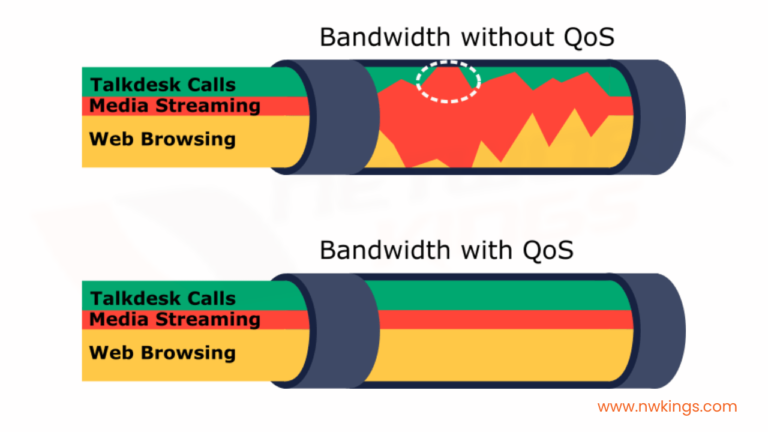
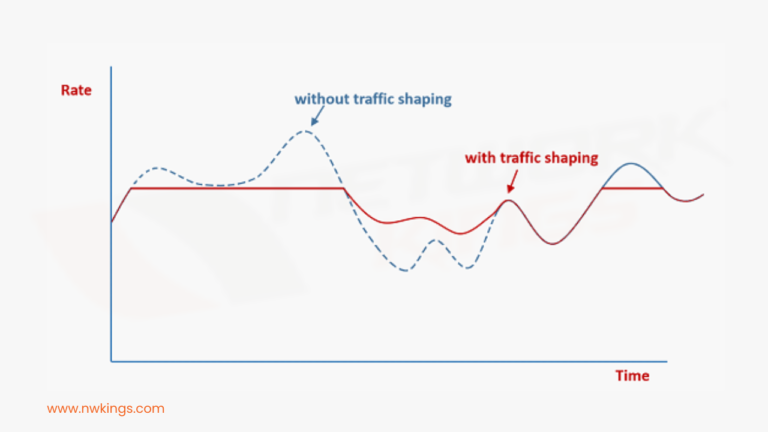
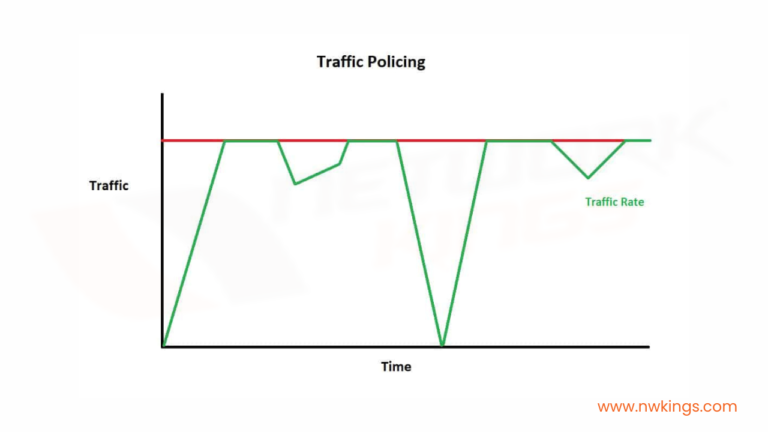
Network security is an important part of any business, organization, or individual’s online safety and protection. Cybercriminals are continuously developing new and advanced methods of attack, making it crucial to stay up-to-date on the different types of attacks in network security.
This comprehensive guide provides a detailed overview of the most common threats and the best practices for protecting your network. From Denial of Service (DoS) attacks to phishing scams, you’ll learn about the different types of attacks, the risks associated with each, and the steps you can take to mitigate them.
Note: If you haven’t read the previous blog of our CCNA 200-301 series, I highly recommend you do so.
Knowing about the different types of network security attacks is very important from CCNA 200-301 exam point of view. In this blog, we will discuss all the attacks that are asked in the CCNA certification exam.
Make sure to understand each one of them. Let’s begin!
What is Network Security?
Network security is the process of protecting your networks from unauthorized access, breaches, or damage. It can also be applied to protecting your systems and data from potential threats on networks such as intranet or extranet connections.
Network security is an important part of data security, but it is only one part. Data security is the practice of protecting valuable information by keeping it secure. It is important to remember that network security is a process, not an end result. It is an ongoing process that requires ongoing vigilance and attention.
