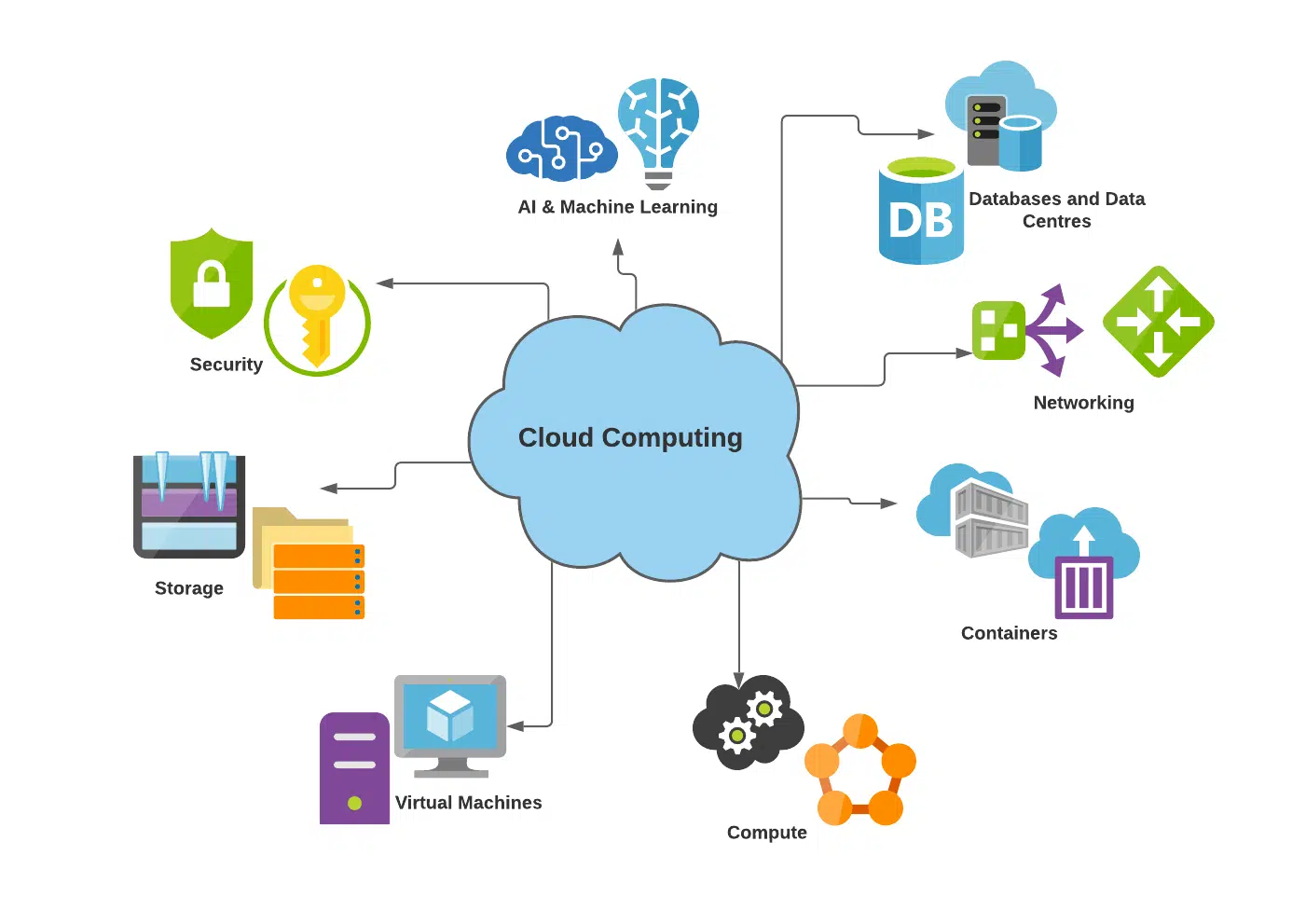
Need to know about cloud computing security in detail? You have come to the right place if you want to learn about all things cloud computing security. This blog will delve into different cloud computing security protocols, policies for data protection, and authentication systems that help protect your confidential information from potential threats.
