Are you aware of the goals of cyber security? If not, now you will know. Nowadays, cyber security is a top priority as we find ourselves in this digital age. It is all about protecting our precious data, networks and endpoints from malicious forces out there that may try to cause damage or steal info. This means businesses, organisations and individuals must take extra care to ensure they are safeguarding their online assets – with everything becoming more interconnected it can be a minefield!
In this blog post, let us explore the importance of spotting risks before they occur so you can do something about them; also look at how implementing effective defence systems & strategies can help mitigate dangers. So join us while we delve deeper into what makes up great cyber security goals!
What is the importance of Cybersecurity?
Considering the importance of achieving our organisational ambitions, cybersecurity is an essential factor. All organisations big and small understand their need to protect data and keep customer privacy safe however not all have a genuine grasp on what it means or just how many implications there are towards this topic.
Hence, for us to construct a culture that prioritizes safety we must first acquire an understanding as to why investing in strong cyber security measures is so important. To make sure these objectives can be met three core attributes should always be kept in mind: preserving confidentiality, consistency and also accessibility.
Confidentiality means guaranteeing that only approved users have access to delicate data, such as passwords or monetary records. Integrity implies ensuring this information is precise and unscathed. Furthermore, availability stresses making sure the data is consistently accessible when required by its suitable crowd of people. All these three elements collaborate for an organization’s data to remain safe from any external meddling and misuse.
Nonetheless, shielding your info isn’t only about lessening risks; it also encompasses upholding trust between businesses and consumers! By taking the necessary steps towards safeguarding our sensitive information – so both parties can feel reassured with their customary relationships – we are setting up a strong foundation of mutual understanding which ultimately helps us keep using technology without fear or worry.
Consumers depend on business owners to look after their data so they can feel at ease trusting them with sensitive info such as credit card numbers or other personal details. For businesses to maintain customer trust, they need to invest in a complete cyber security plan – one that copes with both internal issues (like staff inadvertently sharing private information) and external threats (for instance hackers attempting to access confidential systems).
By grasping the value of cyber security related to organizational goals, companies can put themselves up for success right now and into the future – supplying assurance for customers all over. What’s more, how does investing in cybersecurity protect an organization from malicious attacks? How do you ensure your employees are properly trained when it comes to keeping company data secure? These questions can go a long way towards protecting not only consumers but also employers’ investments in the digital world.
