Cloud computing has certainly taken the world by surprise, and it is now an indispensable part of many businesses. It offers a staggering amount of computing power and access to a multitude of services, plus large amounts of data can be stored safely in such an environment. But as always there are always advantages and disadvantages of cloud computing when one is considering the usage – that said let’s go through them all right now!
The cost savings, scalability agility and reliability associated with this tech are clear-cut advantages; whilst data security compliance regulations breach and privacy concerns might raise red flags before you dive into using clouds within your own company—so make sure you read on further to get well informed about what getting onto the cloud involves!
Understanding What Cloud Computing entails

In recent years, cloud computing has become an ever more talked-about topic and it is essential to grasp the basics. Put plainly, cloud computing can be described as a catchall term for providing computer services on the web. This covers multiple activities such as storage facility, networking and server hosting – simply put being able to outsource tech-related tasks while making sure firms have access to tools required to remain competitive.
Ah yes! Here comes probably one of its greatest assets: scalability; which means you can adjust capacity according to your needs (whatever they may be). Cloud computing makes it much simpler for businesses to be able to adjust their IT solutions according to the requirements they have, without needing any extra hardware or software. This ability adds a whole lot of convenience as companies can invest in fewer resources while still tailoring them perfectly into whatever project needs may arise – and also helps cut costs related to investing in new equipment or relying on people’s time for maintenance purposes.
What’s more, cloud computing is incredibly reliable too! Its well-known high amount of reliability has proven invaluable when meeting business objectives and delivering projects most effectively.
Cloud services are hosted on servers that have been designed with reliability and uptime in the forefront, making them much more dependable than self-hosted solutions which could be exposed to system malfunctions or downtime because of inadequate maintenance or lack of resources. Additionally, many cloud providers also give innovative safety measures such as encryption and use their systems automatedly so they always apply the latest security patches – meaning these methods are way safer than those used by self-hosted solutions.
This last advantage is flexibility – users can access their data from anywhere at any time providing only they have an internet connection; a bonus for remote working situations where teams need rapid admission to records stored over several gadgets in various locations.
In general, if correctly tapped into, cloud computing has plenty to offer businesses – scalability, stability and mobility along with cost savings resulting from decreased investments in equipment and workforce. So why not take advantage?
Exploring the Various Types of Cloud Services

Cloud computing has become quite the popular choice for businesses of all sizes, from large corporations to small start-ups. This is because it provides a wide range of services that can help companies cut down time and costs. The huge variety of cloud solutions though could be overwhelming; so doing your homework beforehand would surely pay off in making an informed decision about which might be right for you. If you’re thinking about jumping on board with cloud computing then having a good look at the different types first would certainly make sense as step number one!
When it comes to cloud services, there are three main types: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS) and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each of these has its pros and cons which need considering before making any decisions about what kind of cloud service your business requires.
Nevertheless, this convenience involves a price tag: IaaS generally comes with hefty costs for data storage and bandwidth utilization – although there are plenty of budget-friendly options if you hunt around. Moreover, PaaS is made especially for software engineers who need a platform to construct applications on top of fundamental hardware or program components. Through this, they receive access to personalised development instruments that make creating apps simpler than it has ever been before!
Some PaaS providers also offer databases in addition to other features like analytics and message queues – but be wary that these facilities usually come at an extra cost. At the same time, SaaS offers pre-built application packages which can be used without any additional setup or installation steps – put simply users don’t have to worry about administering the service on their own. However, since everyone is using a similar software package customisation options may sometimes be restricted meaning your exact requirements might not always get fulfilled – something else worth thinking of when deciding whether SaaS would suit your organisation’s needs?
Delving into the Benefits of Cloud Computing

Cloud computing has caused a real stir in the world due to its convenient scalability and cost-saving attributes which makes it appealing for businesses. Over recent years, this technology hasn’t just gained popularity but is now commonly used by every kind of organisation. Getting into why cloud computing can be such an advantage helps explain why companies are making the transition from conventional IT facilities to these sorts of cloud-based services.
The main benefit of cloud computing is that firms no longer need their costly IT infrastructure – what a relief!