Types of Attacks in Network Security
Before we learn about different types of attacks in network security, it’s important to understand the basic components of a network. Networks can be made up of a variety of devices, ranging from computers to routers to network storage devices to printers. The devices on a network are connected together either wirelessly or over a wired connection.
These devices communicate with each other using a variety of protocols and standards, including IPv4, IPv6, and Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol (TCP/IP). IP addresses are the protocols and addresses used to identify and identify devices on a network.
In order to send and receive data, devices on a network must be able to communicate. This communication is typically done through ports, which are used to assign devices a specific amount of bandwidth in order to allow them to send and receive data. Systems on a network may also use services, such as SMTP to send e-mail or HTTP to access a website.
Let us now begin learning about different types of attacks in network security.
1.Denial-of-Service (DoS) attacks:
- DoS attacks threaten the availability of a system, the A of the CIA triad.
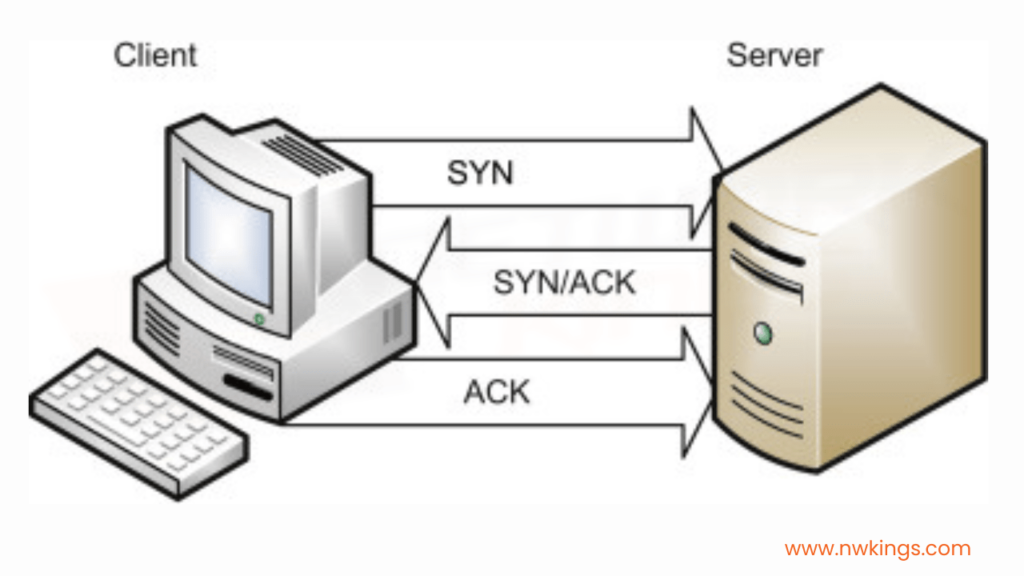
- There are many kinds of DoS attacks and we will discuss a few of them. One of the most common DoS attacks is TCP SYN flood. It exploits the TCP three-way handshake which consists of the SYN, SYN-ACK and ACK.
- In a TCP SYN flood, the attacker sends countless TCP SYN messages to the target.
- The target sends a SYN ACK message in response to each SYN it receives.
- The attacker never replies with the final ACK of the TCP three-way handshake. This final ACK is never sent.
- The target waits for the final ACK of each handshake, and the incomplete connections fill up the target’s TCP connection table.
- The incomplete connections will be timed out and they will be removed from the table after a certain amout of time.
- The attacker continues sending SYN messages to fill up the table.
- In the end, the target is no longer able to make legit TCP connections because it has reached the maximum limit of the number of TCP connections it can maintain.
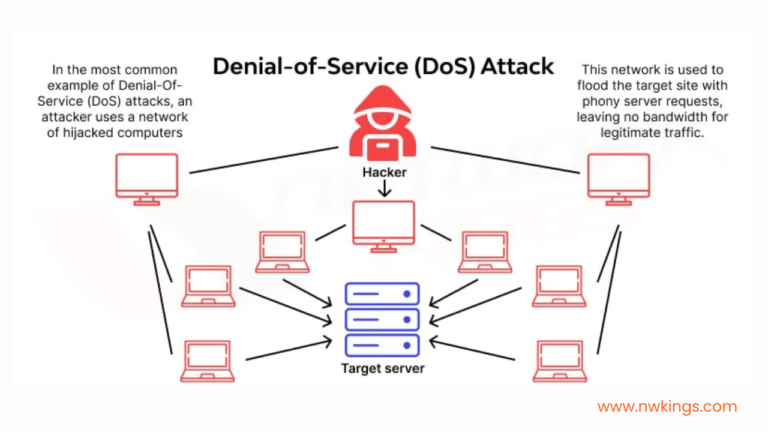
- A hacker can rent a website and then rent a server to launch a flood.
