Are you scared after watching the cybercrime report? Well! You should be. Hackers are trying to become the masters of this digital world. But we don’t have to allow them! But how?
Ethical Hacking knowledge is the solution. We can execute ethical hacking by simulating the techniques used by hostile actors ethical hackers find system defects, misconfigurations, or openness in software applications. They help organizations comprehend their safety posture and make instructed judgments to mitigate risks.
Ethical hackers use their ability to ensure and enhance the technology of organizations. They provide a crucial service to these organizations by looking for exposures that can lead to a security violation. An ethical hacker conveys the determined vulnerabilities to the organization.
By understanding ethical hacking, you can secure the systems and data from dangers and attacks. As an ethical hacker, your roles will be: Conducting investigations and analyzing the target systems to specify any security or system vulnerabilities from the hacker’s viewpoint and offer a remedy.
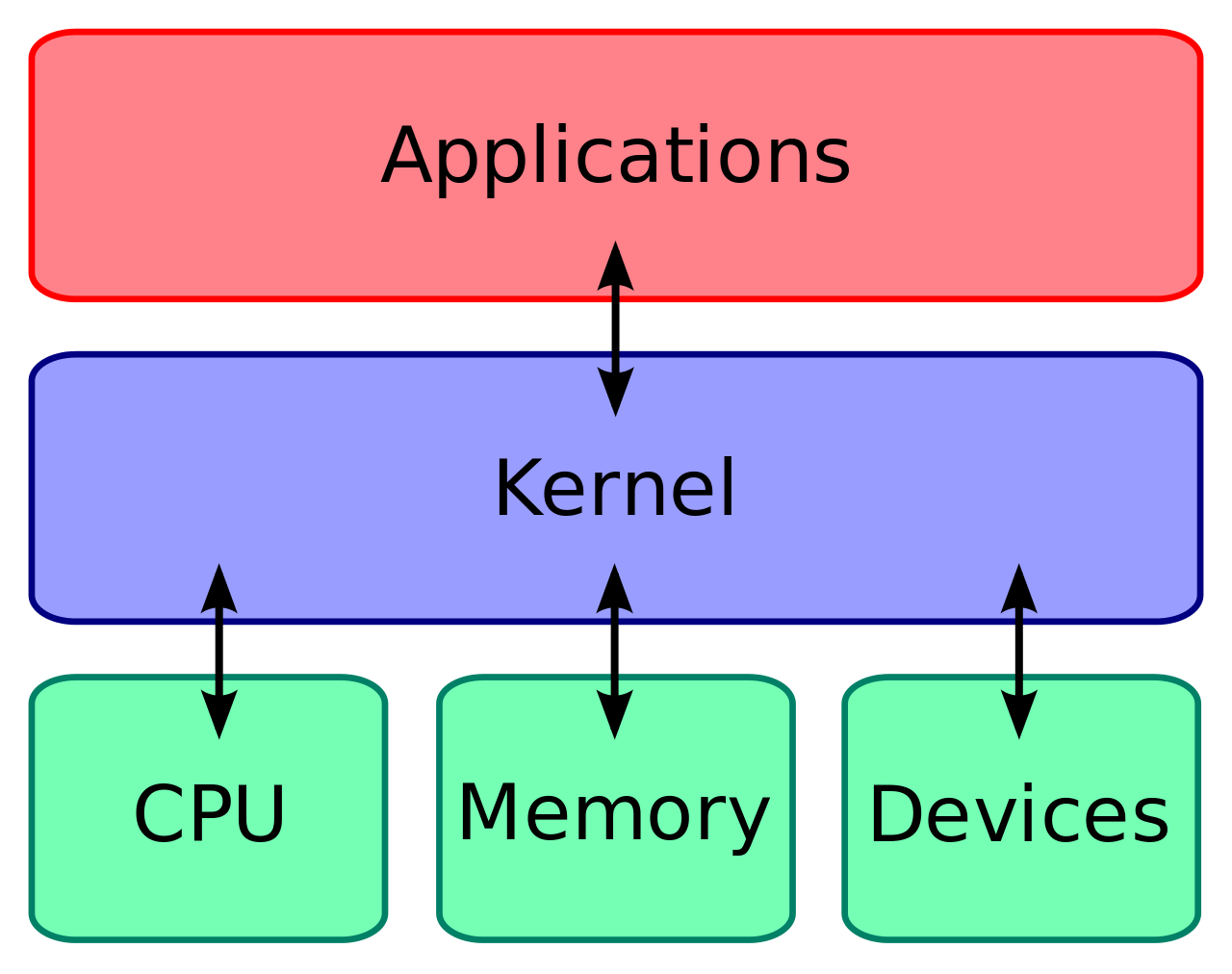
Understanding Ethical Hacking

Ethical hacking is the authorised attempt to gain access to computer systems, applications or data by duplicating the strategies and methods that may be used by a malicious hacker.