We will also look at how these technologies can be used wisely to gain maximum benefit from using cloud services while ensuring your private info is kept safe. With contributions and insights by industry experts, this blog aims to equip its readers with knowledge on ways best suited for safeguarding their data when utilizing the power of cloud computing technology.
Understanding the Essentiality of Cloud Security
When it comes to Cloud Computing, security is a must-have component. As companies switch over to the cloud, they have to make sure that their data remains safe and secure from any potential malicious activities. It is, therefore, crucial for businesses to get clued up on how important cloud security is and what measures can be taken to implement this efficiently into their operations. Cloud security covers an array of technologies and processes created specifically for safeguarding information stored in cloud systems against unauthorised access or tampering in mind – quite essential when you think about all the sensitive info these days being uploaded onto digital platforms!
The use of cloud-based storage systems is not just about storing data and files but also involves taking measures to ensure misuse or abuse of services can be prevented. This might include encrypting the data as well as having strict access control policies in place. Regular vulnerability checks and audits need to take place too so that any potential issues are spotted quickly.
So while it is important for organizations using such systems to understand their compliance requirements with local laws concerning data storage; there may very well be standards prescribed by industry associations like ISO, which must also be adhered to – making sure your online security needs are taken care of from all angles!
Companies need to make sure that all their staff are aware of these regulations, as failing to stick by them could cause legal troubles or pricey fines. Furthermore, companies may want to think about investing in the right tools and techniques for spotting any potential hazards against their cloud system before they become an issue; this can include endpoint detection solutions such as anti-virus software, firewalls, intrusion detection systems (IDS) and other kinds of security programs.
Additionally, it is necessary for organisations to continuously monitor system logs so that if something suspicious should appear they would be able to recognise it straight away and take immediate action when needed. All in all, understanding how significant cloud safety is crucial for any business aiming at taking advantage of what the cloud has got offer while making certain its data stays secure from external threats. By being proactive – like deploying apt cyber-security setups and educating employees with relevant laws – businesses can protect themselves from possible risks related to using clouds but still reap its benefits too!
Exploring the Concept of Cloud Computing

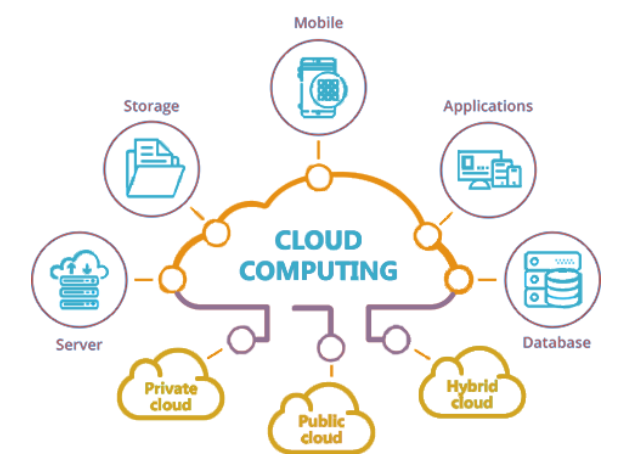
Cloud computing has been garnering more and more popularity of late, as businesses are incorporating cloud services to optimise their operations. But what exactly is it? Well, in short, it is a method of technology which gives people remote access to shared computer resources such as software applications, hardware and data. In other words, users can gain access from different locations with the same programs or documents without having any worries about security issues. This could be especially beneficial for organisations that operate across multiple countries or areas – they’re able to work together whilst ensuring all info stays safe thanks to cloud computing services!
Despite its potential risks, cloud computing can offer significant benefits for any organization looking to increase efficiency through improved collaboration and sharing capabilities without compromising on security. There’s no need for storing sensitive information locally either since it can be accessed from anywhere with an internet connection – handy whether you’re a large organisation or a small company. But when it comes to security breaches in the cloud there have been some reports of malicious activities such as unauthorised access to info or data leaks so proper measures should always be taken.
Encrypting data stored in the cloud is one way, as well as using private networks for transmission between devices; strong passwords and two-factor authentication methods ensure privacy and safety online too. All this means that exploring what advantages Cloud Computing brings could pay off – especially if done safely!
