How to get CCNA certification is what we will discuss in this article. In today’s interconnected world, where digital highways weave together businesses, individuals, and communities, the art of networking stands as a crucial pillar supporting our modern infrastructure. As organizations rely on seamless data transfer, communication, and information exchange, the demand for skilled networking professionals has reached an all-time high.
Imagine a world where communication ceases, data remains stagnant, and connectivity grinds to a halt. In today’s fast-paced reality, such a scenario is not just inconvenient; it’s almost inconceivable. The heartbeat of our digital age relies on the intricate web of networks that allow information to flow seamlessly, enabling businesses, individuals, and entire industries to thrive.
Thus, let’s discuss the CCNA certification in detail.
NOTE: Know if you can become a Network Engineer without CCNA Here!
What is CCNA?
The CCNA (Cisco Certified Network Associate) is a beginner-level certification in networking that Cisco offers. It confirms your core abilities in setting up, running, and resolving issues within smaller to mid-sized networks. It encompasses network fundamentals, routing, switching technologies, network security, and basic wireless principles.
CCNA is a well-respected qualification for those entering IT, networking, and telecom careers. This certification forms a solid base for pursuing more advanced Cisco certifications. By obtaining a CCNA certification, you prove your skill in essential networking tasks, paving the way for success in roles related to network administration and beyond.
Why choose the CCNA training?
Opting for CCNA training is an entry point to networking, furnishing you with crucial proficiencies in configuring networks, overseeing their management, and honing troubleshooting skills. CCNA endows you with expertise spanning routing, switching, security, and wireless technologies. This training acts as a catalyst for prosperous pathways in IT, telecommunications, and beyond.
The globally esteemed CCNA certification enhances your standing, unveiling avenues for advanced Cisco certifications and career advancement. In essence, CCNA training furnishes you with a robust groundwork to stand out in the dynamic domain of network administration, positioning you for triumph in the ever-progressing technology landscape.
What is the scope of CCNA certification?
The CCNA certification expands career possibilities by confirming crucial networking skills. It opens doors to high-earning positions such as network administrator, technician, or support engineer. Those with CCNA expertise can thrive in tasks like setting up, overseeing, and resolving network issues, gaining acknowledgement in IT, telecommunications, and beyond.
This certification is a foundation for advancing to higher-level Cisco certifications, allowing focused learning in fields like security, wireless technology, or data centers. CCNA-equipped professionals are well-prepared for diverse opportunities in our tech-focused society, where their skills are in demand for designing, executing, and sustaining vital network systems across various sectors.
NOTE: Learn the scope of CCNA in detail Here!
What is the importance of CCNA certification?
The CCNA certification is crucial in IT as it validates essential networking skills. It solidifies your credibility in configuring, running, and upholding networks in IT and telecommunications careers. CCNA demonstrates expertise in areas like routing, switching, and network security. This certification acts as a launchpad for career advancement, opening doors to roles like network administrators or support specialists.
It is an internationally recognized benchmark, showing employers your proficiency and creating a path to more advanced certifications. In our rapidly evolving tech world, CCNA provides a strong base, ensuring professionals are well-prepared to make meaningful contributions to network design, implementation, and solving challenges.
What are the benefits of pursuing CCNA training in IT?
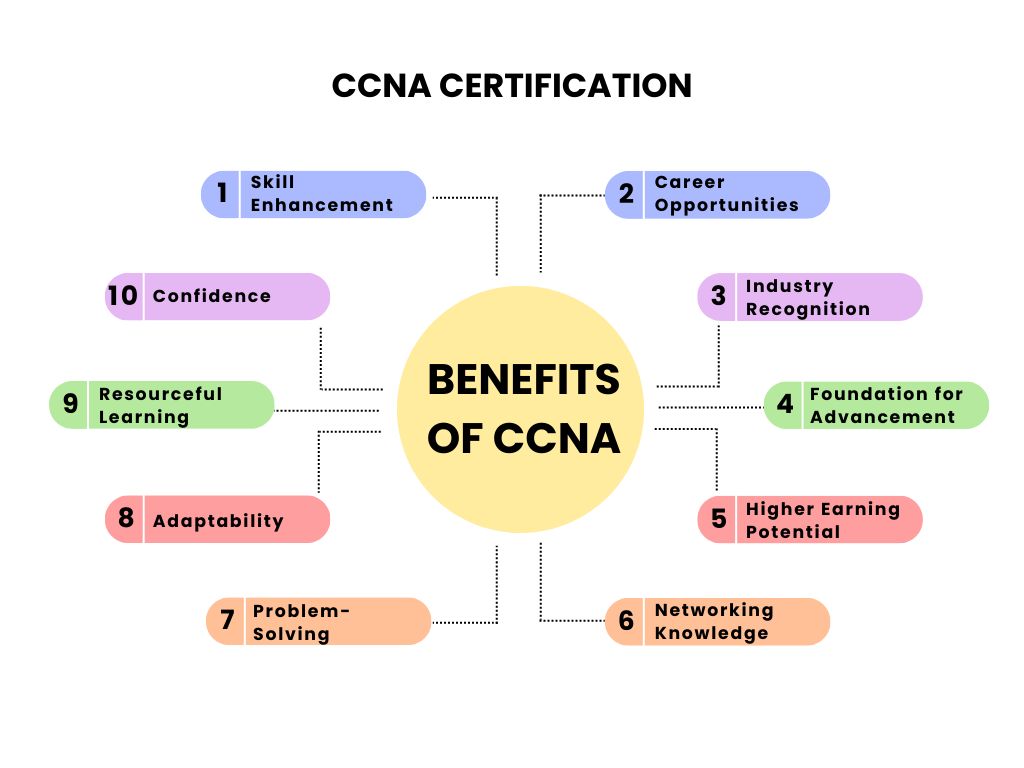
The benefits of pursuing the CCNA training in IT are as follows-
Skill Enhancement
CCNA training equips you with practical skills in networking, including configuration, troubleshooting, and management.