What are the key goals of Cyber security?
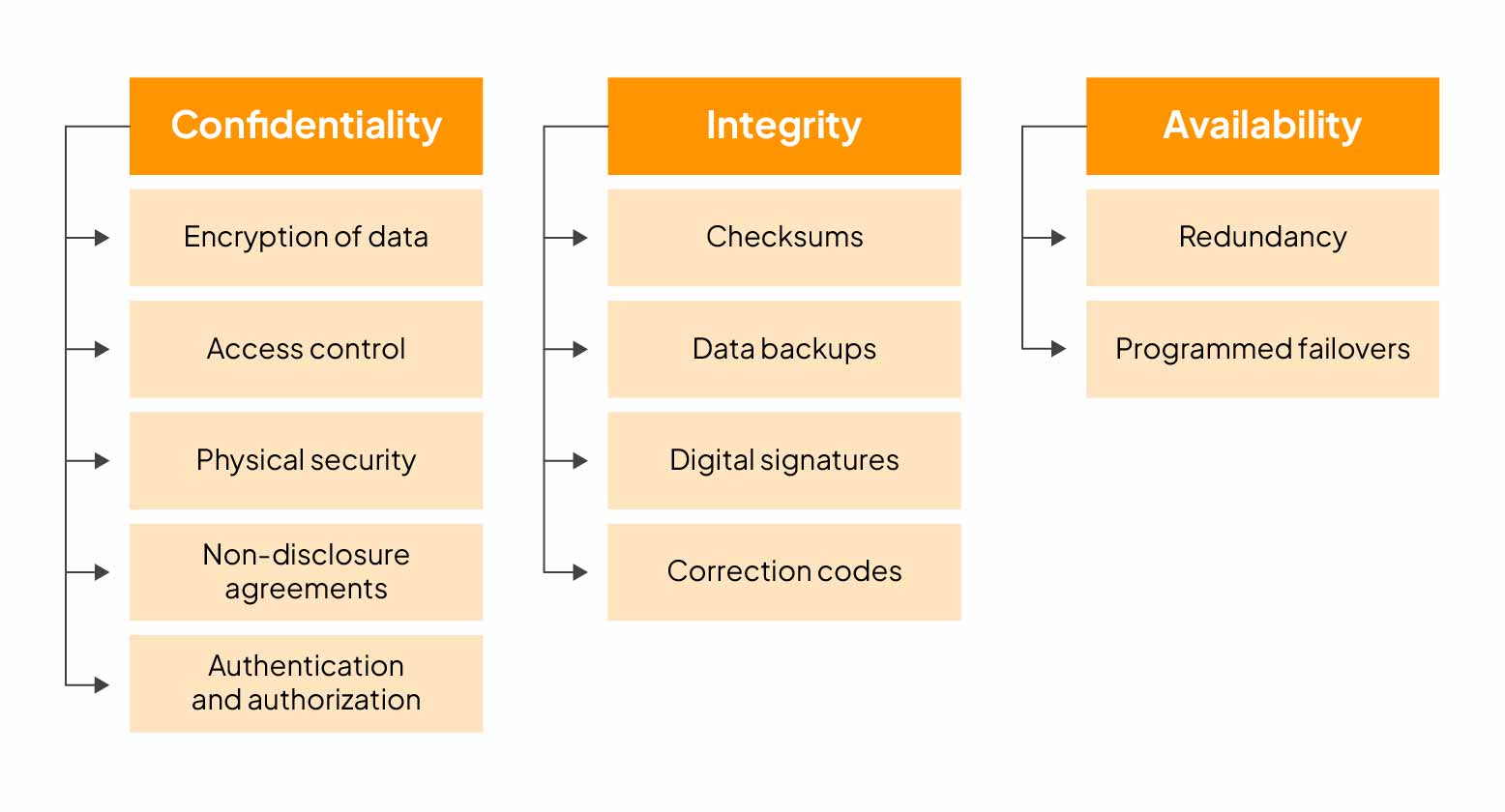
The key goals of cyber security are as follows-
Confidentiality
Ensuring that sensitive information remains private and is only accessible to authorized individuals or systems, preventing unauthorized disclosure or access.
Integrity
Maintaining the accuracy and reliability of data and systems, guarding against unauthorized changes or tampering.
Availability
Guaranteeing that systems and data are accessible when needed, preventing downtime or disruptions.
Authentication
Verifying the identity of users or systems to ensure they are who they claim to be.
Authorization
Granting or denying access to resources based on a user’s permissions or privileges limits what actions they can perform.
Non-repudiation
Providing proof that a specific action or transaction occurred, makes it difficult for individuals to deny their involvement.
Data Encryption
Securing data by converting it into a coded format to protect against unauthorized access or interception.
Network Segmentation
Dividing a network into smaller segments to contain and limit the impact of potential security breaches.
Intrusion Detection
Monitoring systems to identify and respond to unauthorized access or suspicious activities.
Intrusion Prevention
Implementing measures to actively block or stop unauthorized access or malicious activities.
Patch Management
Keeping systems and software up to date by applying security patches to address known vulnerabilities.
Vulnerability Assessment
Identifying and evaluating weaknesses in systems or networks to proactively address security risks.
Incident Response
Developing plans and processes to manage and mitigate the impact of security incidents when they occur.
Firewalls
Implementing security barriers that filter and control network traffic to prevent unauthorized access.
Malware Protection
Employing defences to detect, prevent, and remove malicious software such as viruses, worms, and Trojans.
Access Control
Regulating access to resources based on user authentication and authorization, and enforcing security policies.
Security Awareness Training
Educating users and employees about security best practices and potential threats to enhance their awareness and vigilance.
Data Backup and Recovery
Creating and maintaining copies of data to restore information in case of data loss or disaster.
Secure Software Development
Integrating security practices and controls into the software development lifecycle to prevent vulnerabilities.
Penetration Testing
Conducting controlled simulated attacks on systems to identify and address security weaknesses.
Mobile Device Security
Implementing measures to protect mobile devices and their data from security threats.
Cloud Security
Ensuring the security of data and applications hosted in cloud environments, addressing unique cloud-related risks.