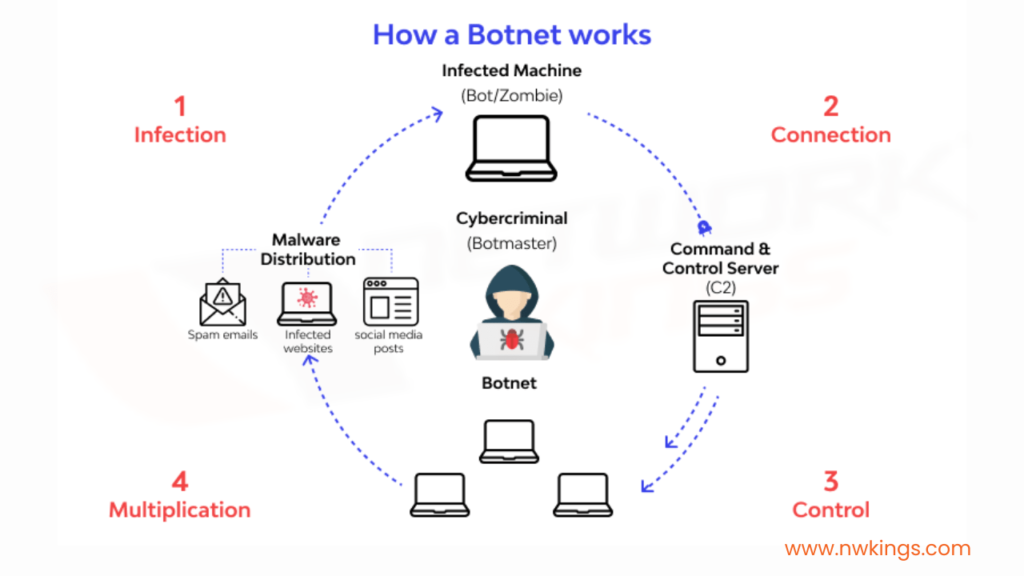
2. Distributed Denial-of-Service (DDoS) attack:
- In distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack, the attacker infects many target users with malware and uses them to begin a Denial-of-Service (DoS) attack, for example, a TCP SYN flood attack.
- The infected computers together are called a botnet.
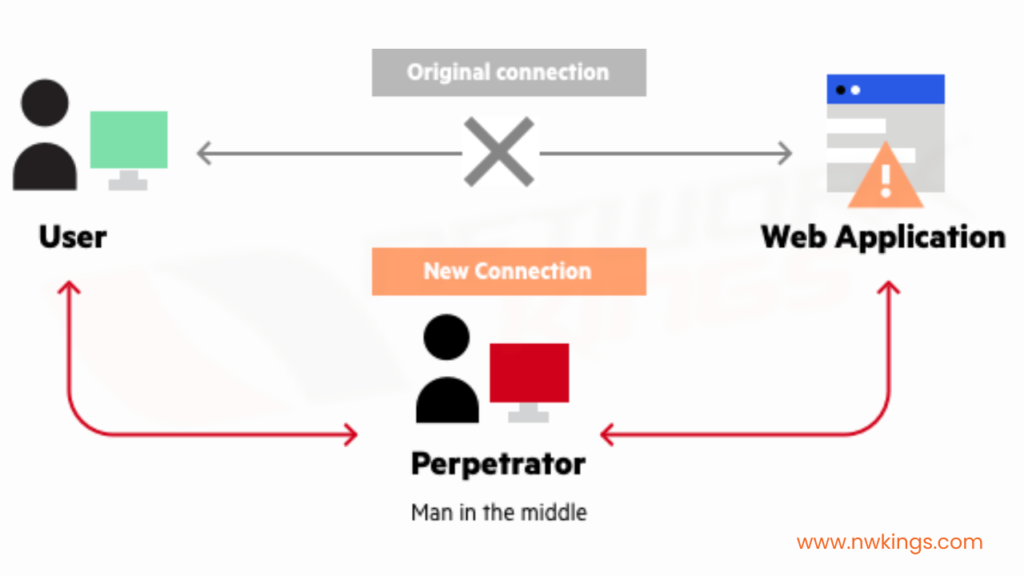
3. Man in the Middle (MITM) attacks
- Man in the Middle attacks (MITM) is some of the most common types of network security attacks.
- If you’ve ever wondered how hackers hijack computers and steal personal information or disrupt businesses, it’s all thanks to man in the middle attacks.
