
Top 13 Up-to-Date BGP Interview Questions and Answers in 2023:
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is one of the most important topics to cover in Cisco Certified Network Professional’s core exam or BGP Interview Questions, i.e., ENCOR 350-401. In this blog, we will cover most-asked BGP interview questions and answers.
In this blog we have covered frequently asked BGP questions such as scenario based BGP interview questions and BGP troubleshooting interview questions and answers.
Assuming you have looked up BGP interview questions, you already know what BGP is. But if you don’t, let’s start right from the basics.
1. What is BGP in CCNA?
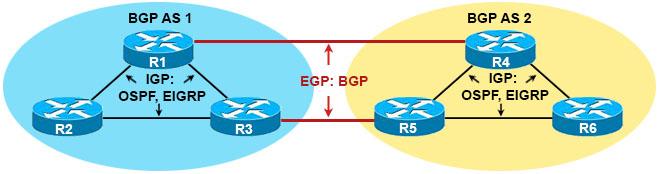
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is the routing protocol of the Internet. Meaning it chooses the best path for communication to happen between two or more routers. Some of the distinguishing features of BGP include:
- It is the biggest routing protocol in the world.
- It manages the trusted and untrusted routes.
- It enables routing through autonomous systems instead of routers.
- It is the slowest routing protocol in the world.
- It is primarily used for service providers.
- It can also be used for enterprise customers.
Now that you are completely aware of BGP, we can move ahead. Also, this works as the very first interview question.
It is time to graze over some other tricky BGP interview questions and answers.
2. How does BGP work?
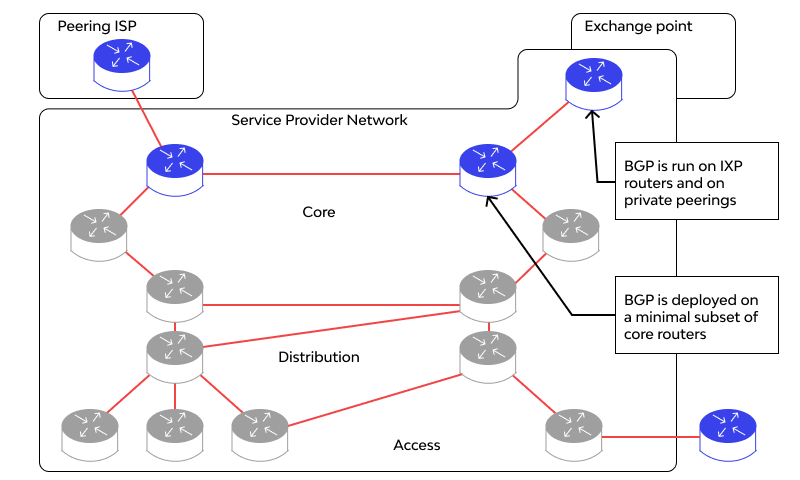
BGP connection between two routers is called a peering session. This simply means that the two routers have established a communication channel. This would allow the exchange of information.
Once peering occurs, here is how BGP works step by step:
- It will look for routes among all the External BGP routers it has in the neighborhood.
- It will also look for the Internal BGP routers it has in its own Autonomous System (AS).
- After applying filters, it picks up the best path.
- It installs it in the routing table (RIB).
- Then, the best route is sent to the external BGP neighbors.
This further leads to several sub-processes. These are:
BGP ‘in’ Process:
- It receives path information from peers.
- The results of the best BGP path selection are placed in the BGP table.
- The best path is then ‘flagged’.
BGP ‘out’ Process:
- Share the best path information to peers.
3. What does BGP mean in networking?
BGP makes the Internet work. The Internet is nothing with BGP.
BGP allows every Autonomous System (AS) to discover routes to other ASs. It is only the responsibility of BGP to filter and change the routes. In short, BGP lets you apply a wide range of policies to control the traffic. It can change the path of traffic.
As we know, the Internet is a network of networks. If we zoom into them, networks work on BGP. That’s how important BGP is!
4. Why is BGP used?
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) works as a GPS for the packets of information. The BGP comes up with the best possible route for the packets to travel. It takes into consideration various factors, one of them being the situation of the network nodes.
BGP is designed for the following functions:
- Exchange routing information
- Exchange reachability information between autonomous systems on the Internet.
Each BGP speaker is called a peer, and exchanges routing information with its neighboring peers as network prefix announcements.
An Autonomous System (AS) doesn’t need to be connected to the other AS to know its network prefix.
BGP chooses the most suitable route on the basis of collected information such as an organization’s routing policy, based on cost, speed and reliability, etc.
5. Why is BGP used over OSPF?
Both BGP and OSPF are dynamic routing protocols. However, there are a few reasons why BGP is used over OSPF. These reasons are mentioned below:
- OSPF is an intra-domain routing protocol and it uses link routing protocol. BGP, on the other hand, is an inter-domain routing protocol and it uses path vector routing.
- OSPF is used to determine the fastest route whereas BGP tells the best path.
Now, why to use BGP over OSPF:
- BGP is often used in Wide Area Network (WAN) and IaaS environments.
- It is also used for Internet redundancy.
- OSPF is used for Local Area Network (LAN) and data center.
- BGP is primarily used in large networks.
Through the above-mentioned pointers, it can be concluded that BGP is better than OSPF.
6. Is BGP faster than OSPF?
OSPF has faster convergence time than OSPF. Network convergence is the is the speed at which a router adjusts path used to a destination network in the times of network outrage.
OSPF works better in Local Area Network (LAN) and private data centers.
7. What is the AD value of BGP?
Administrative Distance (AD) is a value that a router uses in order to choose the best path.
- It helps the router to select the best path when there are two or more different routes to the same destination from two different routing protocols.