Regulatory Compliance
Adhering to legal and industry-specific requirements to protect sensitive information and maintain customer trust.
Asset Management
Tracking and managing all hardware and software assets to maintain an up-to-date inventory for security and compliance.
Security Policy and Governance
Establishing rules, procedures, and oversight to guide an organization’s overall security strategy and decision-making.
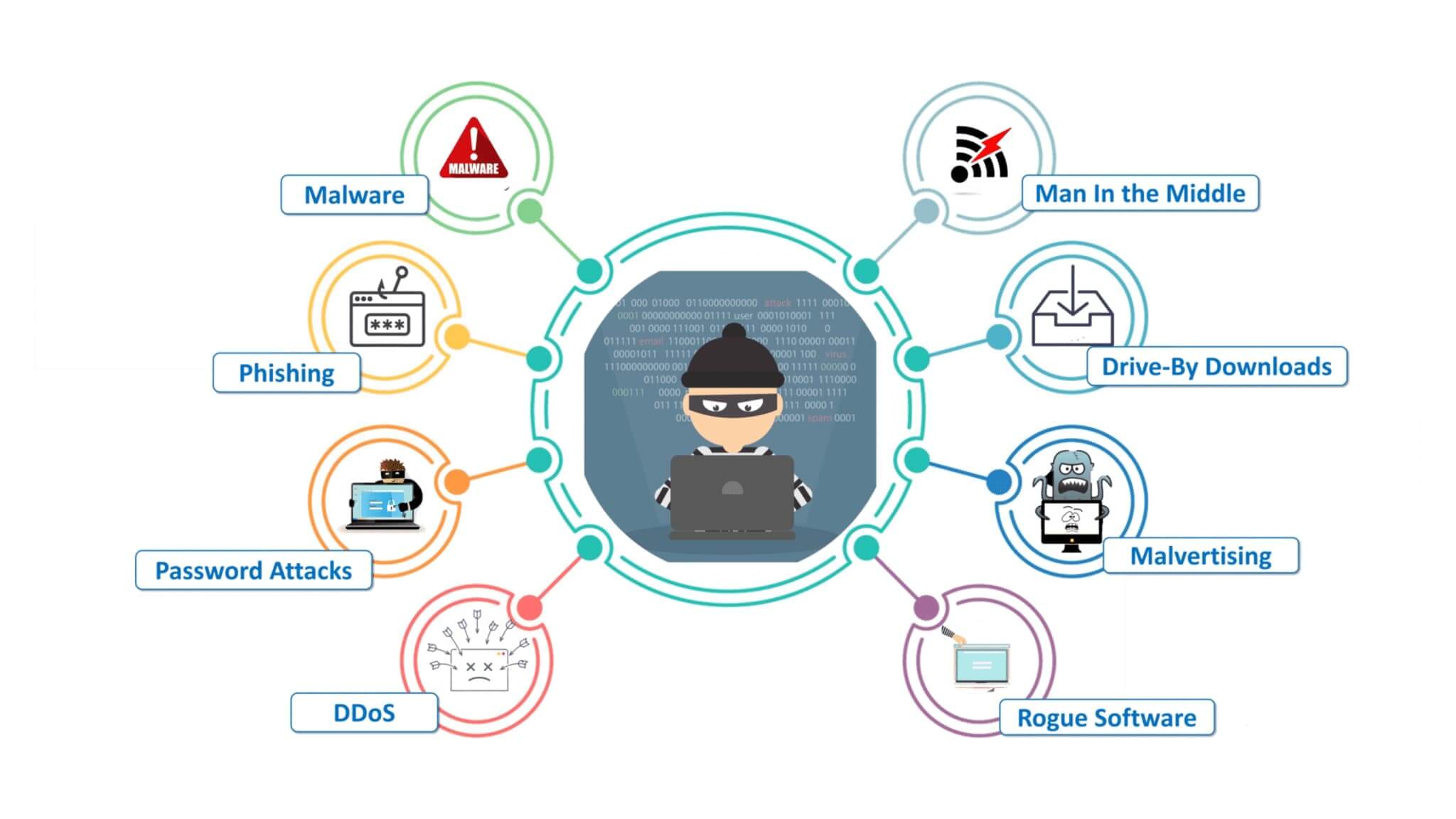
Discoursing Cyber Risk - A Major Threat

Cyber risk is something that has majorly been focused on by organisations looking to invest in cybersecurity. From data breaches to malware attacks and network infrastructure failures – the danger of a cyber threat coming into play can be extensive. It is therefore really important for businesses to ensure they are focusing on preventing these risks from happening in the first place – this can involve addressing Cyber Risk Management (CRM). CRM looks at identifying, assessing, managing, measuring and monitoring all possible types of these threats; so it should always be prioritised when seeking out ways to protect against them.
