In the previous blog, I introduced you to the concept of network automation. It is a very important topic when it comes to preparing to take the Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA 200-301) exam.
Now, it is time to dive deeper into the concept of network automation. Therefore, I will introduce you to the more foundational concepts in network automation to help you understand the whole technology in a better way.
Therefore, in this blog, we will cover why we choose network automation, and the various logical ‘planes’ of network automation, such as the data plane, control plane, and management plane. I will explain what they are, as they are essential to understand the next topic, Software-Defined Networking (SDN).
We will also learn about APIs and data serialization. This guide is an introduction to these topics. These will be discussed further in detail in the upcoming blogs.
Without any further ado, let us begin learning, techies!
Why Network Automation?
The previous versions of CCNA focused on a traditional model of managing/controlling networks. The current version focuses on the traditional model as well, but the candidates are expected to have a good understanding of various topics such as network automation.
In the traditional model, engineers manage devices one at a time by connecting their CLI with the help of SSH. Telnet connections as well as connections to the console port are possible too. Some devices even support GUI. The important point here to note is that the devices are managed and configured one by one.
Some of the drawbacks of managing networks one-by-one are:
- It is common to make some typos and other small mistakes while running configurations in networking devices such as routers.
- It is time-consuming and very inefficient, especially in large-scale networks. Repetitive tasks can be automated and performed in a few seconds.
- It is difficult to ensure that all devices follow the company’s standard configurations.
Therefore, it is very important to learn how to automate networks.
Various Logical ‘Planes’
In order to under SDN, it is very important to learn about the Logical planes of network functions first. To understand the logical planes, let us first answer a simple question.
What do a router and switch do?
Most of you will answer that both of them forward messages at Layer 2 and Layer 3.
But what about the other functions that these network devices perform?
A router also uses a routing protocol such as OSPF to share routing information with other routers and build a routing table. A switch uses STP to ensure that there is no Layer 2 loops. These are just a few of the important functions that these networking devices perform.
These various functions of network devices can be logically classified into planes:
- Data plane
- Control plane
- Management plane
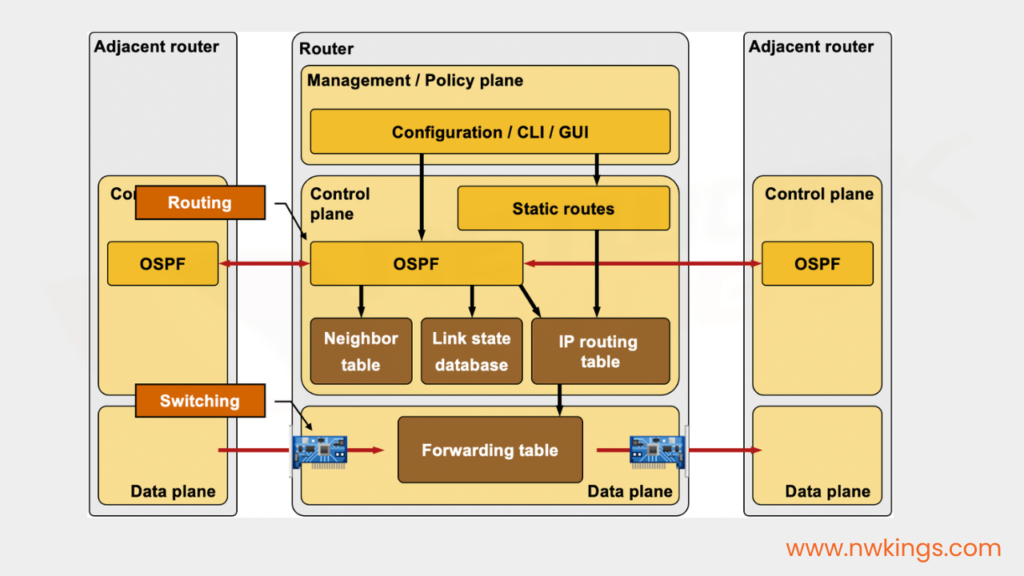
1. Data Plane
- The data plane is also called the ‘forwarding plane’.
- All the tasks that are involved in forwarding user data or traffic from one interface to another are part of the data plane.
- A router receives a message. Looks for the most specific matching route in its routing table and forwards it out of the appropriate interface to the next hop or to the destination in case it is directly connected.