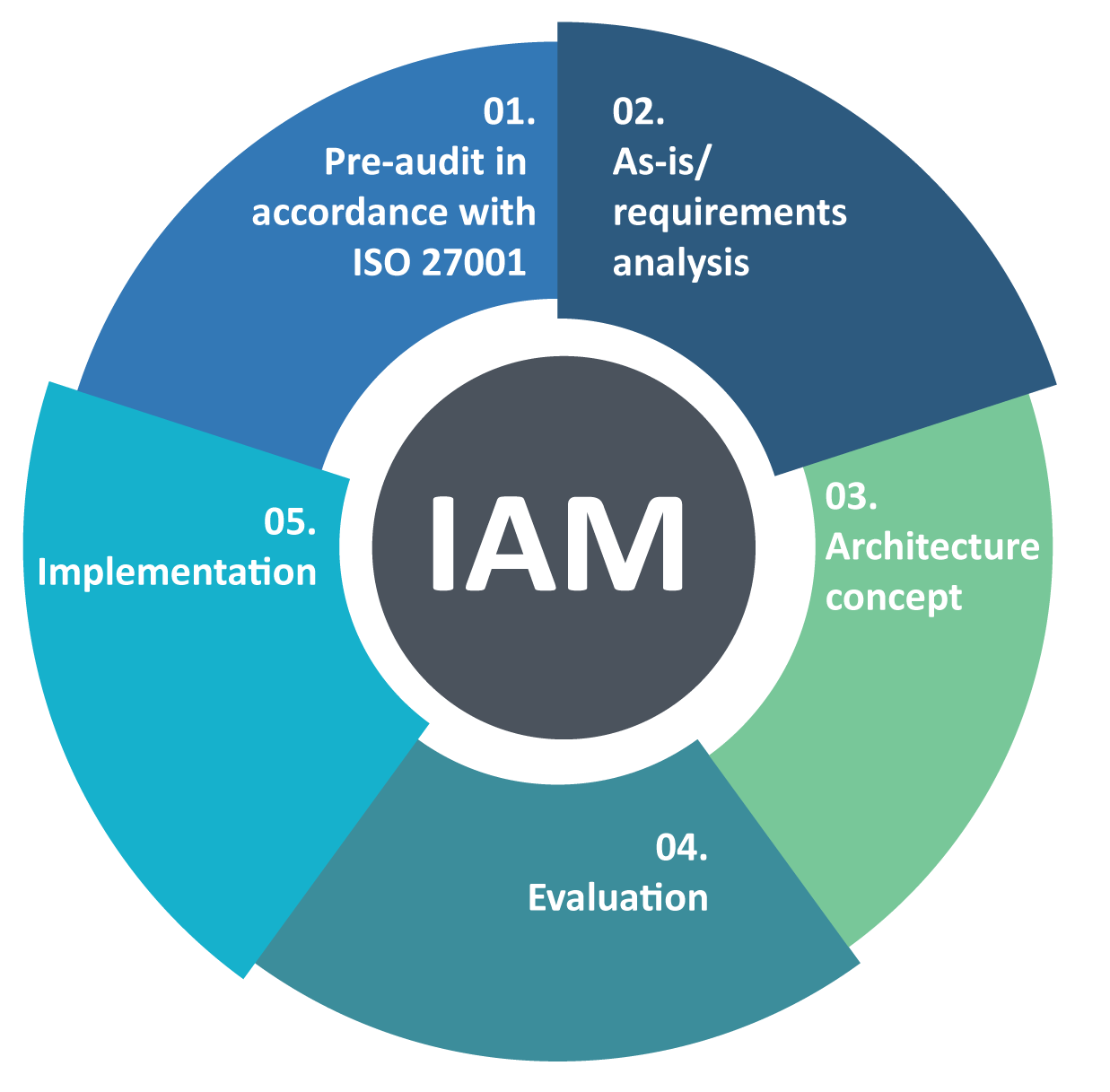
Unraveling The Different Types of Cloud Computing Security
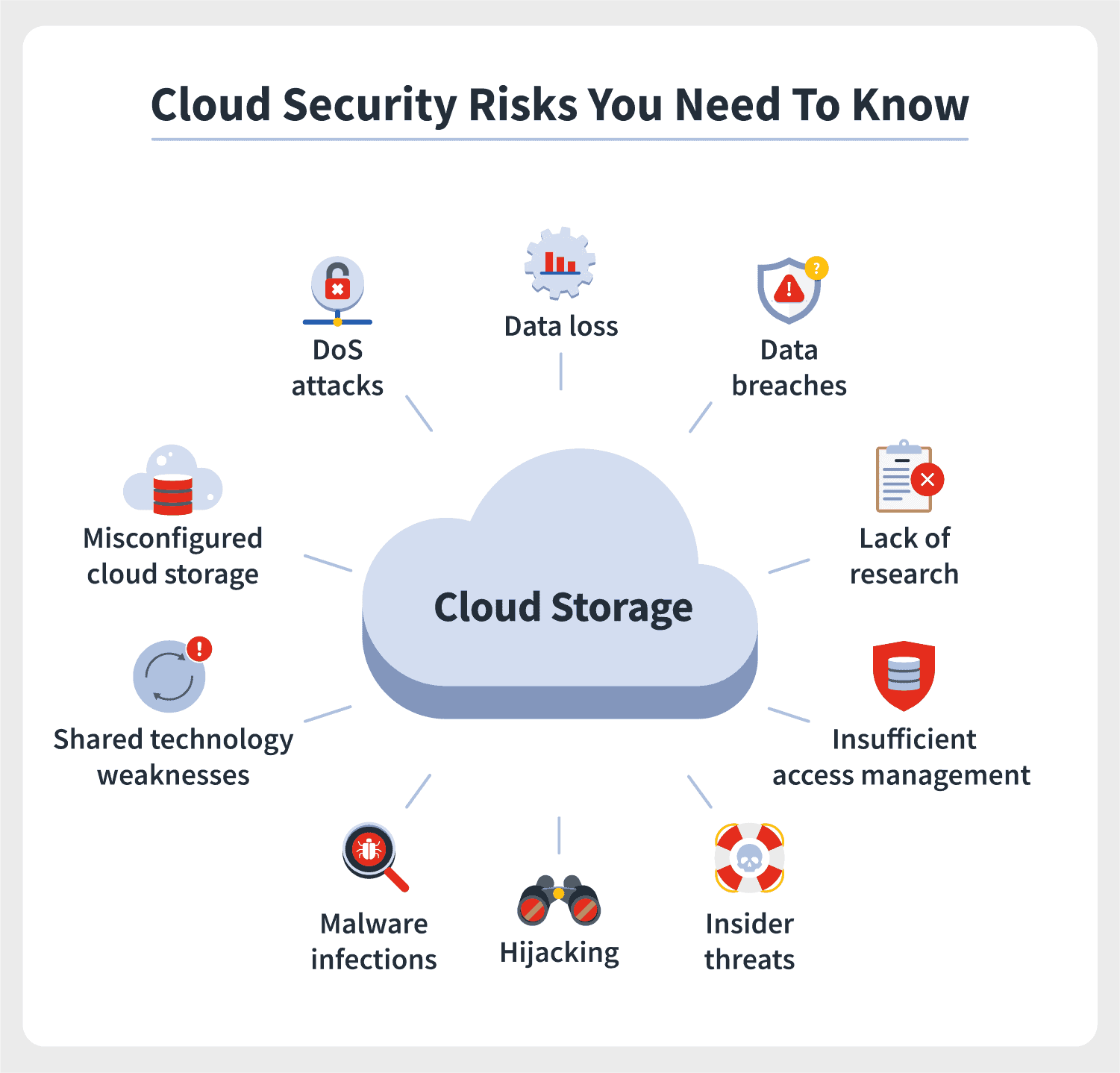
When it comes to Cloud Computing Security, cloud security is a huge consideration for businesses and organisations. The phrase ‘cloud security’ refers to the processes, technologies and rules that are employed to protect data stored on cloud servers from any kind of attack or modification. A big part of fully understanding what cloud security entails involves being aware of the diverse types of cloud safety available nowadays. The most popular form of this type of safety is Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS). What implications does such protection have when working with confidential business information? How secure do you feel knowing your work can be accessed by third parties?