- An example of a man in the middle attack would be if your email exchange is going to a third party, such as Gmail or Microsoft Outlook.
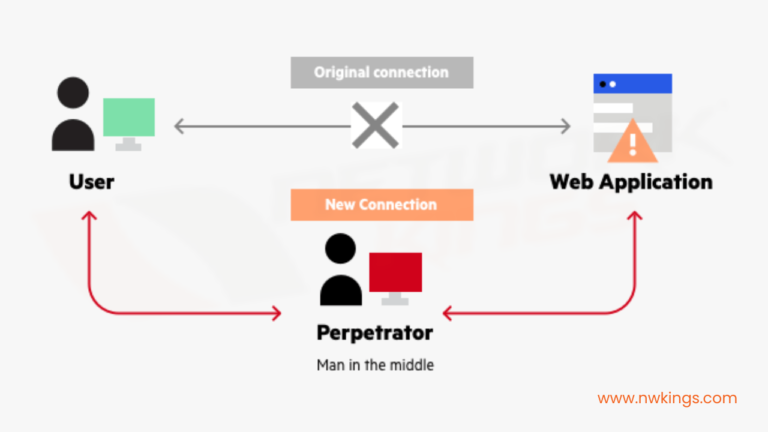
- Another example of a man in the middle attack is when data is being sent over a network, such as when a browser is communicating with a website.
- These attacks occur when an attacker captures traffic between two parties and modifies the traffic so that it looks as if it is coming from the victim and going to the attacker.
- This is done by using eavesdropping and interface manipulation.
- This can cause all kinds of problems, such as sending a hacker’s password or downloading malicious software.
- The attacker can also alter the content of a packet by adding new information to the packet as opposed to modifying the packet.
- If a hacker is in the middle of a conversation, he can alter the conversation to make it look like he’s the one talking to the other person. This is similar to a MITM attack, except the hacker is in the middle and not the victim.
- The attacker can change the information being sent so that it appears as if it is coming from the victim.
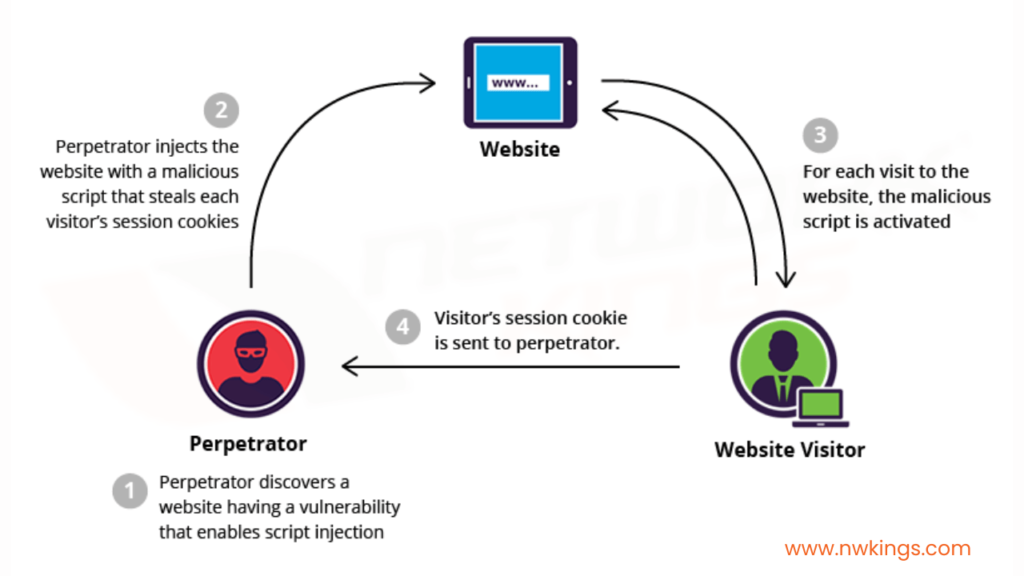
4. SQL injection attacks
- SQL injection attacks are some of the most dangerous types of network security attacks.
- The basic premise of this type of attack is that malformed SQL code is injected into the web application.