Moving to cloud computing eliminates the need for companies to purchase costly hardware that may depreciate quickly or build a devoted IT crew just to manage their systems. Using this service reduces overhead costs, and more time can be spent on core activities which will return higher returns – both financially and in terms of productivity.
Security is also an important consideration when it comes to employing cloud services as they ensure customer data stays safe from malicious attack or theft. With remote servers providing all necessary resources, businesses can benefit greatly without risking sensitive information falling into the wrong hands!
Cloud providers take on advanced security measures to secure customer data, aiming at keeping customers’ trust and making sure all the stored information remains safe. This removes any concern about breaches in safety from companies, enabling them to pay full attention towards driving growth through innovation that leverages these strong platforms.
Furthermore, cloud computing offers another major advantage which is its capacity of hosting multiple applications together without having an impact on performance or facing any hardware-related trouble.
Companies have more leeway when it comes to expanding and growing their operations, as cloud storage capacity isn’t restricted like with conventional IT infrastructure solutions where physical space is regularly a boundary. Also, this makes software upgrades smoother; they don’t need an enormous team devoted to managing installations and overhauls any longer – updates can simply be done from the remote server whenever needed.
These are only some of the examples that make cloud computing so attractive for businesses nowadays but there’s much more one can experience from using these services such as online collaboration tools, increased efficiency through automation processes, better tracking capabilities insights into user behaviour etcetera! In conclusion, then considering how progressed our technology has become lately transitioning from typical IT infrastructure arrangements to nor could bring great added benefits for your business activities.
The Convenience of Data Storage in the Cloud
Data storage in the cloud is becoming a more and more popular choice for businesses and individuals who want to keep their data secure. Not only does it bring convenience, but also peace of mind that your valuable information won’t be damaged or lost. So what are the good parts about storing stuff on the web? Let’s explore some advantages of using cloud computing when it comes to data storage!
First off, you don’t need any physical equipment if you’re opting for saving your info online – all those terabytes can easily fit onto someone else’s server while taking zero space from yours! That way there will be no hassle with purchasing new drives every time there isn’t enough memory left – just move your documents or files into ‘the clouds’ instead!
Cloud computing does away with the requirement for users to install software or look after servers, which can be draining and expensive in the long run. Plus, keeping large amounts of data on a cloud means that there’s no need to worry about storage limitations on physical devices as everything is kept remotely. This eradicates many potential problems such as power outages or hard drive malfunctions that might result in valuable data stored onsite being destroyed – something we would all rather avoid!
Another plus side when it comes to using a cloud-based system for storing your information is increased flexibility when accessing what you have saved Data stored on the cloud can be accessed anytime and from any corner of the world as long as you have an internet connection. Also, numerous individuals can get to this information simultaneously without worrying about conflicts concerning accessing the same file at once – provided they are granted permission by its owner.
This makes it simpler for teammates to collaborate and reach up-to-date versions of files from any device whenever they wish – so there’s no need to wait to make changes or receive updates when getting back to their workstations. What’s more, security features delivered by cloud systems stand out considerably in comparison with traditional data storing techniques which could easily be penetrated if proper safety regulations aren’t set in place; raising the question of whether malicious third parties might access such sensitive material.
Analysing the Advantage of Cloud Computing Power

There is no doubt that the emergence of cloud computing technologies has been a total game-changer in how we access and control data nowadays. Taking advantage of the power of the cloud, individuals are now able to save, share, and get hold of their documents from any device with an accessible internet connection. What happens when a business faces sudden spikes in demand? Cloud Computing offers businesses major advantages like scalability, cost-effectiveness as well and innovation – enabling organisations to swiftly respond to varying market needs without having gigantic start-up costs.
Cloud computing comes with a range of advantages, not least access to powerful resources that might otherwise be out-of-reach for many organisations. Take machine learning and data mining as examples – resource-intensive tasks which could prove prohibitively expensive if done in-house but made possible thanks to the cloud. Furthermore, deploying these services is often far simpler than traditional software systems since there’s no need for any physical infrastructure or IT resources.
Cloud providers usually offer a range of configurations, making them more attractive to customers as they don’t have to fork out extra hardware before using added processing power or storage capacity. This means businesses with limited budgets can use scalable resources on-demand without investing in local infrastructure – an absolute must if you’re looking to widen your customer base.