Organisations must use CRM to detect potential dangers posed by their systems and figure out how they can minimise any risks or vulnerabilities arising from them. Researching new technologies and trends which could be employed as part of a successful CRM strategy is also crucial in defending corporate data better.
Furthermore, educating personnel on cybersecurity best practices will tend to bring down the danger of cyberattacks since it gives staff an insight into safe online behaviour that should be executed always whenever working online. Last but not least, frequent system audits/surveys are necessary when discussing cyber risk – you must stay aware of modifications or updates appearing which may point towards heightened levels of riskiness. Understanding what makes up ‘cyber risk’ well plus having processes for managing it properly assures businesses that their aims on cybersecurity will likely be accomplished with success!
An Insight into Data Security as a Cybersecurity Goal
Data security is one of the most essential components when it comes to cybersecurity. It’s all about ensuring that valuable information stays away from prying eyes and also protects said data against theft, thus keeping malicious cybercriminals far away. To comprehend this goal within the field of digital protection, we need to understand what kind of info needs preserving as well as how exactly can this be achieved.
The range in question stretches anywhere from personally identifiable details like our social security numbers or credit card digits over intellectual property right up to evidence related to authentication such as driver’s licenses and passports – imagine if someone got ahold of those!
When it comes to safeguarding confidential data, secure methods such as encryption and authentication are necessary. This is why many organisations opt for digital certificates or two-factor authentication processes. To protect against malicious attacks like viruses, malware and ransomware that can compromise user accounts and corporate information, companies must implement proactive security protocols such as network segmentation in addition to educating their employees on the dangers of phishing emails. Doing so helps prevent them from being taken advantage of by cybercriminals who use these techniques with nefarious intentions just waiting for an unsuspecting victim!
Companies should also check up on any 3rd parties they might be working with, as this could be the source of a security breach. Having all these precautions in place decreases the chance of an attack greatly and provides you with plan B if one occurs. Data security is now pivotal to cyber protection goals; when it comes to personal data, big organisations must make sure their customers’ information is secure and hack-free at all times. Taking proactive steps ahead will ensure your organisation can stay one step ahead of potential threats in the future days too.
What is the importance of Network Protection in Cybersecurity?
The key target of cyber security is to safeguard networks. Network safety plays a crucial role in every firm’s total cyber defence system and businesses must make sure that their network protection steps are adequate. Network security provides the organisation’s confidential information by forming an obstacle between it and unauthorised access from hackers or other malicious users.
Moreover, this also ensures all data stored on the device stays private so only those who have authorised access can view or change it – but how secure do we feel with these measures in place?
Network protection covers things like getting antivirus installed, having firewalls in place, handling passwords carefully, encryption and managing encryption keys. All of this assists organisations to steer clear of data breaches or cybercrime chances. Furthermore, it keeps unwelcome folks away from sensitive material such as banking records, user details or trade secrets.
Besides protecting a company’s information and systems against hackers purposefully doing bad stuff on it; network defence also helps personnel stay safe by preventing phishing attempts or infective malware infiltrations onto computers etc.. Businesses have got to be sure their security system is constantly up-to-date with the newest patches and updates for safety purposes!
By keeping systems shielded from known vulnerabilities and threats, companies can decrease the danger of cyber-attacks notably. Additionally, businesses ought to routinely carry out appraisals of their network infrastructure which demonstrate any regions where more noteworthy enhancements could be made as far as both speed and security measures. This procedure will help organisations to recognize frail spots in their frameworks before they become a target for aggressors.
What’s more, having powerful approaches and techniques set up for dealing with representative passwords is fundamental for decreasing the hazard posed by unapproved get-to-get-endeavours or malevolent action inside business networks. Organizations should guarantee that representatives are consistently prepared on secure password rehearses just as how to recognise suspicious movement on the framework.
