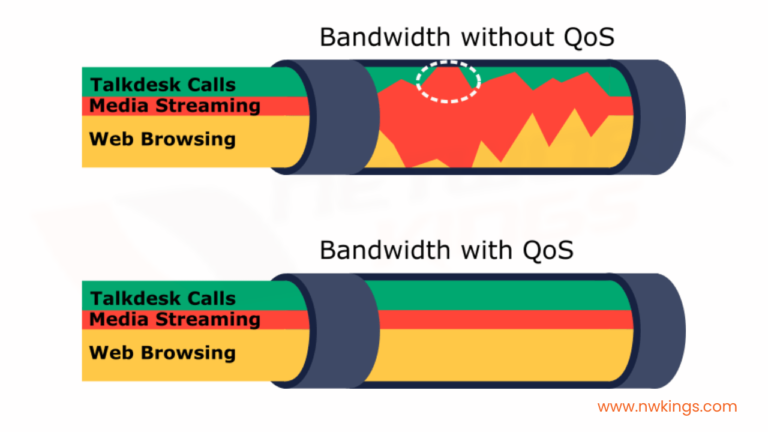
Quality of service refers to a set of techniques and mechanisms used to manage and prioritize network traffic to ensure the performance, reliability, and availability of the packets in the network. QOS helps to set priority for the type of data packets. Key aspects of QoS include traffic prioritization, bandwidth management, latency control, packet loss mitigation, traffic shaping, and congestion management. QOS mechanism enables allocating resources such as bandwidth to critical applications or services ensuring they receive adequate network resources for optimal performance.
By implementing QoS, network administrators can ensure that essential applications (e.g. voice and video communication) receive higher priority and better treatment, with less sensitive traffic operating efficiently without causing congestion or impacting critical services. QoS helps achieve better network efficiency, reliability, and user satisfaction by providing a consistent and optimized user experience across the network.
Below are the parameters that can be controlled and managed by QoS-
- Packet loss: – Packet loss refers to the failure of data packets to reach their destination in a network. It occurs when packets are dropped or discarded during transmission often due to network congestion, hardware issues, or errors. Excessive packet loss can degrade network performance and affect the quality of real-time applications like VoIP or video streaming.
- Jitter: – Jitter is the variation in the delay of received packets in a network, It represents the deviation in packet arrival times caused by network congestion, varying routes, or different queuing delays. In real-time communication applications, high jitter can cause disruptions delays, or inconsistent quality in audio or video streams.
- Latency: – Latency refers to the time it takes for data packets to travel from a source to a destination across a network. It includes various components such as transmission, delay propagation delay, queuing delay, and processing delay. High latency can result in delays and sluggishness in network communications and can impact the responsiveness of the application.
- Bandwidth: – Bandwidth refers to the maximum data transfer rate of a network connection or channel. It measures the capacity of the network to transmit data over a specified period, typically expressed in bits per second. Higher bandwidth allows more data to be transferred within a given time frame, facilitating faster communication and higher throughput.
- Mean Opinion Score (MOS): – MOS is a measure used to assess the perceived quality of audio or video in communication systems. It represents the average opinions of multiple listeners or viewers regarding the quality of media content. MOS values range from 1 to 5 with higher scores indicating better quality. MOS is commonly used in evaluating the quality of voice calls, video calls, video conferences, and multimedia streaming.
How does QOS work?
QoS works by implementing various techniques within a network to manage and prioritize different types of traffic. Below are some the points explaining how Quality of service works: –
- Traffic Classification: – QoS starts by identifying and classifying different types of network traffic based on their characteristics such as source/destination addresses, port numbers, protocols, or specific application requirements. This classification helps in distinguishing between various types of traffic.
- Traffic prioritization: – Once traffic is classified, QoS assigns priorities or levels of importance to different classes of traffic, Critical applications like voice or video conferencing might be assigned a higher priority than less time-sensitive traffic like file downloads.