Plus, the elastic nature of most modern clouds allows users to scale up and down promptly according to their needs without enduring long procurement procedures or appointing fresh staff members. All things considered, analysing the Cloud’s advantage when it comes to computing power discloses that it offers users considerable flexibility when meeting computational requirements while lessening economic hazards and overheads associated with conventional solutions like physical servers or dedicated hosting facilities. In what ways do these benefits appeal?
Discussing the Cost Efficiency of Cloud Computing

The cost efficiency of cloud computing is a major benefit to businesses. It can lead to increased productivity, improved agility and more efficient resource use. Companies can save on costs related to their IT infrastructure by making use of cloud services such as Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS), Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) or Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS). By taking advantage of public clouds like Amazon Web Services(AWS) or Microsoft Azure, organisations have access to resources than ever before without needing to buy extra hardware or software.
When it comes to cost savings, cloud computing offers a huge benefit. Businesses only ever have to pay for what they use – so no more overspending on IT or other capacities! What’s more, with the scalability of cloud computing providers businesses don’t need to worry about buying too much upfront – now you can scale your resources up and down depending upon demand without any additional costs. This is incredibly useful for companies that experience seasonal spikes in workloads; as well as those whose business needs change frequently throughout the year. How good would it be not having to invest large amounts of money into something you may end up never using?
Cloud computing can have a hugely positive impact on businesses of all sizes, from reduced infrastructure spending to improved resource utilization leading to higher productivity in the long run. For instance, if your company experiences an unexpected spike in demand for its services you can easily scale up or down depending on the load – this flexibility helps keep costs under control and ensures systems stay reliable at all times.
In addition, many providers offer discounts when committing to a certain amount of computing power over an extended period; leveraging these deals could significantly reduce IT expenses without compromising performance and reliability. All things considered, it makes perfect sense why so many organisations are now embracing cloud technology!
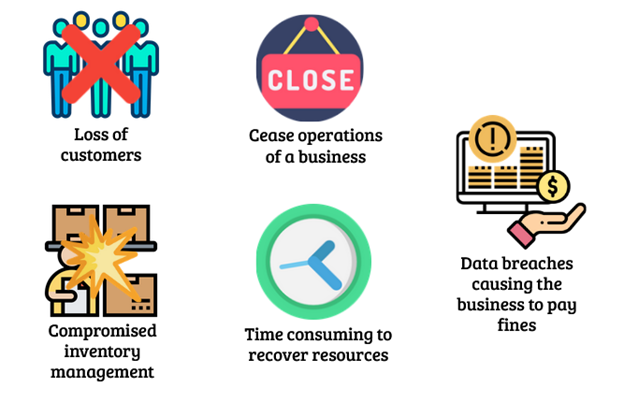
Highlighting the Potential Risks and Disadvantages of Cloud

Considering cloud computing, one of the plus points is that it can assist businesses in cutting IT costs. Nevertheless, there are also certain potential dangers and drawbacks related to this tech. Before deciding to make use of the cloud or not, it’s vital to be aware of these likely worries. The most regularly referred risk about cloud computing is its security certainty – as companies depend on third-party providers for data storage and applications they are putting their confidence into someone else’s structure!
It leaves them open to risks like cybercrime being committed against them; organisations then become vulnerable because their operational technology could be exposed by malicious actors outside of themselves coming from anywhere around the world with an internet connection – alarming isn’t it?
This means that they have to make sure the provider’s security measures are up-to-date and secure enough to protect data from malevolent assaults or unauthorised access. On top of that, a few countries might have different regulations concerning data privacy which could introduce an extra layer of complexity depending on where the information is stored.
An organisation must do their research thoroughly when it comes to selecting a provider before settling down with them as well as having a robust agreement set in place between two sides so everybody knows what is expected from them regarding security matters. How can you be certain about your safety online? What should organisations take into account while assessing various providers?
Cloud downtime can be a huge problem for organisations which rely heavily on always having access to their applications and data. This includes outages caused by natural disasters, cyber-attacks or maintenance windows set up by the provider – all of which could potentially disrupt if not planned accordingly in advance. Therefore, firms should have plans in place so that processes are followed when any such occurrences take place; finding ways to reduce inconvenience while also upholding high-security standards would then become an achievable goal.