These means can incredibly improve an organisation’s system assurance strategies for battling digital wrongdoing today – something which stays significant if we need to remain safe online in tomorrow’s universe of advanced change!
The Relevance of Endpoint Security in Achieving Cybersecurity Goals
Cybersecurity has become a must for businesses all over the world, as malicious cyber attacks persistently grow every year. Endpoint security is an integral part of achieving cybersecurity ambitions and safeguarding a company’s network from prospective intrusions. To put it simply, endpoint security refers to defence actions taken onto single devices such as laptops or computers that are linked to some sort of network; measures include firewalls, antivirus software applications, encryption technologies, authentication protocols and networking monitoring systems. But how can these steps help protect against impending threats?
Endpoint security can help organisations out, as it helps make them less vulnerable to data breaches and keeps them in line with regulations. What’s more, firewall protection and antivirus software are key components of good endpoint security; they provide an extra layer of defence against malware or hackers trying to get into the system. Keeping systems up-to-date is a must if you want your company’s information kept safe – outdated technology will be much easier for malicious actors to exploit.
Keeping up with regular updates is essential for making sure that any security weaknesses are tackled promptly, as well as providing extra protection against malicious threats. Companies should also ensure their endpoint security solutions are regularly kept an eye on – thus ensuring the detection of any untoward activities going on within their networks and subsequently taking suitable action before potential damage is done.
To top it off, conducting periodic reviews helps guarantee that the security measures implemented work properly and meet all expectations set out for them. All things considered, implementing strong endpoint security is necessary if businesses wish to safeguard themselves from unauthorised access or cyberattacks while remaining compliant with regulations in place simultaneously. Properly deploying these solutions can greatly reduce risks associated with online threats and provide peace of mind at the same time.
Cyber Defense Strategies in Mitigating Cyber Threats
It is fair to say that cybersecurity is a major concern for businesses and organisations these days. As the amount of cyber threats continues to grow, it has become more crucial than ever before for organisations to safeguard themselves from them. One approach they can do this through is cyber defence strategies. These strategies have been created to reduce any potential risks due to cyber threats by deploying different security systems, technologies and practices – all in an effort towards detecting problems earlier and responding quicker should one arise.
In other words, such measures seek out trouble ahead of time so as not to prevent serious issues from arising later on down the track.
When it comes to cyber defence, organisations have to carefully weigh up the cost and security that they’re aiming for. To protect against malicious software attacks, companies deploy malware detection systems as well as firewalls; access control lists (ACLs) can be used so only authorised personnel gain access to sensitive data; encryption techniques ensure confidential information is stored securely – all of these measures help bolster an organisation’s defences.
Besides this sort of tech protection, regular backups should also be employed in case a system gets breached – that way any lost data can quickly and efficiently be recovered…but where does this leave you when trying to balance out costs with level of safety?
Deploying strong encryption measures might be costly, but it could give you more protection than just standard firewall settings. In contrast, cheaper solutions such as whitelisting certain programs or limiting user activities may fit some organisations better and still offer decent defence from the most common sorts of attacks. Organizations should take a look at their goals and ambitions to decide what level of security they need before making the decision on which strategy is right for them.
Furthermore, companies ought to think about investing in third-party incident response services too; this way if an invasion does happen despite all prevention efforts put into place then there will be quick remedial action available immediately after detecting any breaches. It’s paramount that businesses today not only employ effective cyber defences but also keep up with modern trends so that when new threats appear they can try to stop those dangers before it’s too late.
Role of Continuous Monitoring in Cybersecurity
When it comes to cybersecurity, having the right goals is essential. One of these objectives must be continuous monitoring. Continuous monitoring is a process which takes place constantly to spot and deal with any risks or dangers that could affect an organisation’s systems, networks, applications and data. It allows companies to identify potential weaknesses so they can sort them out long before they become an issue.
By proactively keeping tabs on security issues organisations are more enabled to protect against cyber-attacks as well as other malicious behaviour – what better way than being prepared?
With the rise in cybercrimes such as phishing attacks, ransomware and data breaches, organisations must make sure their cybersecurity measures are up-to-date and effective. Continuous monitoring helps them achieve this by granting visibility into what’s going on inside their networks and systems right away. This allows them to pick out suspicious activity quickly so they can take action before any harm is caused.