Ethical Hacking is enhanced by ‘white-hat hackers’ whose work of system hacking is the same as that of ‘black-hat’ hackers, but the purpose is different. In the case of ethical hacking, the hacker hacks to save the system. Cyber Security professionals, on the other hand, don’t have to hew into the system.
What are the benefits of learning Ethical Hacking?
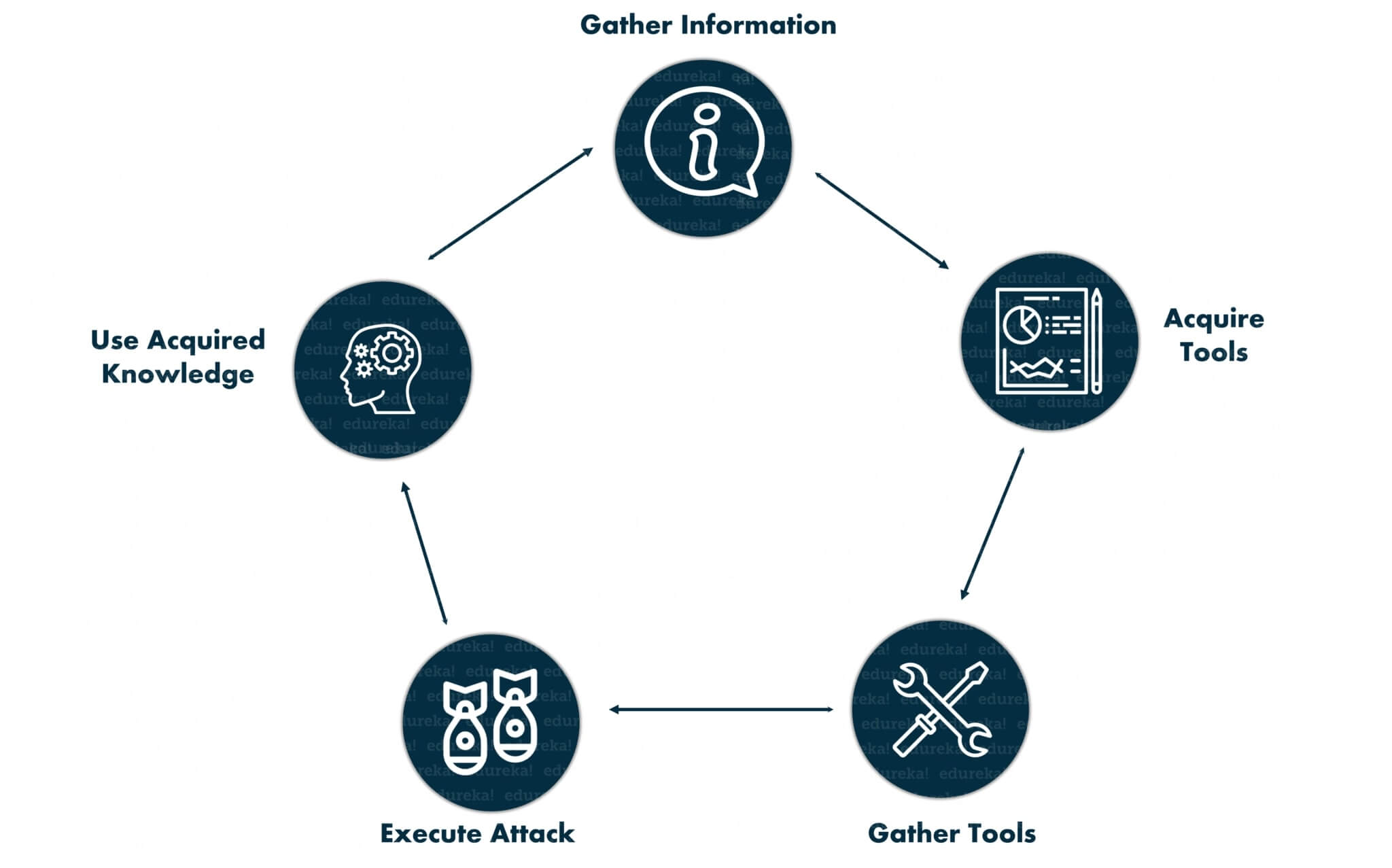
Ethical hackers serve a key role in cybersecurity by actively recognising and remediating vulnerabilities. Their duties include leading comprehensive security checks, conducting penetration testing, and producing reports tracing identified weaknesses and recommendations for improvement.