In conclusion, another problem of utilising the cloud is price uncertainty if a company chooses to go for public cloud adoption instead of private clouds. As opposed to paying in advance like you would with a private cloud provider, when it comes to public clouds customers can pay on an as-used basis – thus companies must have appropriate budgeting contingent upon how much they anticipate their usage costs will upsurge over time compared with what’s included within fixed payment model associated with using private networks which may be more suitable depending on particular requirements.
To summarise then; though numerous advantages come from making use of this technology such as scalability and flexibility; grasping potential hazards and disadvantages linked with employing the service should also be taken into account before any decisions are made so organisations don’t get themselves caught by surprise further down the line!
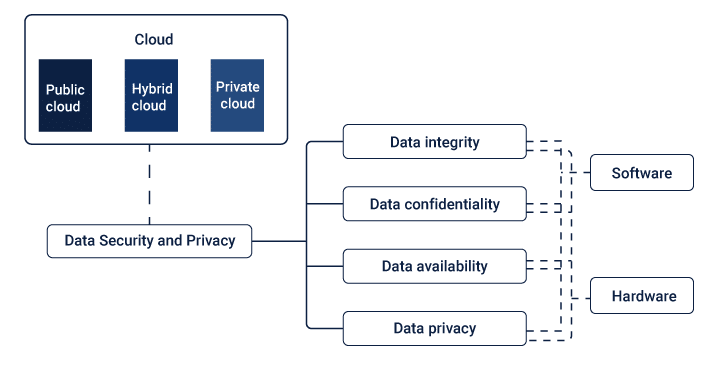
Looking at the Security Concerns in Cloud Services

As businesses become more and more reliant on digital technology, cloud computing has been growing in popularity. It brings a lot of advantages for companies such as cost savings, flexibility and scalability – but there are also some security issues that organisations should bear in mind before fully immersing themselves into the cloud.
Data stored in up cyber sphere is exposed to all sorts of threats like malicious software or hacker attacks which can be very dangerous. Encryption techniques and authentication processes help to provide an extra layer of safety yet they might not always give a guarantee against break-in attempts – what could we do about this?
Hackers can get their hands on user accounts or break encryption protocols to see confidential info. What’s more, cloud service providers aren’t always the best at controlling their data centres which makes them vulnerable points of attack. So, businesses must pay attention and make sure their cloud provider takes all possible measures necessary to protect customers’ data from risks out there. Furthermore, companies must be aware of what harm could potentially come from malicious insiders who have access to sensitive files stored within the clouds – a real security hazard if ever there was one!
Using cloud infrastructure can provide organisations with plenty of advantages, but there are also a lot of potential security risks to be aware of. If misused or left unchecked, individuals who have access could use their privileges for undesirable purposes which may lead to data loss and other breaches. To make sure those accessing the system comply with proper safety protocols, companies need to ensure they understand these themselves first.
What’s more, businesses should look into what backup plans are in place by their chosen service provider – you don’t want any downtime if an attack occurs so having thorough fallback protection can help minimise disruption when things go wrong. All this considered; it is essential for firms considering moving over to the cloud to evaluate all associated risks before making any final decisions about adoption – simply put: ensuring your critical information stays safe while keeping business continuity during unexpected events should be a top priority!
Discussing the Issue of Cloud-Dependence

Cloud computing has seen a major surge in popularity recently, and it’s easy to see why. We no longer need physical computers or servers to store huge amounts of data or program files- cloud-based services make that much easier by storing these things digitally! This not only saves space but also makes our lives so much simpler. Having said that, it is important to be aware of both sides of this story – while there are definite perks associated with leaning heavily into cloud technology, there can be some drawbacks as well.
One advantage of being cloud-dependent is without a doubt the potential to access files from any corner of the world instead of having to trust physical hardware. Not only does this make companies and people more adaptable and reactive, but it also assists them in cutting down their expenses by avoiding investing in their storage facilities.