- The AD value is used to rank routes from most preferred route to the least preferred route.
- The most-preferred route has the lowest AD value while the least-preferred route has the highest AD value.
8. What is OSPF used for?
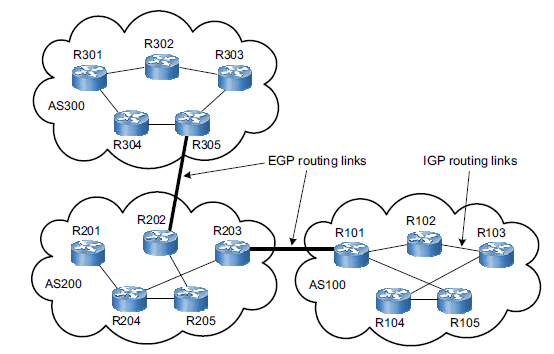
Open Shortest Path first (OSPF) is also a routing protocol such as BGP. It is an Interior Gateway protocol. OSPF is used for the following:
- OSPF is used in large and very complex networks.
- OSPF is a link state routing protocol. Thus, you can use it to converge fast.
- OSPF converges faster than distance vector protocols such as BGP.
- It is a routing protocol that is used to share routes between routers.
- It is relatively easy to configure and is easily understood.
- OSPF is used in multi-site networks.
- With OSPF, you do not need to add a new route to every other site’s router. OSPF can automatically update the routing tables of various routers.
9. Do home routers use BGP?
Yes, BGP is used by routers present at our homes. BGP helps to route your e-mails and web requests across the Internet. In short, Internet routing cannot happen without BGP.
10. Why is BGP not a routing protocol?
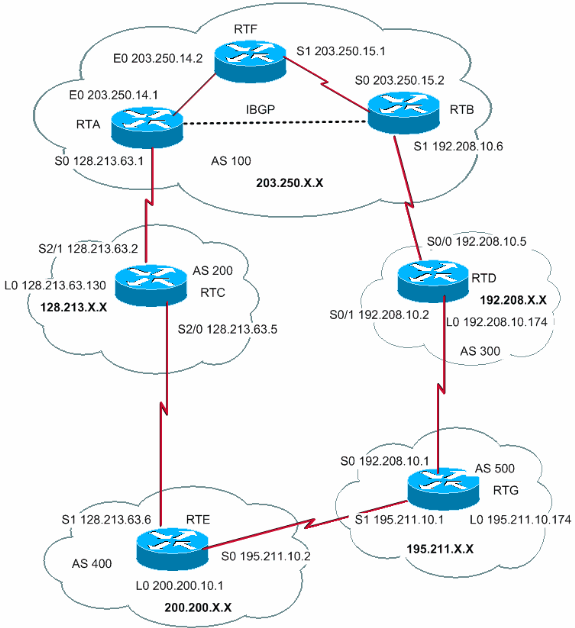
BGP is an inter-domain routing protocol. It uses path vector routing, with the routing operations performed between two or more autonomous systems. BGP works on finding the best path possible.
11. What are LSA types?
OSPF communicates by using Link State Advertisement (LSA) to communicate for the Internet Protocol (IP). OSPF uses a Link State Database (LSDB) and it uses LSA to fill it up.
OSPF consists of many types of LSAs. There are given below:
- LSA Type 1: Router LSA
In this LSA, you can find the list of all the directly connected links of this router. These types of routers always stay within the area.
- LSA Type 2: Network LSA
This type of LSA is constructed for multi-access networks. Network LSAs are made by DR.
- LSA Type 3: Summary LSA
The summary LSA is developed by the ABR. This is why ABR will generate a summary ASBR LSA. It will consist of the router ID of the ASBR.
- LSA Type 4: Summary ASBR LSA
The summary ASBR LSA consists of the router ID of the ASBR in the link-state routing field. It makes it easy for other routers to find ASBR.
- LSA Type 5: Autonomous System External LSA
These are generated by the external ASBR.
- LSA Type 6: Multicast OSPF LSA
It is not used and is not supported.
- LSA Type 7: Not-so-stubby area LSA
It is also referred to as not-so-stubby (NSSA) LSA. NSSAs do not allow external LSAs which are Type 5 LSA. With LSA Type 7, you can allow them.
- LSA Type 8: External Attribute LSA for BGP
12. What is RIP OSPF EIGRP BGP?
RIP:
- Routing Information Protocol (RIP) is a distance vector routing protocol.
- It can be used to configure the hosts as a part of a RIP network.
OSPF:
- OSPF is a link-state routing protocol.
- It is developed for IP networks.
- It is based on the Shortest Path First (SPF) algorithm.
- It comes under the group of interior gateway protocols.
EIGRP:
- Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol (EIGRP) is a network protocol.
- It allows routers to exchange information in a better way than the network protocols that were present earlier.
- It is a dynamic routing protocol used for routing and configuration decisions.
BGP:
- BGP is the biggest routing protocol in the world.
- It manages the trusted and untrusted routes.
- It enables routing through autonomous systems instead of routers.
- It is the slowest routing protocol in the world.
- It is primarily used for service providers.
- It can also be used for enterprise customers.
13. When should BGP not be used?
If you only want to connect to an external domain and if there is only one connection then you should not use BGP.
It’s a Wrap!
We have summed up the Cisco BGP interview questions and answers altogether. Also, the questions and answers consist of scenario-based BGP questions, BGP troubleshooting questions and BGP attribute questions and answers.
Go over all these questions and you are all set to ace your exam!
People also search for
Basic BGP interview questions
BGP interview questions and answers for beginners
BGP interview questions and answers for experienced
BGP interview questions and answers cisco
BGP attributes interview questions