Here are the benefits of learning Ethical Hacking:
- Ethical Hacking enables us to fight against cyber terrorism and to oppose national security breaches.
- It allows us to take preventative action against hackers.
- Ethical Hacking allows building a system that controls penetration by hackers.
- Ethical Hacking presents security to banking and financial establishments.
- Ethical Hacking helps to recognize and complete the open holes in a computer system or network.
How to get started with Ethical Hacking?
Choosing the Right Ethical Hacking Course is crucial. Let’s see how to get started with ethical hacking:
- Note your Interest Areas: Ethical hacking courses protect different subjects, including social engineering, network sniffing, cryptography and IoT hacking. Comprehend your interest areas and then go through the programmes available with numerous institutes. Inspect which programme shows you the areas of your interest and shortlist the institutes that make the best offer.
- Research & Seek Advice: Go online to learn more about the course of your preference to get a deep understanding. You can also scan for online reviews. Join with experts on the subject and comprehend their views on the usefulness of following the Ethical Hacking course you have selected. Another factor, you must consider is whether the programme delivers practical ethical hacking training. Employers are looking for candidates ready to smash the floor running and have functional hands-on learning. Practical experience will help you gain certifications that can help you land the job of your dreams.
- Verify the Market Value of the Course: Review if the institute has recognized accreditations and associations. A confirmed credential can assist you to stand out amidst the competition. Ethical hacking classes having national or global acclaim boost your value as a candidate and can aid you in locating employment options with top-notch companies.
Note: You should choose the online option for the ethical hacking course will save you time and provide you the education by sitting at home with flexible learning hours. Various institutions are providing online institutions.
Steps to Learn Ethical Hacking Techniques
Learning Ethical Hacking tools includes knowing about Ethical Hacking tools and skills. Here are the basic steps to learn Ethical Hacking Techniques:
– Acquaint yourself with common Ethical Hacking Tools.
– Achieving mastery in Networking, Programming, and System Security.
– Get an online course to learn Ethical Hacking.
– Suggested reading list for deepening your knowledge.
– Learning from industry experts in the field.
What is the Future of Ethical Hacking?

Recently, there has been a meteoric rise in the membership of the ethical hacking community, with hackers of differing degrees of experience joining together to work and learn from one another.
As the community continues to grow, the need for ethical hackers who possess the skills and essential knowledge to defend enterprises from possible cyber-attacks continues to rise.
Because the cyber security environment is moving, Ethical Hacking has become a crucial process for enterprises to operate and connect themselves. The demand for ethical hackers will grow as the world grows more dependent on digital technology.
Ethical Hacking and Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity and Ethical Hacking are critical for ensuring online data, user authentication, and privacy protection. Ethical hackers focus on recognizing and determining security vulnerabilities, while cybersecurity specialists desire to defend networks and data from unauthorized access.
Ethical Hacking is used to ensure crucial data from competitors. It stops negative users from using the organization or an individual. It lowers the risk of being blackmailed by a person or organization with unhealthy intentions.
Collaborative actions permit transferring threat intelligence and best techniques, allowing organizations to defend against new and arising threats. Cybersecurity needs considerable resources in terms of technology, personnel, and expertise.
What are the Emerging Trends in Ethical Hacking and Cybersecurity?
Here are the emerging trends in Ethical Hacking and Cybersecurity:
- Rise of Automotive Hacking
- The potential of Artificial Intelligence
- The new target is the mobile
- Cloud is also powerless
- Data breaches are the only target.
- 5G networks, a new era of inter-connectivity
- Automation and Integration
- Targeted Ransomware
- Insider Threats
- Social Engineering attacks
Ethical hacking has an endless future. Many areas, including government, corporate enterprises, health care, entertainment, banking, and others, are rapidly rising in this arena.
Even though only 32% of individuals work in the ethical hacking industry. As an outcome, the need for new staff is on the pitch. Compared to last year, the number of ethical hackers is guessed to advance by 20% by the end of 2023. As a result, this digit will resume to thrive in the future.