Career Opportunities
CCNA certification opens doors to IT roles like network administrator, support engineer, or technician.
Industry Recognition
The CCNA credential is recognized globally as a mark of your networking proficiency.
Foundation for Advancement
CCNA is a foundation for pursuing advanced Cisco certifications in specialized areas like security or wireless.
Higher Earning Potential
CCNA-certified professionals often command higher salaries due to their specialized expertise.
Networking Knowledge
CCNA training imparts in-depth knowledge about routing, switching, protocols, and network security.
Problem-Solving
You learn effective troubleshooting techniques essential for maintaining network reliability.
Adaptability
CCNA training helps you adapt to evolving technologies and stay relevant in the ever-changing IT landscape.
Resourceful Learning
You gain access to Cisco’s educational resources, tools, and community, fostering continuous learning.
Confidence
CCNA certification boosts your confidence in tackling real-world networking challenges and contributes to professional growth.
Is the CCNA certification worth it?
The CCNA certification holds significant value for those venturing into networking and IT fields. It confirms crucial proficiencies in configuring networks, resolving issues, and overseeing their management qualities sought after for positions like network administrator or support specialist.
This certification carries worldwide acknowledgement and serves as a pathway to more advanced Cisco qualifications. The insights gained from CCNA training prove invaluable in tackling practical networking hurdles and fostering your career progression and accomplishments within IT.
What are the prerequisites for the CCNA course?
The prerequisites for the CCNA course are as follows-
- Graduation
- Basic understanding of the IT industry
Guide on How to get CCNA certification in IT
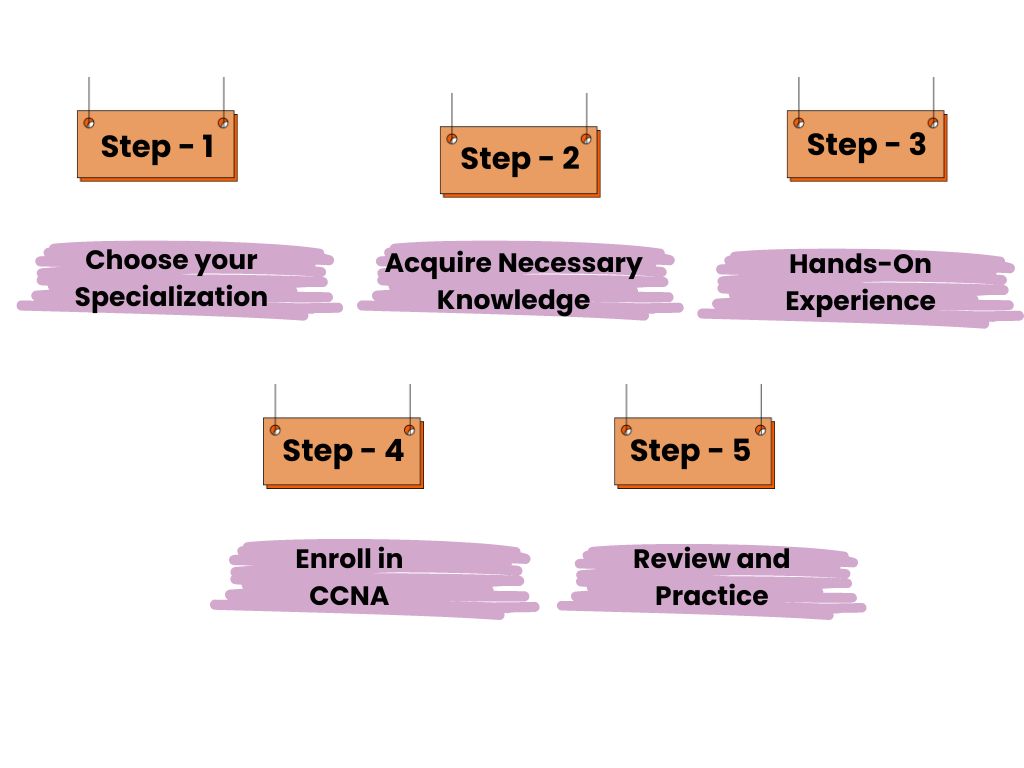
Step 1: Choose Your Specialization
Before diving into IT training, one must decide on a specialization that aligns with your career goals. For stepping into IT networking, choose CCNA. Cisco offers CCNA certification as an entry-level credential to understand and learn the fundamentals of IT networking.
