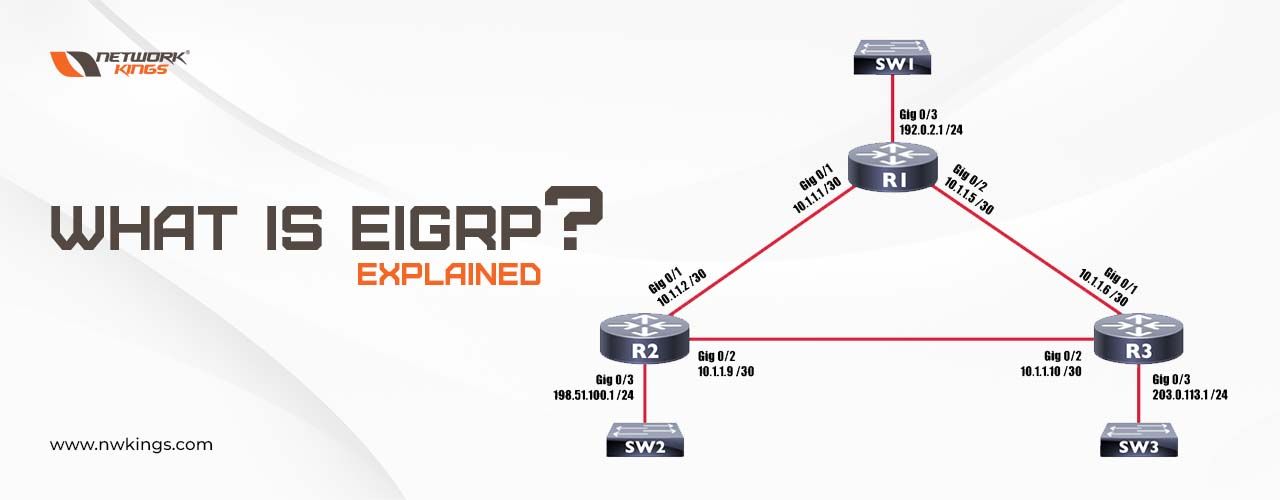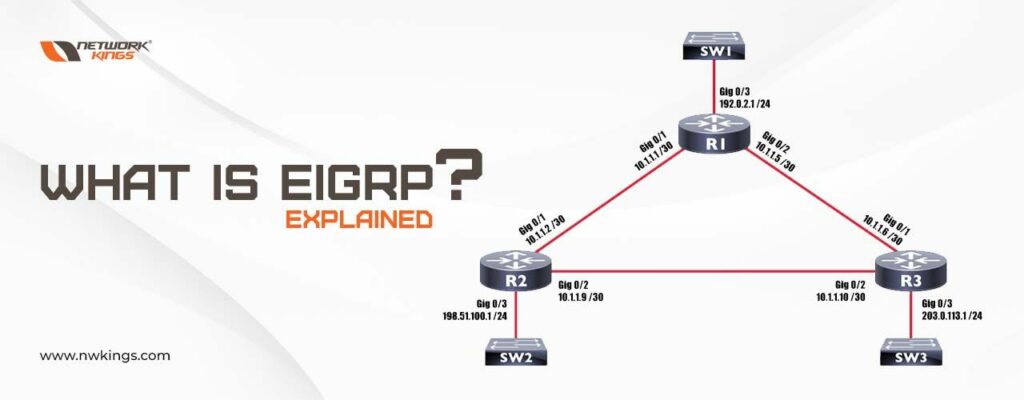
EIGRP in networking, also called Enhance Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), works on layer 3 of the OSI model and helps find the best path. It is an updated version of the IGRP protocol. EIGRP used to be a Cisco Proprietary protocol but it became an Open standard protocol and can be configured on devices other than Cisco. Administrative distance for EIGRP is 90 for internal routes and 170 for external routes. EIGRP uses protocol number 88.
EIGRP in networking is an advanced distance vector routing protocol, also called hybrid routing protocol, that uses the properties of Distance vector routing protocol as well as link-state routing protocol.
In the Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP), multicasting efficiently exchanges routing information between routers within the same Autonomous System (AS). EIGRP uses a specific multicast address for this purpose. The multicast address used by EIGRP for IPv4 is 224.0.0.10. In the case of IPv6, EIGRP uses the multicast address FF02::A.
EIGRP routers send their routing updates and queries to this multicast address, allowing other routers in the same EIGRP AS to receive and process the routing information. Multicasting helps reduce unnecessary network traffic by ensuring that EIGRP updates are only sent to routers interested in receiving them, which is especially important in larger networks.
What are the features of EIGRP in Networking?
The features of EIGRP in Networking are as follows-
- EIGRP uses a Diffusion Update Algorithm (DUAL). This algorithm helps EIGRP routers to perform rapid convergence when changes occur in the network. EIGRP also sends updates when there is a change in the network topology, unlike traditional distance routing protocol that sends updates periodically. This helps EIRGRP become efficient and saves bandwidth.
- EIGRP supports Variable Length Subnet Mask (VLSM) and Classless Inter-Domain Routing (CIDR) which allows efficient use of IP Address.
- EIGRP supports route summarization which helps to reduce the size of the routing table and minimize the amount of routing information exchanged between routers.
- EIGRP uses loop prevention mechanisms such as the split horizon to prevent routing loops in the network.
