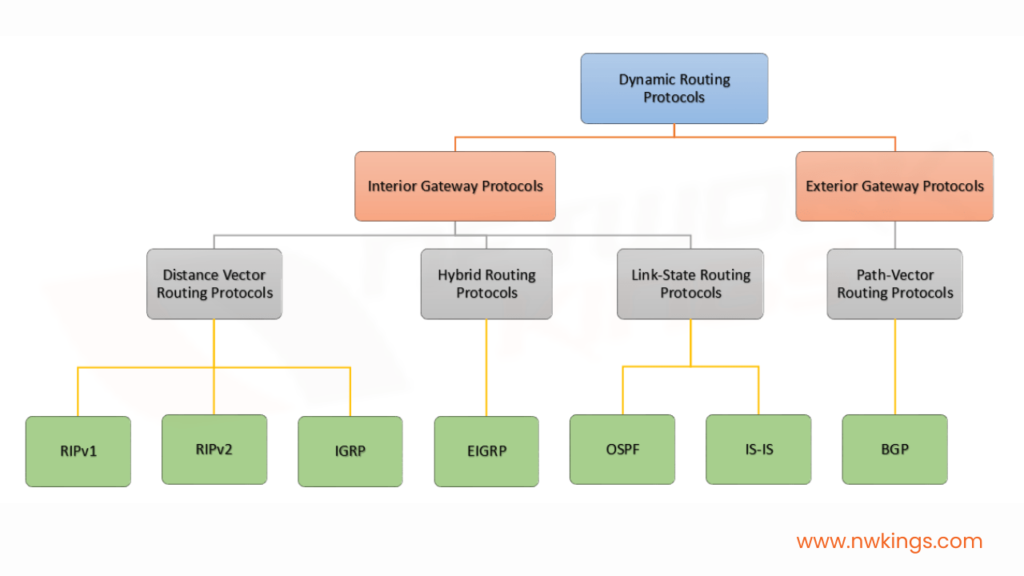
OSPF, as we already know, is a Link- State routing protocol, and being a Link state routing protocol, each router in a network exchange information about the state of their directly connected links with all the routers in a network.
It looks fine when we talk about a limited or small number of routers in a network but what happens when we have a significant number of routers?
A lot of information will be flooded within a network leading to unnecessary network congestion, poor performance, and wastage of bandwidth. For that purpose, we use the OSPF area concept.
But, by dividing a network into areas we are restricting router information flooding, and hence network would not have access to the necessary information required to find the best path.
For that purpose, OSPF has a “Brahmastra “which is known as Link State Advertisements.
In this article, we will discuss Link State Advertisements and various OSPF LSA types.
ALSO READ: OSPF Interview Questions if you’re preparing to crack a Network Engineer job position.
What is OSPF LSA?