What are the Future Challenges in the Ethical Hacking field?
The future challenges in the Ethical Hacking field are:
- Inconsistency of quality.
- Ethical hackers drive system interruption.
- Over-reliance on automated tools.
- Ethical hacking meetings are time-limited.
- There is a scope limitation.
Ethical hackers donate to defending sensitive data. Preventing cybercrime and bracing the security of digital systems. Such efforts benefit businesses, organizations, and individuals who rely on these systems for their daily activities.
Where to pursue an Ethical Hacking course?
The Ethical Hacking course or Certified Ethical Hacking [CEH] helps learn about Organizations under cyber-attack, Unraveling the hacker mindset, Development and Quality Assurance, Professional Development, Transition to Cloud, and Employment.
Now, you might be thinking, where should I pursue ethical Hacking tools? The answer is Network Kings. Network Kings provides CEH, a professional training program including topics, like network security, cryptography, web application security, and system hacking.
The candidate will also learn penetration testing, Ethical Hacking Vulnerability Assessment, and CEH V12 course certification. To get certified in the Ethical Hacking course, the candidate needs to clear the Certified Ethical Hacker (312-50) exam.
What are the exam details of certified ethical Hacking or CEH?
Here is the list of exam details for the Certified Ethical Hacking course:
Exam Name Certified Ethical Hacker (312-50)
Exam Cost USD 550
Exam Format Multiple Choice
Total Questions 125 Questions
Passing Score 60% to 85%
Exam Duration 4 Hours
Languages English
Testing Center Pearson Vue
What is the eligibility of Ethical Hacking tools?
The eligibility for the ethical Hacking course is:
- Graduation is a must.
- Basic knowledge of the IT industry.
- 2-3 years of background in Networking.
- Fundamental understanding of Servers.
- Comprehending Ethical Hacking.
- Knowledge of Cloud management.
What skills will you learn in the CEH course of Network Kings?
There are various modules that one will learn in the CEH course of Network Kings:
- Information Security and Ethical Hacking Overview
- Reconnaissance Techniques
- System Hacking Phases and Attack Techniques
- Network and Perimeter Hacking
- Web Application Hacking
- Wireless Network Hacking
- Mobile Platform, IoT, and OT Hacking
- Cloud Computing
- Cryptography
What are the job roles after the Ethical Hacking course?
The job roles after the CEH certification are as follows-
- Certified Ethical Hacker
- Penetration Tester
- Security Analyst
- Information Security Manager
- Network Security Engineer
- Cybersecurity Engineer
- Security Architect
- Security Engineer
- Incident Response Analyst
- Forensic Analyst
- Malware Analyst
- Vulnerability Analyst
- Cybersecurity Trainer/Instructor
- IT Security Consultant
- Security Researcher
- Cybersecurity Project Manager
- Security Operations Center (SOC) Analyst
- Cryptographer
- Cybersecurity Lawyer
- Cybersecurity Journalist
What are the salary prospects for a candidate after the CEH v12 training?
The salary prospects for a candidate after the Certified Ethical Hacking v12 training in different countries are as follows-
- United States: USD 95,000 to USD 110,000 per year.
- Canada: CAD 80,000 to CAD 95,000 per year.
- United Kingdom: £50,000 to £65,000 per year.
- Australia: AUD 80,000 to AUD 110,000 per year.
- Germany: €60,000 to €75,000 per year.
- France: €45,000 to €65,000 per year.
- India: INR 500,000 to INR 1,000,000 per year.
- United Arab Emirates: AED 140,000 to AED 180,000 per year.
- Singapore: SGD 60,000 to SGD 90,000 per year.
- Malaysia: MYR 60,000 to MYR 90,000 per year.
- Saudi Arabia: SAR 100,000 to SAR 150,000 per year.
- Qatar: QAR 180,000 to QAR 220,000 per year.
- South Africa: ZAR 400,000 to ZAR 600,000 per year.
- Nigeria: NGN 3,000,000 to NGN 5,000,000 per year.
- Brazil: BRL 80,000 to BRL 120,000 per year.
Conclusion
It is estimated that the job of an Ethical Hacker is going to increase by 17.5% across the world by the year 2025. Apart from being Ethical Hackers, candidates can also start their careers as information system analysts, cybersecurity experts, security analyst managers, and many more.
According to the sources, information security professionals will operate 33% more individuals by 2030, which is far quicker than projected six days ago.
You can pursue an Ethical Hacking course from Network Kings as it offers various benefits.