
A Network Engineer has to deal with networking devices such as routers, switches, modems, etc. To understand them better, it is crucial to understand the concept of wireless network security. This topic is also very important from the CCNA 200-301 exam’s point of view.
Note: If you have been following up with our new CCNA series, you might have come across the wireless LANs in the computer networks guide. If you haven’t, I recommend you do so if you are new to the concept of wireless networks.
In this blog, we will go through a brief introduction to wireless network security. We will also learn various authentication methods, covering not-so-secure methods to the most secure methods in modern networks.
Let us now begin with the new concepts!
What is Meant by Wireless Network Security?
When it comes to networks, security is a very important aspect that cannot be compromised. However, it is even more important in wireless networks. Do you know why?
So, it is because the wireless signals are not present in a wire, any device that comes within the range of the signal can receive the traffic. On the other side, wired networks encrypt the traffic when sending it over an untrusted network such as the Internet.
For example, we usually don’t encrypt the wired traffic within a LAN.
However, in wireless networks, it is very important to encrypt the traffic between the wireless client and AP. This is why encryption is very important in wireless networks. Therefore, we need to cover the three most important concepts:
- Authentication
- Encryption
- Integrity
We will learn about encryption and integrity in detail in the next blog. So, we will focus on authentication in this blog.
Introduction to Authentication from Wireless Perspective
As the traffic is sent from a wireless client to the AP, it is very important to authenticate all the clients in a particular wireless network. Therefore, authentication can be described as verifying the identity of a user or device.
Only trusted users and clients should be given access to the network, especially in a corporate setting. In the case of guest users, a separate SSID can be used to provide access to the corporate network.
The authentication process is not just limited to the AP to authenticate the clients. It is also for the clients to make sure that they do not connect with a malicious AP. A malicious AP can trick users by being an imposter and then, it can carry out attacks such as a Man-in-the-Middle attack.
There are many ways to carry out authentication. Some of them are:
- Password
- username/password
- Digital certificates installed on the devices
What are the Various Wireless Authentication Methods?
There are over seven different methods to authenticate. These are:
- Open authentication
- WEP (Wired Equivalent Privacy)
- EAP (Extensible Authentication Protocol)
- LEAP (Lightweight EAP)
- EAP-FAST (EAP Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling)
- PEAP (Protected EAP)
- EAP-TLS (EAP Transport Layer Security)
Let us now cover each one of them in brief.
Less Secure Methods for Authentication
1. Open Authentication
- The client first sends an authentication request and the AP accepts it. No questions are asked and there is no need to enter credentials.
- This is NOT a secure authentication method.
- The AP accepts all authentication requests.
- This method is still used today in combination with other authentication methods.
- Consider connecting to Wi-Fi in a restaurant that does not require you to enter any password to connect to the Wi-Fi. However, after the connection is built, it asks the user to authenticate himself through his user id, etc.
2. Wired Equivalent Privacy (WEP)
- WEP is not just an authentication method. It provides encryption as well to wireless traffic.
- It uses the RC4 algorithm for encryption.
- It requests the sender and receiver to use the same key. Therefore, it works on the ‘shared-key’ protocol to authenticate.
- WEP keys can be 40-140 bits in length.
- WEP encryption is NOT secure. It can easily be cracked.
More Secure Methods for Authentication
3. Extensible Authentication Protocol
- It is an authentication framework that is used by various EAP (LEAP, EAP-FAST, PEAP, EAP-TLS) methods.
- It defines a standard set of authentication functions.
- It provides port-based network access control as it is integrated with 802.1X. It is used to limit network access for clients connected to LAN or WAN until they are authenticated.
4. EAP Authentication Methods Used in Wireless LANs
- 4. LEAP (Lightweight EAP)
- It has been created by Cisco as a better version of WEP.
- The clients need to provide a username and password to connect with the AP to authenticate.
- Mutual authentication is provided by both the client and the server, unlike WEP where only AP sends the authentication message.
- The keys used are dynamic WEP keys. Therefore, they keep changing.
5. EAP-FAST (EAP Flexible Authentication via Secure Tunneling)
- It has also been developed by Cisco.
- It consists of three phases:
- Protected Access Credential (PAC) is created and sent over to the client via the server.
- A secure TLS server is created between the user and the authentication server.
- The server and client then community further for mutual authentication in the TLS server.
6. Protected EAP
- PEAP also creates a secure TLS tunnel between the client and server like EAP-FAST.
- The server consists of a digital certificate instead of a PAC.
- This certificate is used to certify the server by the client.
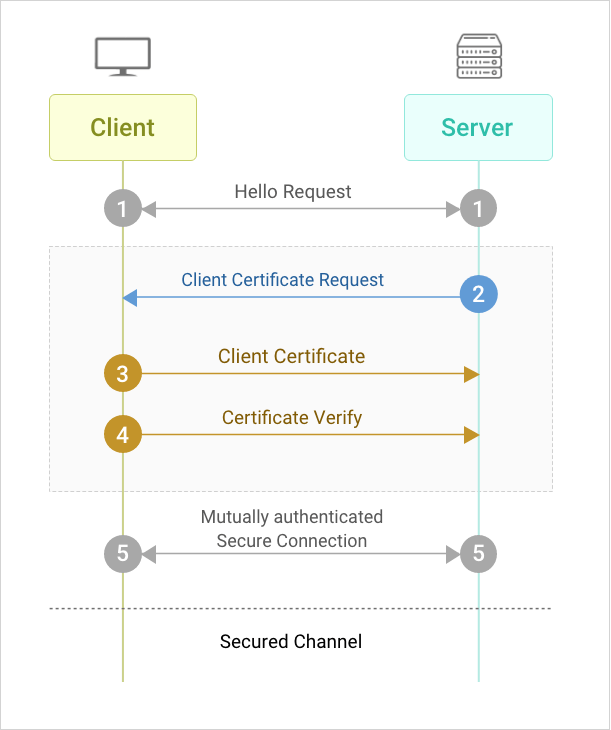
7. EAP-TLS (EAP Transport Layer Security)
- EAP-TLS requires all the ASs as well as clients to have a certificate.
- It is the MOST secure wireless authentication method.
- It is more difficult to implement PEAP because every client device needs a certificate.
- The TLS tunnel is still used to exchange encryption key information.
Conclusion
This marks the end of all the important concepts in wireless network security. We have majorly covered all the authentication methods in this blog.
In the upcoming blog, we will cover authentication and integrity. Stay tuned
Happy learning!