In the Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) routing protocol, LSA also known as Link-State Advertisements helps to spread the routing information within an OSPF network. Routers configured with OSPF exchange LSAs to build a map of the network topology and find the best path possible to reach from one network prefix to another. All the information collected using LSA is stored in a database known as Link-State Database (LSDB) which is used to calculate the shortest path to different destinations.
Understanding OSPF LSA Types: A Comprehensive Overview
Link State Advertisements are of different types with different functionality which are listed below:-
Router LSA | LSA Type 1 |
Network LSA | LSA Type 2 |
Summary LSA | LSA Type 3 |
Summary ASBR LSA | LSA Type 4 |
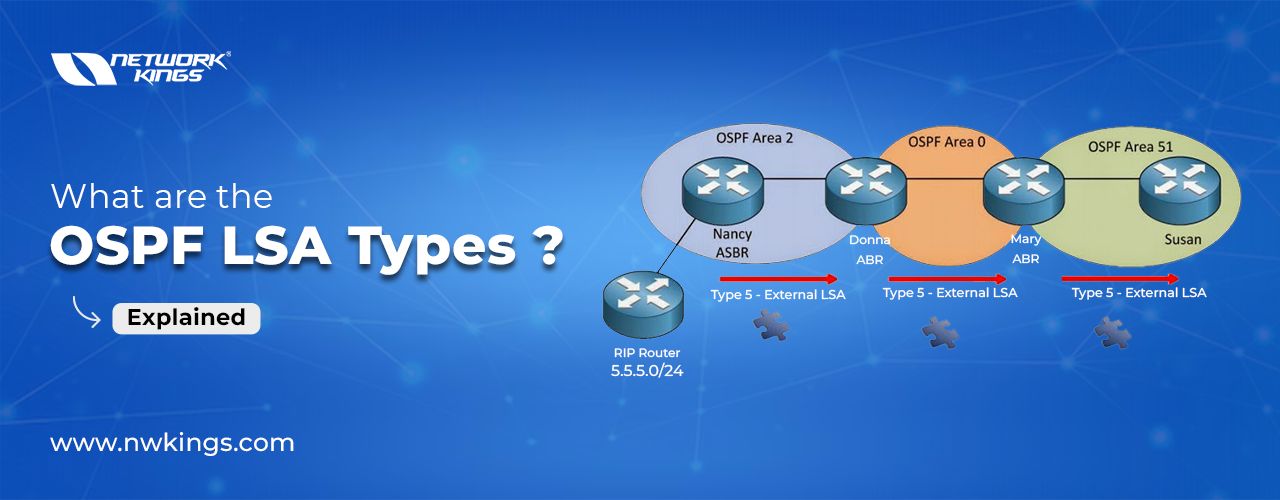
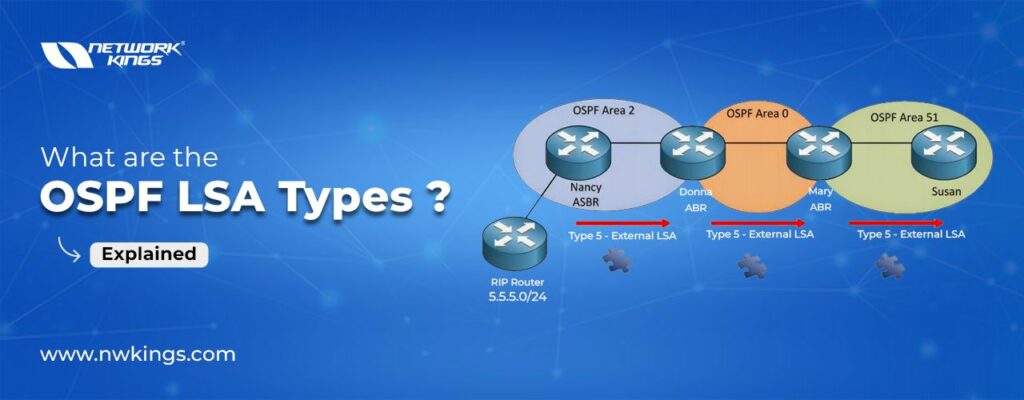
Autonomous System external LSA | LSA Type 5 |
Multicast OSPF LSA | LSA Type 6 |
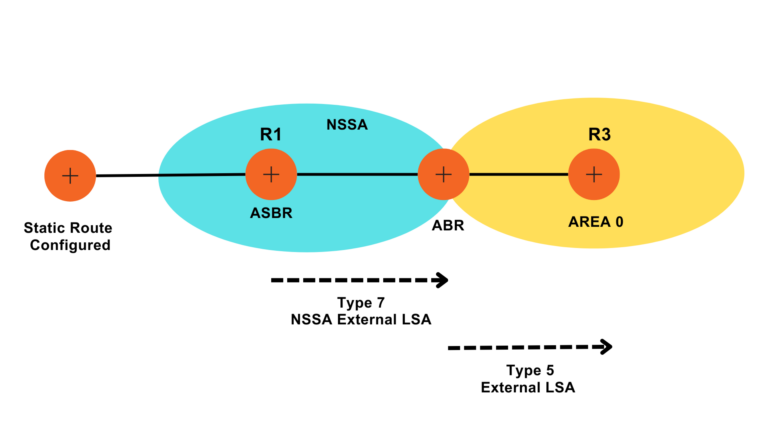
NSSA External LSA | LSA Type 7 |
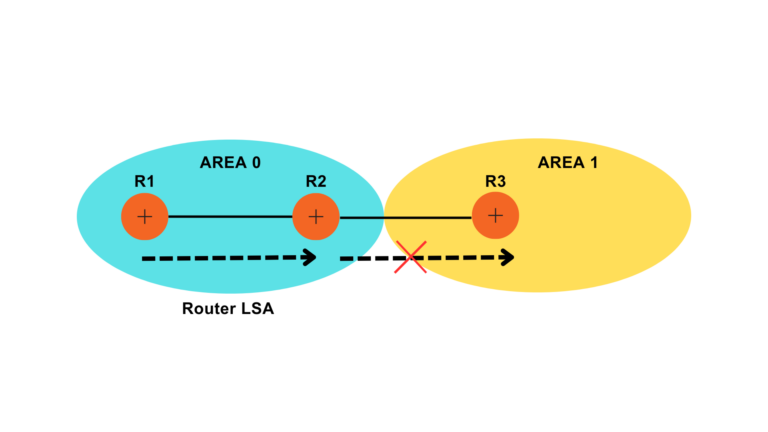
What is LSA Type 1?