Step 2: Acquire the Necessary Knowledge
- Self-Study Resources (Books, Online Courses, Videos): Begin by accessing self-study materials like books, online courses, and video tutorials. These resources help you grasp networking concepts, protocols, and technologies.
- Cisco’s Official Learning Materials: Utilize Cisco’s official study materials to align with the exam objectives. These materials provide a comprehensive understanding of the topics covered in the CCNA exam.
- Practice Labs and Simulations: Hands-on practice is vital. Set up virtual labs or use simulation tools to emulate real networking scenarios, allowing you to experiment and gain practical experience without affecting actual networks.
Step 3: Hands-On Experience
- Utilizing Network Simulation Tools: Network simulation software like Cisco Packet Tracer or GNS3 allows you to build virtual network environments. You can practice different configurations and scenarios without needing physical equipment.
Step 4: Enroll in a CCNA Training Course
- Benefits of Structured Courses: Enrolling in a CCNA training course provides structured learning guided by experienced instructors. It ensures comprehensive coverage of exam objectives and enables interaction with fellow learners.
- Online vs. In-Person Training: Choose between online and in-person training based on your preferences and availability. Online courses offer flexibility, while in-person classes provide direct interaction with instructors.
Step 5: Review and Practice
- Mock Exams and Practice Questions: Access mock exams and practice questions that simulate the CCNA exam environment. These help you gauge your readiness and become familiar with the exam format.
- Identifying and Addressing Weak Areas: Analyze your performance in practice exams to identify weak areas. Focus on improving your understanding of these topics through targeted study and practice.
By following these steps, you will be well-prepared to tackle the CCNA certification journey with a strong foundation of knowledge, practical skills, and the confidence to succeed in IT networking.
NOTE: Familiarize yourself with the CCNA certification path Here!
How can I prepare for the CCNA exam?
To prepare for the CCNA exam, you must understand the exam pattern first. Hence, the exam details for the CCNA exam are as follows-
Exam Code | CCNA 200-301 |
Exam Level | Associate |
Exam Cost | USD 300 |
Exam Duration | 120 Minutes |
Exam Format | MCQ & Multiple Response |
Total Questions | 90 to 110 Questions |
Passing score | Variable (750-850 / 1000 Approx) |
Language | English and Japanese |
NOTE: Prepare for the exam tips to crack CCNA Here!
What skills will you learn with the CCNA training?

The skills you will learn with the CCNA training are as follows-
Network Configuration
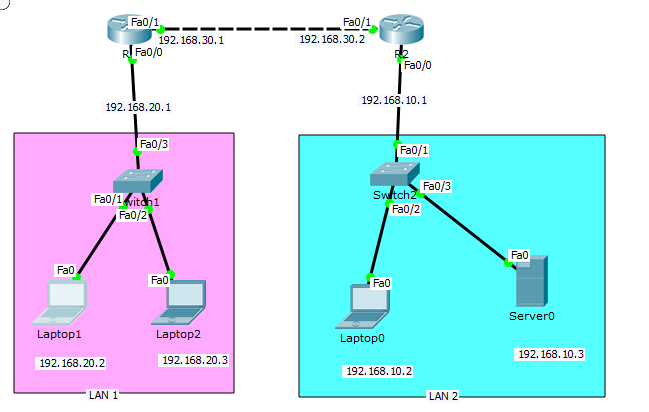
Configure routers, switches, and other network devices for optimal performance
Routing and Switching
Gain expertise in routing protocols, dynamic routing, and Ethernet switching techniques.
IP Addressing and Subnetting
Understand IP addressing schemes, subnetting, and how to allocate IP addresses effectively.
Network Security
Learn about network security concepts, including firewalls, access control, and basic security best practices.
Wireless Networking
Grasp the fundamentals of wireless networking, including setup and security considerations.
Network Troubleshooting
Acquire skills to identify and resolve common networking issues efficiently.
