Potential for Network Congestion
- Dependency on Internet Connectivity
- Management Complexity
What are some other types of computer networks? - Personal Area Network (PAN) Explained
Another kind of computer network is PAN.
The Personal Area Network (PAN) refers to the kind of network that connects digital devices within a range of a few meters. PAN comprises both wired and wireless connectivity modes. PAN technologies include Bluetooth and Wi-Fi, allowing seamless communication and data sharing among these devices.
What are the attributes of PAN?
The key attributes of PAN (Personal Area Network) are as follows-
- PANs cover a short distance.
- PANs connect personal devices such as smartphones, laptops, tablets, and wearable gadgets.
- PANs provide a private and secure environment.
- PAN devices often prioritize low power consumption.
- PANs are designed for short-term connections.
What are the advantages and disadvantages of PAN?
The advantages of PAN (Personal Area Network) are as follows-
- PANs provide a private network environment.
- PAN devices often prioritize energy efficiency.
- PAN technologies ensure interoperability between different devices.
- PAN utilizes wireless technologies.
- PAN facilitates easy and convenient data sharing.
The disadvantages of PAN (Personal Area Network) are as follows-
- PANs restrict communication to a few meters.
- PANs are vulnerable to security threats.
- PANs may face limitations in terms of scalability.
- PAN devices are dependent on battery power.
- PANs experience interference and network congestion.
What is a Network Topology?
Network Topology shows how computers and devices are connected within a network. It decides how information gets exchanged between these devices. The specific design you choose affects things like how fast data moves, how well the network handles problems, and how easy it is to grow the network.
What are the different types of Network Topologies?
The different types of Network Topologies are listed as follows-
- Bus Topology
- Star Topology
- Ring Topology
- Mesh Topology
- Tree Topology
- Hybrid Topology
- Point-to-Point Topology
- Point-to-Multipoint Topology
- Dual-Ring Topology
- Circular Topology
Where to learn the computer network types in detail?
Learning about computer network types in detail is vital if you wish to step into the IT industry. Therefore, Network Kings is the best platform to become familiar with A to Z IT-related concepts. Enroll in the best programs designed by industry experts today to fuel your engineering journey to stand out in the crowd of experts.
Wrapping Up!
In the above blog, we learned about the types of computer networks and their advantages along with disadvantages. For further information about the same, enroll with Network Kings. For help and queries, feel free to reach us in the comment section below.
Happy Learning!
FAQs:
What are different types of network?
The 4 types of networks are as follows-
- LAN (Local Area Network)
- MAN (Metropolitan Area Network)
- WAN (Wide Area Network)
- PAN (Personal Area Network)
What is the full form of LAN?
The full form of LAN is a Local Area Network.
What is the full form of MAN?
The full form of MAN is Metropolitan Area Network.
What is the full form of WAN?
The full form of WAN is a Wide Area Network.
What is the full form of PAN?
The full form of PAN is Personal Area Network.
Is LAN better than WiFi?
No, LAN and Wi-Fi serve different purposes; LAN refers to a local wired network, while Wi-Fi is a wireless technology used for local wireless connectivity.
What is the importance of LAN?
The importance of LAN is as follows-
- LANs allow efficient sharing of resources among connected devices.
- LANs provide high-speed data transfer rates.
- LANs enhance communication within an organization.
- LANs are easily scalable.
- LANs are relatively easy to maintain.
What is the importance of WAN?
The importance of WAN is as follows-
- WANs support a wide range of communication services.
- WANs enhance business continuity by enabling data backup.
- WANs facilitate resource sharing among organizations.
- WANs provide sufficient bandwidth for remote sites.
- WANs can be designed with redundancy to ensure reliable connectivity and minimize downtime.
What is the importance of MAN?
The importance of MAN is as follows-
- MANs interconnect multiple LANs.
- MANs offer high-speed connectivity.
- MANs provide increased bandwidth.
- MANs offer a cost-efficient solution for organizations.
- MANs are flexible and scalable.
What is the importance of PAN?
The importance of PAN is as follows-
- PANs provide a private network environment.
- PAN devices often prioritize energy efficiency.
- PAN technologies ensure interoperability between different devices.
- PAN utilizes wireless technologies.
- PAN facilitates easy and convenient data sharing.
What are the three types of network?
LAN, MAN, WAN are three types of network