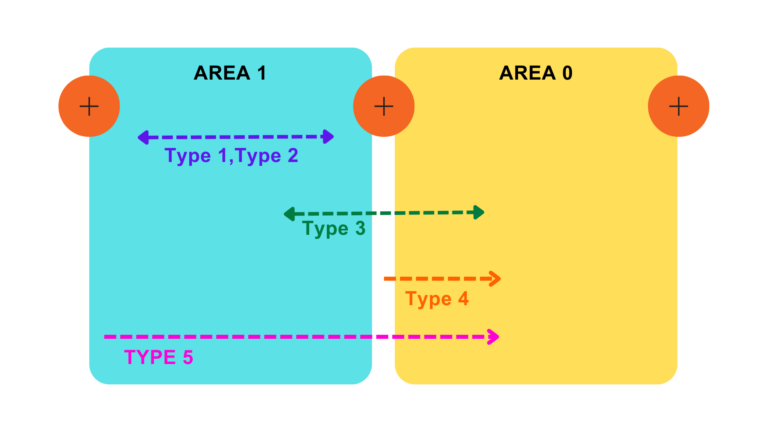
All routers generate their own Router LSA. It describes the state of its own links/interface. Type 1 LSA is flooded within an area and does not cross it. Router LSA includes information like Router ID, the status of links, and interface IP details.
What is LSA Type 2?
It represents the multi-access network segment. Network LSA is flooded by Designated routers only. It contains information about all the routers that are directly connected to multi-access network segments, information about DR and BDR routers, and subnet information. Similar to Router LSA, Network LSA is flooded within the same OSPF area and ensures that all the routers within an area have an accurate understanding of the network topology.
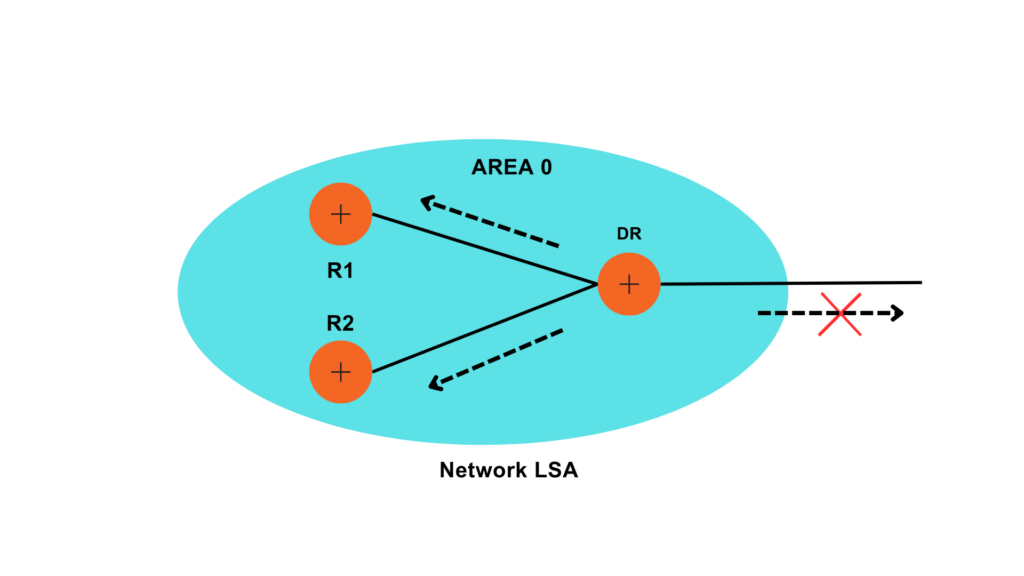
What is LSA Type 3?
Since Router LSA and Network LSA remain within the area, we need something to share information about a particular area with another area. For that purpose, Summary LSA or Inter-Area LSA is used. Type 3 LSA advertises routes between OSPF areas. These LSAs are generated by Area Border Router i.e. ABR. In the OSPF routing table, they are denoted as O IA.
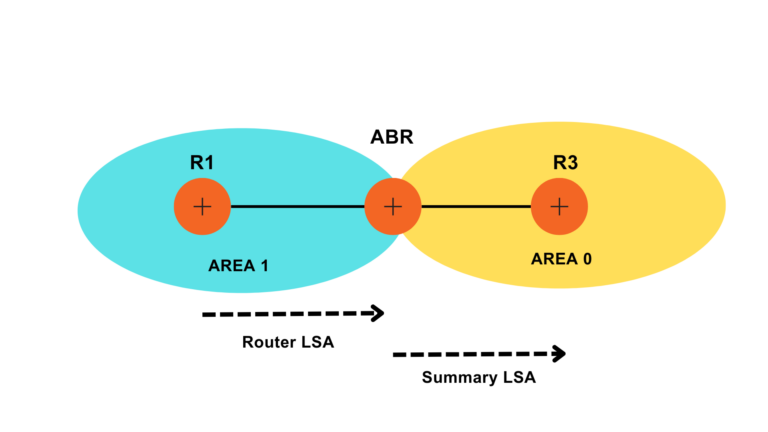
What is LSA Type 4?