Additionally, cloud-based solutions are often able to obtain higher levels quickly if storage requirements jump suddenly due to an increase in business activity – how useful! However, depending too much on cloud technology holds its risks as well; something worth keeping an eye on…
Storing sensitive info on the cloud can be a risky business as you have very little control over how it’s stored and managed by third-party services. And of course, there is always the danger that malicious actors might breach your security protocols – something no company would want to happen! It’s vital then for businesses considering switching up to ensure they’ve got suitable laws in place protecting their users’ privacy rights too.
But whether or not companies should use cloud services isn’t an easy answer – rather, each organisation needs to weigh up both pros and cons depending on what fits best with their individual needs & goals so they’re making an informed decision when it comes to future growth strategies. After all, if done right, cloud-dependence may prove incredibly beneficial down the line; but get things wrong and disaster could await…
Evaluating the Overall Pros and Cons of Cloud Computing
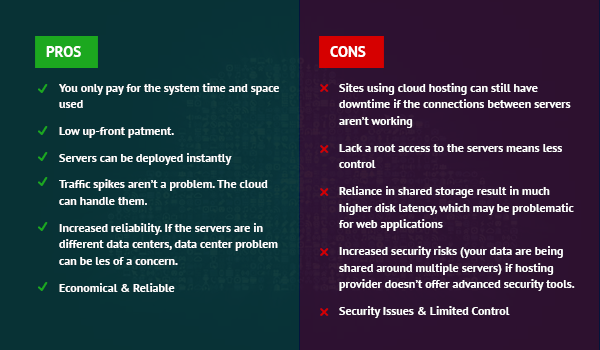
Cloud computing has taken off in a big way lately. While it’s certainly useful to businesses, there are some pros and cons that need to be weighed up when you’re assessing the overall advantages of cloud computing. One major plus is cost savings. Shifting operations into the cloud can substantially reduce expenditure on software licences and hardware, as well as maintenance and support fees – potentially leading to great financial gains if your business goes for a pay-as-you-go model rather than paying upfront costs for technology or hardware. Could this be an option worth exploring?
Despite the potential benefits that cloud solutions offer to businesses, some may find themselves faced with reliability issues. When opting for services by third-party providers such as Amazon Web Services or Microsoft Azure, companies must closely assess their track record for uptime and availability before making a decision. Furthermore, organisations should be wary of security breaches which could put sensitive information at risk if adequate protections are not in place.
For remote working employees who crave flexibility and mobility to access applications from anywhere they have an internet connection, cloud technology provides them just that – without having to compromise on productivity due to poor connectivity problems. Although this is great news for many people working remotely away from the office environment; others might struggle with staying productive due to all the distractions it can bring alongside itself!
Above everything else when contemplating using cloud computing techniques within your business operations – you ought to weigh up both pros & cons rigorously first so you make sure to get the most out of its fantastic features whilst avoiding risks which accompany its use simultaneously!
To wrap up, there’s no getting away from it that cloud computing comes with both pros and cons. On the plus side, you’d be looking at savings in terms of data storage and processing power without compromising on access to information – wherever you might want it. But then again, things aren’t always rosy: security is a concern as well as potential disruptions to service if something goes wrong server-side. Despite these issues, many companies still see using cloud computing services as worth exploring – just take into account all possible risks before taking any steps forward!
Are you ready to join the rapidly progressing world of cloud engineering? Then why don’t you sign up for our Cloud Architect Master Program?
Our program provides a thorough course which will arm you with all the fundamental skills and knowledge necessary for success. With our team of experts, custom-made practical tests and advanced credentialing from top industry players, we promise that we’ll give you the best possible chances to jumpstart your career as an esteemed Cloud Architect. So why wait any longer then – enroll today and be amongst those kickstarting this promising new profession!
Are you eager to become a Cloud Architect? Then our Cloud Architect Master Program is the right choice for you! It’s an amazing opportunity for everyone who has an eye on cloud and IT technologies. Our program includes comprehensive modules which will help in become proficient with architecture, design, planning as well and operations. And if that wasn’t enough already then here comes the best part- we have highly experienced instructors and an unbeatable support system so your success is certain. So why wait any longer? Enrol now and embark on an incredible journey of transforming yourself into a certified professional Cloud Architect!
Happy Learning!