- It also de-encapsulates the original Layer 2 header and re-encapsulates with a new header for the next hop’s MAC address.
- Likewise, a switch receives a message, looks at the destination MAC address, and forwards it out of the appropriate interface.
- This also includes functions like adding or removing 802.1q VLAN tags.
- NAT is also a part of the data plane.
- The decision to forward or delete the message due to ACLs, port security, etc. is also a function of the data plane.
2. Control Plane
- Networking devices such as routers use routing tables, MAC address tables, ARP tables, STP, etc. to make forwarding decisions.
- The functions that build these tables and other functions that affect the data plane are part of the control plane.
- So, the control plane controls what the data plane does. For example, by creating the router’s routing table.
- The control plane manages and monitors network resources like bandwidth, CPU, and memory usage, ensuring they’re used efficiently and effectively.
- Network protocols such as OSPF and BGP are part of the control plane and help build routing tables.
- The control plane can be centralized or distributed, with a single controller or multiple devices sharing control functions.
- Software-defined networking (SDN) technologies can implement the control plane (explained later in the blog).
- Security is critical for the control plane, with mechanisms like access control lists (ACLs) and firewalls protecting it from unauthorized access and attacks.
3. Management Plane
- The management plane manages and configures networking devices, letting administrators control devices, monitor their performance, and troubleshoot issues.
- Network management protocols like SNMP are part of the management plane, allowing remote management and monitoring of devices.
- The management plane is separate from the data and control planes and configures but does not directly affect network traffic.
- The management plane uses various tools like CLIs, GUIs, and APIs to manage devices.
- Network management platforms like Cisco Prime, SolarWinds, and HP IMC centralize network device management and monitoring.
- The management plane is critical for maintaining network security, with administrators able to configure security policies, and access controls, and monitor activity.
- Automation and orchestration technologies are increasingly used in the management plane to automate management tasks and improve network efficiency.
- Network virtualization technologies like SDN and NFV are changing the management plane, enabling software-based provisioning and management of network functions for greater flexibility and scalability.
Software-Defined Networking
SDN stands for Software-Defined Networking, which is an approach to networking that separates the control plane and data plane functions of traditional networking devices. In traditional networks, switches and routers perform both control and data forwarding functions, making it challenging to manage and scale the network.
In SDN, the control plane is separated from the data plane and is centralized, which enables administrators to programmatically control network behavior using the software.
The controller makes forwarding decisions based on pre-defined policies, which are programmed into the controller using the software. By separating the control plane from the data plane, SDN enables network administrators to manage and optimize network traffic flows more easily, improve network security, and reduce costs.
Benefits of SDN
- SDN is highly programmable:
The ability to program network behavior in SDN makes it highly flexible and adaptable to changing network conditions. Network administrators can use programming languages such as Python to create and customize network applications.
- SDN is NOT vendor-specific:
Since SDN separates the control and forwarding planes, it can be used with different vendors’ networking hardware and software. This makes it easier for organizations to use equipment from multiple vendors in their networks.
- SDN can automate network management:
With SDN, network administrators can automate many tasks, such as configuring network policies, traffic flows, and security settings. This automation can significantly reduce the time and effort required to manage and maintain networks.
- SDN improves network visibility:
By separating the control and forwarding planes, SDN enables administrators to have greater visibility into network traffic and performance. They can use this information to troubleshoot network issues more quickly and effectively.
- SDN increases network security:
The centralized control in SDN enables administrators to implement security policies and rules more easily, improving overall network security. It also allows for easier integration with other security technologies, such as firewalls.
- SDN can enable new use cases:
SDN’s flexibility and programmability can enable new use cases, such as network slicing in 5G networks, virtualized network functions (VNFs), and cloud-based networking.
- SDN can improve network performance:
By dynamically managing traffic flows and resources, SDN can improve network performance and reduce latency. This can be particularly beneficial for applications that require high network performance, such as real-time video and gaming.
Conclusion
Network automation is essential for modern network management, allowing organizations to automate routine tasks, reduce costs, and improve network reliability. Understanding the different network planes – management, control, and data is important for designing efficient and scalable networks.
Software-Defined Networking (SDN) uses automation and separation of control and data planes for flexible, centralized network management. As networks become increasingly critical to business operations, network automation, and SDN will continue to be of high importance.
Stay tuned for more blogs for the CCNA 200-301 series!