These LSAs are generated by ABR to inform routers in an area about the existence of an Autonomous System Boundary Router (ASBR) in another area. This LSA informs about the path to reach external routes.
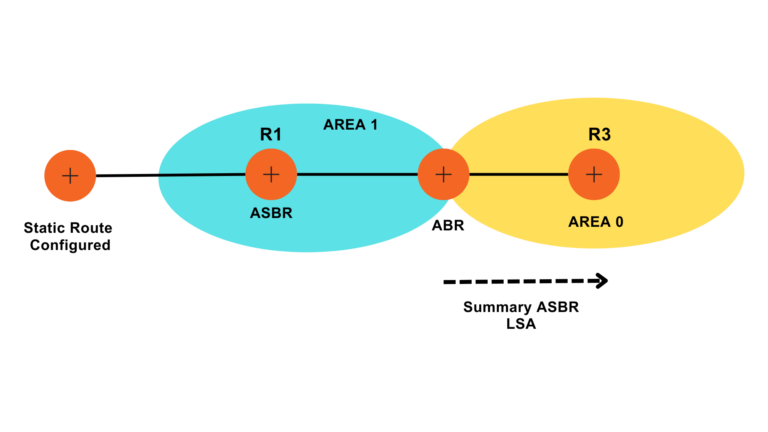
What is LSA Type 5?
These LSAs are generated by an ASBR to advertise external routes into OSPF. They are flooded throughout the OSPF domain.
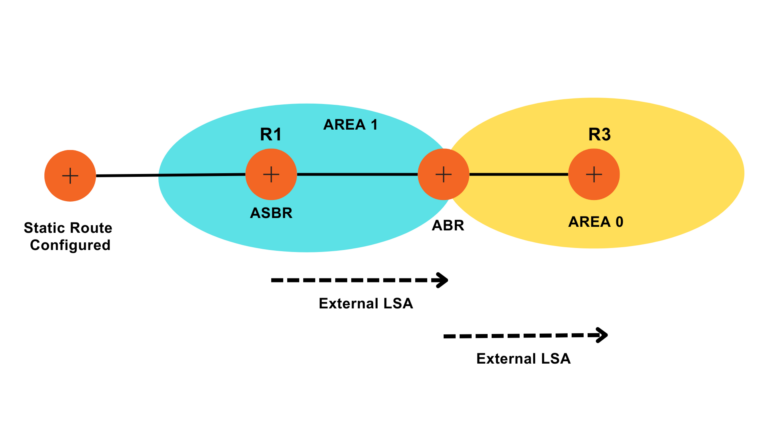
What is LSA Type 6?
Group Membership LSA or Type 6 LSAs are used in OSPFv3 for multicast group memberships within the link.
What is LSA Type 7?
It is also called NSSA External LSA. In Not-So-Stubby-Area (NSSA) configurations, these LSAs are used to carry external route information. Since in Stub areas, LSA 5 is not allowed hence we use LSA 7 in this case. ABR routers convert LSA 7 into LSA 5 when it is flooded outside the stub area and convert LSA 5 to LSA 7 when LSA 5 enters the stub area.
We can see that LSA is the backbone of OSPF. It helps to understand network topology within OSPF routers. It also helps to calculate the shortest path to reach the destination. Not only it helps to find the shortest path but also finds the redundant path quickly whenever the primary path goes down for any reason. Hence it ensures fast route convergence which helps the network to quickly adapt to changes.
To make sure that you thoroughly understand OSPF, do watch out this video by Atul sir wherein he dives deep into the topic with simple explanations for a better understanding of the topic.
Let us quickly see the difference between each LSA.
LSA TYPE | Description | Originator | Flooded To | Purpose |
Type 1 | Router LSA | Router | Same Area | Describes router’s Link |
Type 2 | Network LSA | DR | Same Network | Describes routers on a network segment |
Type 3 | Summary LSA | ABR | Other Area | Advertise routes between areas |
Type 4 | Summary ASBR LSA | ABR |
| Informs about an ASBR |
Type 5 | Autonomous System external LSA | ASBR | OSPF Domain | Advertises external routes |
Type 6 | Multicast OSPF LSA | OSPFv3 router | Same Area | Used for multicast group memberships |
Type 7 | NSSA External LSA | ASBR in NSSA | NSSA | Carries external routes in NSSA configuration |