VTP in networking is one of the crucial topics in IT. One can acquire the skills required to manage, configure, troubleshoot, and analyze the VLAN by learning VTP in networking.
Therefore, keep reading the blog till the end to learn everything regarding VTP in networking.
What is VTP in networking?
VTP stands for VLAN Trunking Protocol. It is a layer-2 protocol. In a small network, the number of switches is less, so we can configure VLANs individually. But it is not an easy task to configure VLANs individually in large networks. Therefore, VTP is the one-stop solution for this.
Putting one switch in VTP server mode and the other in VTP client mode, you can configure VLANs in one go. VTP allows you to configure VLANs on a central VTP server switch while VTP clients coordinate their VLAN database to the server.
What are the techniques of VTP in networking?
There are two techniques of VTP in networking, namely-
- Frame Filtering
The frame filtering method analyses information regarding each frame (MAC address or a layer-3 protocol) in the VTP domain.
- Frame Tagging
The frame tagging method sets a distinctive identifier in the header as it gets forwarded to the VTP domain.
What are the modes of VTP in networking?
There are three modes of VTP in networking, namely-
- VTP Server Mode
- VTP Client Mode
- VTP Transparent Mode
- VTP Server Mode
- It allows you to add, modify and delete VLANs.
- It stored the VLAN database in NVRAM.
- The revision number (CR value) increases whenever a new VLAN is added or deleted.
NOTE: What is the configuration number (CR number)?
CR number represents the total count of changes done in configuration. Whenever there is any update, the CR value is incremented by 1. CR value and revision number are the same things.
The VTP server advertises all VLANs on a trunk port, and the VTP client synchronizes their database to it so that whenever a new VLAN gets added to the VTP server, it automatically gets created in VTP clients. The CR number also gets updated automatically (the CR value is the same as the VTP server).
VTP servers also behave as VTP clients. Therefore, a VTP server synchronizes with another VTP server with a higher revision number.
- VTP Client Mode
- You can’t add, modify or delete VLANs in this mode.
- Don’t store the VLAN database in NVRAM.
- VTP Transparent Mode
- A switch configured in transparent mode does not participate in the VTP domain and forwards the advertisements in the same domain.
- Maintain their own VLAN database in NVRAM. You can add or delete VLAN in this mode. But these VLANs will not advertise in the VTP domain.
What are the components of VTP in networking?
There are three components of VTP in networking, namely-
- VTP Domain
The VTP domain limits configuration changes in the network while resolving the fallacies. One can never construct or alter VLANs on a VTP server mode until the domain name gets specified since it consists of single or multiple interconnected switches.
- VTP Pruning
The VTP pruning component precludes unnecessary flooding of broadcast information from one VLAN across all trunks in the VTP domain, as it allows pruning on one VTP server switch and gets disabled by default.
- VTP Advertisements
The VTP advertisements mode uses a scale of advertisements to coincide and disperse VLAN configurations in the network.
What are the kinds of VTP advertisements in IT?
There are three kinds of VTP advertisements in IT, namely-
- VTP Summary Advertisement
The VTP summary advertisement includes the VTP version, VTP domain, CR number and time stamps. VTP summary advertisement occurs every 300sec (5 min.) when a VLAN gets added, removed or changed.
- VTP Subset Advertisement
The VTP subset advertisement contains all the information on VLANs required by VTP clients to coordinate the VLAN database to the server.
- VTP Request Advertisement
The VTP request advertisement gets sent by a VTP client. After receiving the summary advertisement, when the VTP client finds a higher CR value in the summary advertisement, it sends the client a request advertisement for detailed subset advertisements.
How does VTP work?
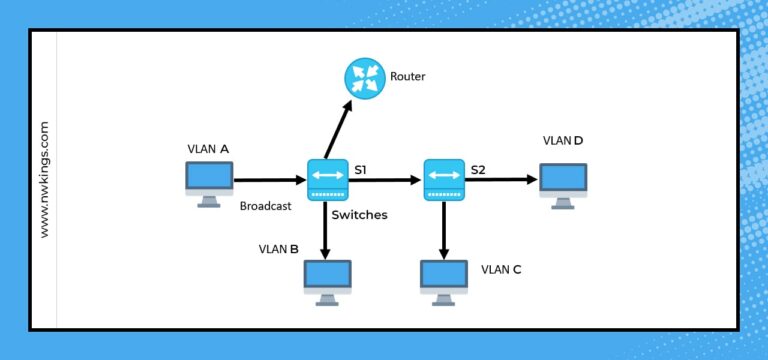
Step 1) On switch S1, VLAN A and VLAN B get transmitted via a single port to the router and another port to switch S2.
Step 2) VLAN C and VLAN D are trunked from switch 2 to switch S1 and the router.
Step 3) The trunk link from switch S1 to the router must get carried to all four VLANs.
Step 4) If VLAN A needs to get to a computer on VLAN B (or VLAN C or VLAN D), it must traverse from the S1 or S2 to the router and return to another S2 or S1 simultaneously.
What are the advantages of working with VTP in networking?
The advantages of working with VTP in networking are as follows-
- VTP helps in separating the network
- VTP allows accurate VLAN tracking and monitoring
- VTP provides dynamic reporting of VLANs
- VTP offers management of the VLAN database
- VTP reduces the VLAN management
What are the different versions of VTP?
There are three versions of VTP in networking, namely-
- V1
- V2
- V3
NOTE: V1 & V2 are almost similar, except that V2 adds support for token ring VLANs while V3 is the advanced version of VTP in networking.
Wrapping Up!
VTP is a crucial concept in networking. And since now you are familiar with the topic, dive into the configuration process to manage the functionality of routers and switches with VLANs.
Therefore, feel free to write to us with any queries regarding VTP in networking.
Happy Learning!