What’s more, advanced technologies like artificial intelligence (AI) could help identify potential threats with increased accuracy than humans would be able to do manually – leaving little room for error! But have we gone too far? Are AI-assisted surveillance methods really necessary or is it just another example of Big Brother watching us?
Continuous monitoring gives organisations valuable insights into how their cyber security measures are performing over time, so they can judge if their solutions are working as expected or require more tools and configurations. For example, when an organisation notices a rise in unsuccessful login attempts across specific servers or applications, then it is possible to tweak access policies and/or implement extra authentication layers accordingly.
To conclude, continuous monitoring carries out a fundamental role in keeping secure IT environments for any business today; without it would be much trickier to keep security incidents from happening – not to mention being able to quickly respond when something transpires!
How Cyber security Goals Contribute to Business Continuity?
Considering the goals of cybersecurity, there are various points to take into account. Safeguarding organisations and people from cyber-attacks is paramount; however, an often forgotten element exists – business continuity. Cybersecurity objectives not only support shielding companies against potential threats and attempted break-ins but also ensure these operations work efficiently without any complications.
Business continuation planning isn’t exclusively about having a strategy when things don’t go as expected, it’s much more than that…it emphasises being prepared for anything which could lead to disruption within any given organisation or company. Have you ever considered how your organisation would fare?
When it comes to staying in business, your company is only as secure and stable as its defences against external threats. Natural disasters, system breakdowns, cyber-attacks or employee exits due to retirement or illness can all have a devastating effect if the right security protocols aren’t put in place – such as multi-factor authentication; encryption; firewalls etc. That way you stand more chance of ensuring that no matter what’s going on outside your control your systems remain firmly intact.
But there’s another factor which plays a huge role in keeping things running smoothly – making sure processes are up and running again swiftly after something goes wrong so any disruption has minimal impact on operations. It could be having an effective backup plan for crucial data recovery should problems arise; otherwise you risk falling behind with deadlines and customer service quality dropping through the floor!
It’s also essential to have the knack of being able to restore or shift IT infrastructure quickly – allowing companies to return in full swing with minimum non-operational time or disturbance. As well as safeguarding confidential data, arrangements must be made so employees can work remotely if required. A lot of organisations nowadays demand their staff members should access cloud-based programs such as Office 365 and Google Suite for them to get ahold of information on tablets or mobile phones when away from the office; this ensures teams can keep going without interruption during an unexpected event.
In general terms, these solutions supply flexibility and robustness which let businesses remain functional no matter what unanticipated events may occur. The ultimate aim of cybersecurity ought always to be prevention; however, establishing approaches aimed at ‘business continuity’ is just as necessary for keeping organisations safe against prospective disruptions that are caused by either malevolent characters or activities beyond their power.
The Future of Cybersecurity - Emerging Trends and Challenges

It is vital to grasp the objectives of cybersecurity for us to fully take on board what lies ahead in this area. Generally speaking, there are two main aims: guarding digital info and assets from unauthorised access or damage, as well as ensuring secure data transmission over networks. It should be remarked that these goals don’t negate each other; both need to be achieved if you want effective cybersecurity measures in place.
A look at new developments reveals AI (Artificial Intelligence) and Machine Learning leading the charge forward here – algorithms based on AI have been created which detect malicious behaviour by looking into patterns within network traffic and spotting any abnormalities.
Network security solutions are now incorporating artificial intelligence (AI) technologies such as deep learning, natural language processing and computer vision into their products to offer more accurate threat detection. AI can also be utilised for automated responses to cyber threats – allowing them to react quickly and effectively.
The challenge here is making sure that these new techs remain safe, so there’s no chance of compromising the safety of data or systems; if an attacker was able to gain access to a neural network using AI for instance, they could get hold of sensitive information, or even disrupt primary operations. How do we stop this from happening?
Hence, organisations must invest in robust cyber-security tactics such as encryption, identity management systems, secure development lifecycle processes and any other measures to aid in defending critical infrastructure from malevolent actors.
A further predicament experienced by cybersecurity pros is keeping ahead of continually changing threats. Hostile hackers persistently create different techniques to make use of vulnerabilities in networks and systems to gain access to confidential data or disrupt operations. In consequence, organisations should put money into predictive analytics capacities that are capable of finding potential cyberattacks before they take place so swift and effectual preventive steps can be taken forthwith.