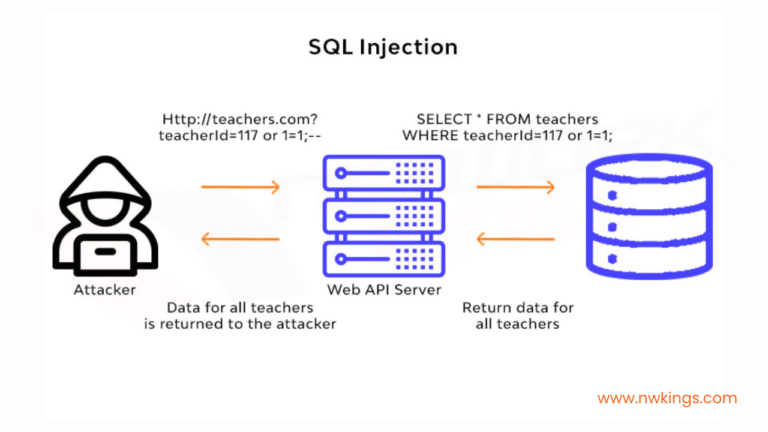
- The code is then executed, and the attacker is able to cause damage to the network, such as stealing data, deleting data, changing data, or even deleting the entire database.
- This type of attack is increasing in prevalence because web applications are getting more and more complex.
- They need to be fast, reliable and secure all at the same time.
- Unfortunately, most applications are not developed with security in mind, making them vulnerable to SQL injection attacks.
- A hacker can easily use a tool, such as SQLMAP, to find and inject malicious SQL code into a website.
- If a hacker is able to inject malicious code and then access a database, he or she can cause all kinds of damage, from deleting data to stealing money.
5. Phishing Attacks
- The term phishing means “fishing” and refers to attempting to fish out a user’s sensitive information such as a password, banking account details, or other confidential data.
- Phishing attacks are often disguised as a trustworthy source, such as a bank website or email.
- Hackers often use malicious links or messages to trap unsuspecting users into providing their login credentials or other sensitive information.
- Phishing attacks are frequently used for financial gain.
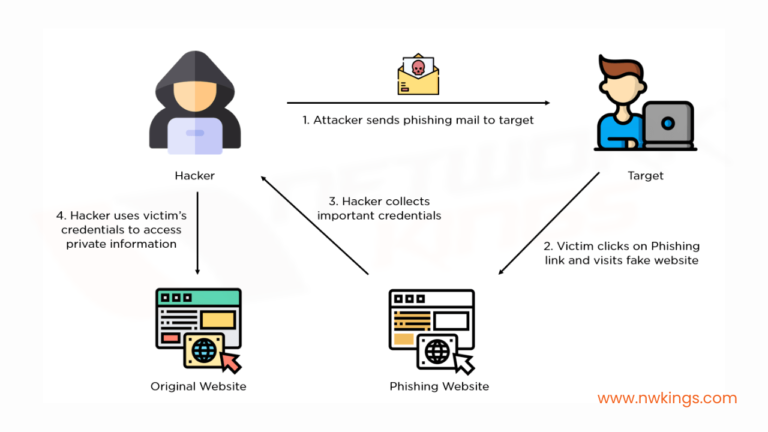
- These attacks often come in the form of an email that appears to come from a legitimate source, such as a bank or credit card company.
- Phishing messages often include links to websites that look like they’re from a legitimate source, such as a brand-new bank website.
- Users are advised to be cautious of any links that are sent to them and to avoid clicking anything they’re not 100% sure is safe.
Best practices for mitigating Network Security threats
Here are some of the best precautions that you can use to reduce your chances of getting exposed to various types of network security attacks:
- Use strong passwords:
Most people reuse simple passwords, make them too short, or choose terrible passwords. Make sure your password meets one of the following criteria:
- Is at least eight characters in length
- Contains numbers, letters, and symbols
- Is different from your email account password
- Is not easily guessable
- Use a password manager
Using a password manager is one of the best ways to make sure your passwords are safe. It will save you time, keep you organized, and help prevent you from making any mistakes that could lead to your information being stolen.
- Install antivirus software:
There are many free antivirus programs available. As an added bonus, many programs block links, offer cloud protection, and provide real-time updates. –
- Use 2-factor authentication:
Many websites now require two-factor authentication to prevent hackers from stealing your information. This is often accomplished through an app or text that is sent to your phone to verify your identity.
Two-factor authentication will help protect against man-in-middle attacks and phishing attacks.
- Keep your software updated:
Keep your devices such as computer, PCs, laptops, etc. updated. Double check that there are no vulnerabilities in your device thay cam be hacked. Update your software and devices as soon as possible.
- Lock your device and/or turn off remote/web access:
Many hackers use remote access tools (RATs) to gain access to a target’s device. A common way to do this is through remote access utility (RAU).
Conclusion
In this blog we have covered what is network security and how it gets suffered because of the most prevailing attacks. We learned how they attacks occur and we understood the approach of these attacks.
Additionally, we also learned how to mitigate these attacks and the important measures that you can take to reduce these attacks.
This was all about the various types of attacks in network security.
Stay tuned for more such free content for our CCNA series!