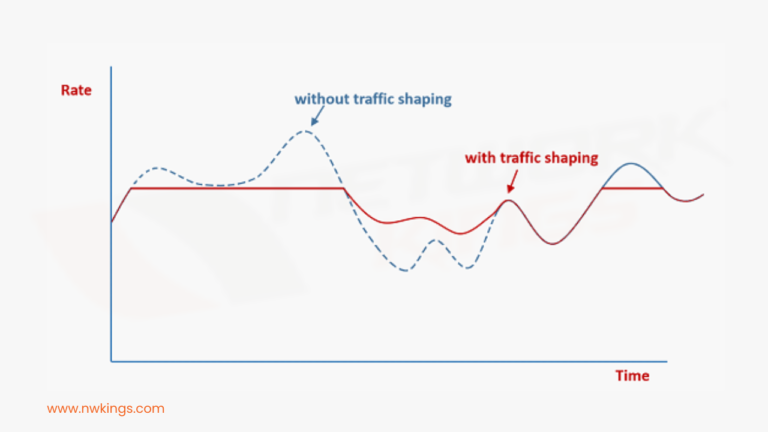
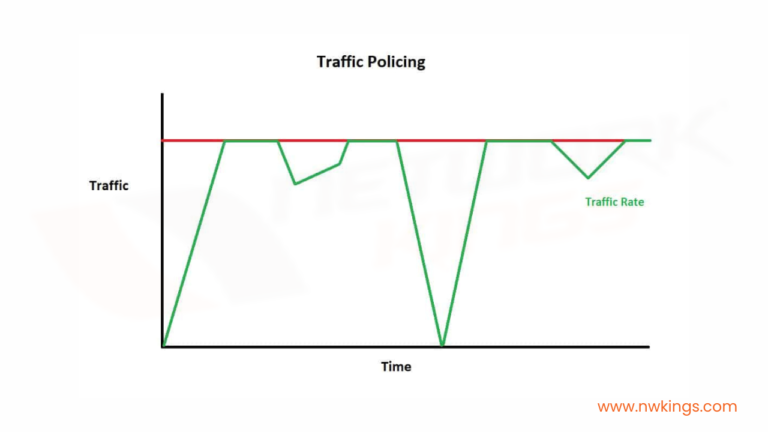
- Traffic shaping and policing: – The QoS mechanism includes traffic shaping and policing to control the flow of data and manage bandwidth utilization. Traffic shaping smooths out a burst of traffic to prevent congestion while traffic policing enforces traffic limits based on predefined rules.
- Queuing and Scheduling: – QoS employs queuing and scheduling algorithms to manage the order in which packets are transmitted when network congestion occurs. These algorithms prioritize and schedule packets according to their assigned priorities or classes.
- Bandwidth Allocation and Reservation: – The Quality-of-service mechanism allocates and reserves specific amounts of bandwidth for high-priority traffic ensuring that critical applications receive the necessary resources for optimal performance. Bandwidth allocation can be dynamic or static depending on the requirements.
- Congestion Management: – QoS helps in managing and mitigating network congestion by using techniques like traffic prioritization, congestion avoidance mechanisms, and buggering to prevent or minimize congestion-related issues.
- Quality parameters:- QoS typically involves defining and monitoring quality parameters such as latency, jitter, and packet loss, These parameters are continuously monitored and QOS mechanisms work to ensure that they stay within acceptable limits for different types of traffic.
- Enforcement and control:- QoS policies are enforced across network devices such as routers switches and firewalls using configuration settings, Network administrators configure QoS policies based on the specific requirements of the network and the applications running on it.
Why Quality of service is important?
QOS is important and is widely used for the following reasons-
- Prioritization: – QoS helps in prioritization of important services and applications over less sensitive traffic. It ensures that essential services like VoIP, video conferencing, and other sensitive traffic receive the necessary network resources minimizing delays and ensuring reliable performance.
- Improved user experience: – By prioritizing and managing network traffic, QoS helps maintain a consistent and optimized user experience. It reduces latency and packet loss ensuring smoother and more reliable communication for real-time applications
- Bandwidth Management: – QoS enables efficient allocation and management of available network bandwidth. It ensures that network resources are used effectively preventing network congestion and optimizing data transfer for different types of traffic.
- Optimized Network Performance: – Implementing a QoS mechanism helps in optimizing overall network performance by preventing bottlenecks reducing latency and ensuring that critical services have the necessary resources to function smoothly.
- Maintaining Service level agreements (SLAs): – In an enterprise or service provider environment QoS is essential for meeting SLAs. It allows organizations to guarantee specific levels of performance and reliability for their services meeting the expectations of the customers.
- Supporting Diverse applications: – Today’s network handles diverse types of traffic including voice, video, data, and IoT applications. QoS ensures that these various applications coexist simultaneously by providing each with the required performance parameters.
What are the types of delays?
- Propagation delay: – The time taken for a signal or data packet to travel from the sender to the receiver. It’s primarily determined by the distance between the two points and the speed of propagation into the transmission medium (fiber optic cable, copper wire, etc).
- Serialization delay: – Serialization delay refers to the time it takes to transmit an entire packet’s bits onto the network medium or link. It is determined by the size of the packet and the transmission rate (bandwidth) of the link. Larger packets take longer to transmit than smaller ones and higher transmission rates reduce serialization delay. The following equation is used to calculate serialization delay
Serialization delay (in seconds) = Packet size (in bits)/ transmission rate (in bits per second)
- Shaping delay: – Shaping delay is a delay introduced deliberately by the traffic shaping mechanisms in network devices such as routers and switches. Traffic shaping is used to control the rates of data transmission, smoothing outbursts of traffic to prevent congestion and ensure that network traffic conforms to predefined traffic profiles or limits. Shaping delay is introduced to regulate and shape the flow of traffic, often by buffering packets temporarily before transmitting them. By controlling the rate of transmission, it ensures that network traffic remains within specified bandwidth limits, preventing congestion and optimizing network performance.
- Processing delay: – The time taken by routers, switches, or other network devices to process and examine the packet headers make forwarding decisions, and perform necessary operations like error checking routing lookups, or security checks.
- Queuing Delay: – The time a packet spends waiting in a queue at a network device, router, or switch before it can be transmitted. This delay occurs when there’s congestion or high traffic and packets have to wait for their turn to be forwarded.