On top of this, businesses ought to consider investing in user education programmes so employees understand proper security protocols when dealing with sensitive information and accessing online resources correctly.
To wrap up companies need to contemplate risk management strategies while strategizing on the future outlooks for cyber-security which includes inspecting likely risks connected with specific activities before implementing them so they could diminish any foreseeable losses or disruptions owing to breach events touching customer data or operational procedures..
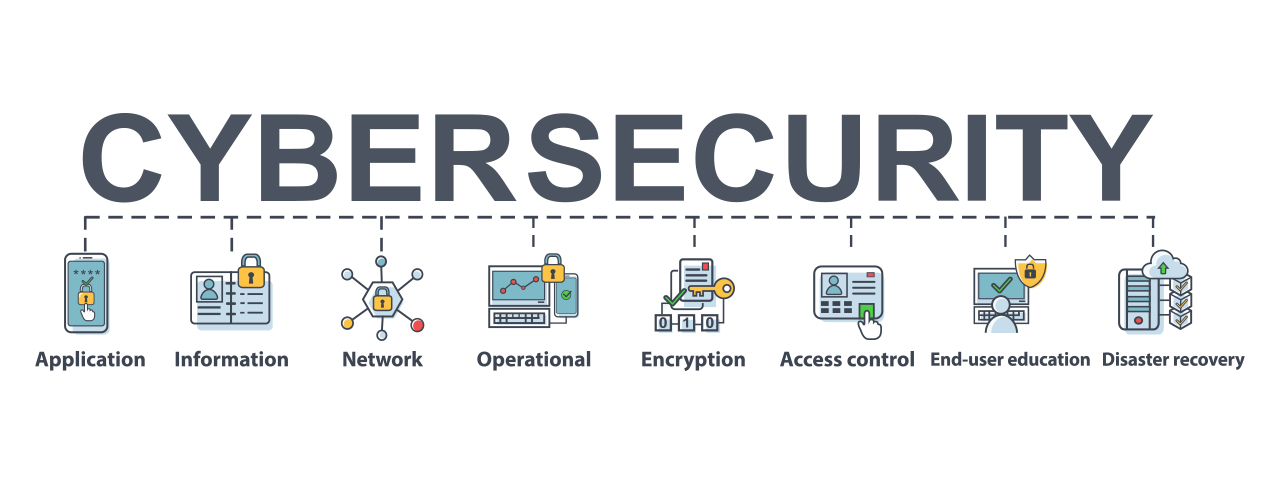
To sum it up, cybersecurity is an absolute must for organisations and their digital strategy. Its purpose is to safeguard networks, data and endpoints from cyber risks through defensive tactics. Companies need to have a thorough method of protecting against cyber threats which should include measures such as network protection, data security and endpoint security.
With these in place, they can more effectively thwart attacks on the vital systems that keep them running smoothly. What do you think? Isn’t good cybersecurity essential when having critical operations?
Are you looking to take the next big jump in your career? Have you ever imagined yourself as an expert in the field of cybersecurity? If that’s what floats your boat, get signed up for our Cybersecurity Master Program!
Our program will give thorough training on a wide variety of topics connected with cyberspace safety, such as risk management and cyber laws, digital forensics, malware analysis and cryptography. Our immensely competent lecturers are available throughout this course offering guidance during debates and aiding to hone your capabilities. We also have online mentorship prospects with experienced professionals from leading organisations within the industry.
By joining this pioneering program, you can become a highly sought-after connoisseur in this tech sector. You’ll acquire invaluable skills which could be employed for any job concerning cybersecurity – no matter which way you decide to go down afterwards. So don’t waste any more time – enrol now while taking advantage of these spectacular learning openings!
Fancy a career in cybersecurity? Don’t pass up the opportunity to join our Cybersecurity Master Program! This one-of-a-kind course is designed for you to cultivate and sharpen your skills as a cyber security expert. Our curriculum has been crafted by some of the foremost professionals out there, so if you’re keen to become an ace at preventing attacks from digital assailants, cryptography, network safety structure or any other related field – we’ve got just what it takes.
On top of that, there’s plenty of hands-on work which will furnish you with the proper tools required to make waves within this exhilarating area. So don’t hang around – get signed up now and seize success at the click of a button!
Happy Learning!