Network Protocols
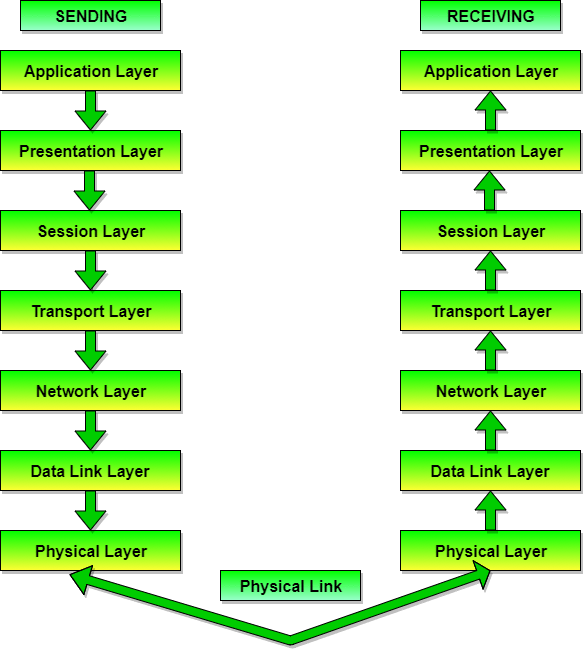
Gain familiarity with TCP/IP protocols, including DNS, DHCP, HTTP, and more.
Network Design Principles
Understand the network design basics, including segmentation, redundancy, and scalability.
Network Monitoring
Learn to use monitoring tools to track network performance, diagnose problems, and optimize resources.
Basic Command-Line Interface (CLI) Skills
Familiarize yourself with command-line interfaces of networking devices for configuration and management.
NOTE: Get the CCNA tutorial Here!
What is the next step after the CCNA exam?
After completing the CCNA training and earning the certificate, you can go for the CCNP certification. Though there are plenty of CCNP certifications available, namely-
NOTE: Industry experts recommend the CCNP Enterprise course after the CCNA training.
Where to enroll for the best CCNA training?
To enroll for the best CCNA training, one must find the answer to the primary question – where to seek help for training? And to track down a suitable response, one wastes a great deal of time in all quarters. But here we are with the answer.
Network Kings is an ideal yet promising option for candidates aspiring to become an in-demand Network expert.
Why choose Network Kings for the best CCNA training?
Network kings is the best ed-tech platform to pursue the CCNA program online, as you can enhance your knowledge and skills by sitting at home. Courses are available in Hindi and English. Timings are flexible here, so you can learn without affecting your working or study hours.
Network kings has experienced trainers and industry experts who provide in-depth knowledge of the particular course. In the CCNA course, you will get 60+ hours of recordings and 60+ hours of live classes covering-
- Basics of network fundamentals
- Routing
- Switching
- Basics of security
- IP services
- Virtual labs
NOTE: Know the complete CCNA syllabus in detail Here!
What are the available job roles after the CCNA course training?
The top available job roles after the CCNA course training are as follows-
- Network Administrator
- Network Engineer
- Network Analyst
- Network Security Analyst
- Network Support Engineer
- Systems Administrator
- Systems Engineer
- Technical Support Engineer
- IT Manager
- IT Project Manager
- IT Consultant
- Network Consultant
- Information Security Analyst
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Network Architect
- Wireless Network Engineer
- VoIP Engineer
- Cloud Network Engineer
- Network Operations Center (NOC) Technician
- Technical Trainer
NOTE: Prepare for the CCNA Interview Questions and Answers Here!
What are the salary aspects after the CCNA course training?
The salary aspects after the CCNA course training are as follows-
- United States: USD 50,000 – USD 120,000 per year
- Canada: CAD 45,000 – CAD 90,000 per year
- United Kingdom: Pounds 20,000 – Pounds 40,000 per year
- Australia: AUD 50,000 – AUD 90,000 per year
- Germany: EUR 35,000 – EUR 60,000 per year
- France: EUR 30,000 – EUR 50,000 per year
- India: INR 250,000 – INR 600,000 per year
- China: CNY 100,000 – CNY 300,000 per year
- United Arab Emirates: AED 70,000 – AED 120,000 per year
- Singapore: SGD 45,000 – SGD 90,000 per year
- Japan: JPY 3,000,000 – JPY 5,000,000 per year
- South Africa: ZAR 200,000 – ZAR 500,000 per year
- Brazil: BRL 60,000 – BRL 120,000 per year
- Saudi Arabia: SAR 80,000 – SAR 150,000 per year
- Mexico: MXN 300,000 – MXN 600,000 per year
Wrapping Up!
From understanding network basics to diving into advanced security measures, CCNA training equips individuals to navigate this evolving terrain. As you embark on this path, remember that your endeavours shape how we connect, communicate, and thrive in the digital age. So, let’s continue this journey, knowing that each skill mastered, each challenge overcome, and each certification earned brings us closer to a world where connectivity knows no bounds.
Happy Learning!