What are the types of EIGRP Packets?
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) different types of packets to facilitate the exchange of routing information and maintain neighbour relationships between routers within the same Autonomous System (AS).
Hello Packet
This packet is used for neighbour discovery and to maintain the neighbourship after it is established. These packets are sent by EIGRP routers periodically. When 2 routers receive the EIGRP Hello Packet, they become neighbours.
Update Packets
These packets are used to update neighboring routers about the changes in the network topology. These packets are only sent when there is a change in network topology like route deletion, new routes addition, link failure, metric update, etc.
Query packet
Query packets are used to request more specific information about a particular route. When a router detects a topology change and updates its routing table, it may send Query packets to its neighbors to ask for more details about routes that have become unreachable. This helps in resolving potential routing inconsistencies.
Reply Packets
Reply packets are sent in response to Query packets. When a router receives a Query for specific routing information, it responds with a Reply packet, providing the requested details about the route.
Acknowledgment (ACK) Packets
Acknowledgment packets are used to confirm the receipt of Update, Query, and Reply packets. When a router receives one of these packets from a neighbor, it sends back an ACK to acknowledge receipt. This helps ensure that the packets are delivered successfully.
RTP (Reliable Transport Protocol) Packets
EIGRP uses RTP as its transport protocol to provide reliable and ordered delivery of packets. RTP encapsulates EIGRP Hello, Update, Query, Reply, and ACK packets for transmission between routers. It ensures that packets are delivered without duplication, loss, or out-of-order delivery.
What are EIRGP tables?
EIGRP uses some tables to maintain routing information, find the best path, and recalculate the paths when the primary path goes down for some reason. The tables used by EIGRP are:-
Neighbour Table
The EIGRP Neighbour Table, keeps information on neighbouring routers with which the local router has formed EIGRP neighbour relationships. It contains information about the IP addresses of neighbours, their interface, hold timers and other parameters required for neighborship maintenance.
The command used to see neighbor table: – R#show ip eigrp neighbors
Topology Table
It keeps detailed information about routes learned from EIGRP neighbours. This table contains entries for all known routes, including feasible successors and any potential backup routes. It includes information such as the destination network, metrics, and the state of the route (active, passive, or stuck in active). It basically includes the information of the whole topology configured within the EIGRP Autonomous System (AS).
The command used to see the topology table: – R#show ip eigrp topology
Routing Table
The Routing Table also called the global routing table contains the best routes to reach various network destinations within the EIGRP Autonomous System (AS). This table is derived from the Topology Table and is used for making forwarding decisions. EIGRP selects the routes with the lowest composite metric values to populate the Routing Table.
Basic EIGRP Configuration
Syntax: –
R(config)#router eigrp <Process ID>
R(config-router)#network <Network IP>
R(config-router)#no auto-summary :- Used to disable auto summarization of routes.
Let us look at the below given topology: –
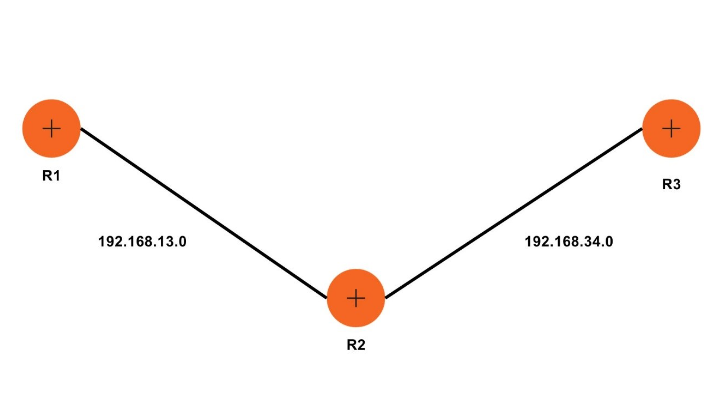
R1(config)#router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)#network 192.168.13.0
R1(config-router)#no auto-summary
R2(config)#router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.13.0
R2(config-router)#network 192.168.34.0
R2(config-router)#no auto-summary
R3(config)#router eigrp 1
R3(config-router)#network 192.168.34.0
R3(config-router)#no auto-summary
Verification: –
R1#show ip eigrp topology
IP-EIGRP Topology Table for AS 1/ID(192.168.13.1)
Codes: P – Passive, A – Active, U – Update, Q – Query, R – Reply,
r – Reply status
P 192.168.13.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2816
via Connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
P 192.168.34.0/24, 1 successors, FD is 2816
via Connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
R2#show ip route
Codes: L – local, C – connected, S – static, R – RIP, M – mobile, B – BGP
D – EIGRP, EX – EIGRP external, O – OSPF, IA – OSPF inter area
N1 – OSPF NSSA external type 1, N2 – OSPF NSSA external type 2
E1 – OSPF external type 1, E2 – OSPF external type 2, E – EGP
i – IS-IS, L1 – IS-IS level-1, L2 – IS-IS level-2, ia – IS-IS inter area
* – candidate default, U – per-user static route, o – ODR
P – periodic downloaded static route
Gateway of last resort is not set
192.168.13.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.13.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
L 192.168.13.2/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/0
192.168.34.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 2 masks
C 192.168.34.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1
L 192.168.34.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0/1