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) allows customers to access a secure computing environment, complete with servers, storage and networking technology. Security tools such as firewalls, antiviruses and intrusion detection systems are also available to help protect data saved in the cloud. This makes it possible for users to take control of their computer environments while still enjoying the cost savings that come from virtualization provided by IaaS providers – pretty neat huh? Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), on the other hand, is an increasingly popular type of cloud security solution too.
When it comes to business operations, software-as-a-service (SaaS) is proving itself as a key tool for organisations. With this cloud technology solution companies can migrate applications into the cloud so users can access them without having to contact their IT department. By using SaaS services, businesses are provided with email platforms, customer relationship management systems (CRMs), web hosting and collaboration tools – all of which give cost savings via virtualisation plus increased scalability due to its pay-as-you-go model. (Is there more?) Yes! Platforms as a service (PaaS) offer another type of cloud security that gives users what they need to develop and deploy apps on the cloud without needing additional hardware or software infrastructure requirements – now doesn’t that sound great?
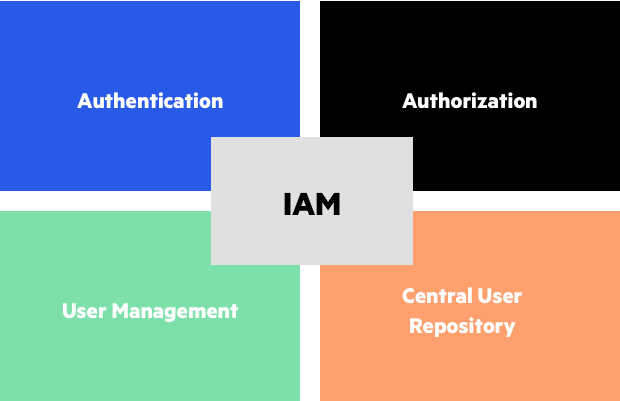
With PaaS, companies can take full advantage of automated deployment abilities that grant them the ability to quickly roll out new applications or updates without having to allocate physical servers or manage software upgrades manually. What’s more, Identity Access Management (IAM) provides customers with secure access control procedures such as authentication and authorization for different types of users who may require access to various parts of an application hosted in the cloud. IAM also helps organisations abide by regulations regarding user privacy like GDPR by allowing them to set up policies including multi-factor authentication or encryption for sensitive data.
You can see there are several facets when it comes to Cloud Computing Security offering its pros and cons depending on your individual needs when guarding confidential info stored on remote servers from unauthorised use or malicious attacks. Knowing each type of solution available will help you pick out the right one for your company’s requirements when implementation time draws near.
The Role of Security Protocols in Cloud Computing

When it comes to cloud computing, security is of the utmost importance. Protecting data and granting secure access to applications and services are ensured through a variety of different security protocols. The aim? To ensure information remains safe from hackers or malicious programs trying to gain unauthorised access. Security protocols work hard for this goal of safety achieved by making use of authentication methods such as encryption, authorisation etc.. By using these techniques only authorised users can get their hands on data stored up in clouds safely guarded away!
Encryption is a process which jumbles data so it can only be read by those with the right passwords or keys. Authorization decides who gets to see what parts of the information. All of these security steps guarantee that unauthorised users cannot get into the cloud network, or any of its contents, without suitable authorization.
What’s also important when it comes to safety guidelines for cloud computing is keeping an eye out on user behaviour and making sure everyone follows company policies and laws – how else would you protect yourself from potential issues?
Having a secure cloud network in place is essential for any business. It means logging each user’s activity, scouring the system for suspicious or malicious actions and actively blocking attempts to breach security protocols. This gives organisations peace of mind when it comes to their data being on the cloud, ensuring confidential information remains private and secure at all times – plus adhering to regulatory compliance requirements that protect customer info as well as other sensitive data held by companies. To ensure safety and privacy are maintained though, businesses must take full advantage of these security functions provided by using cloud services; after they need to protect not only customers but also themselves!
Analysing the Risk Mitigation Strategies in Cloud Security
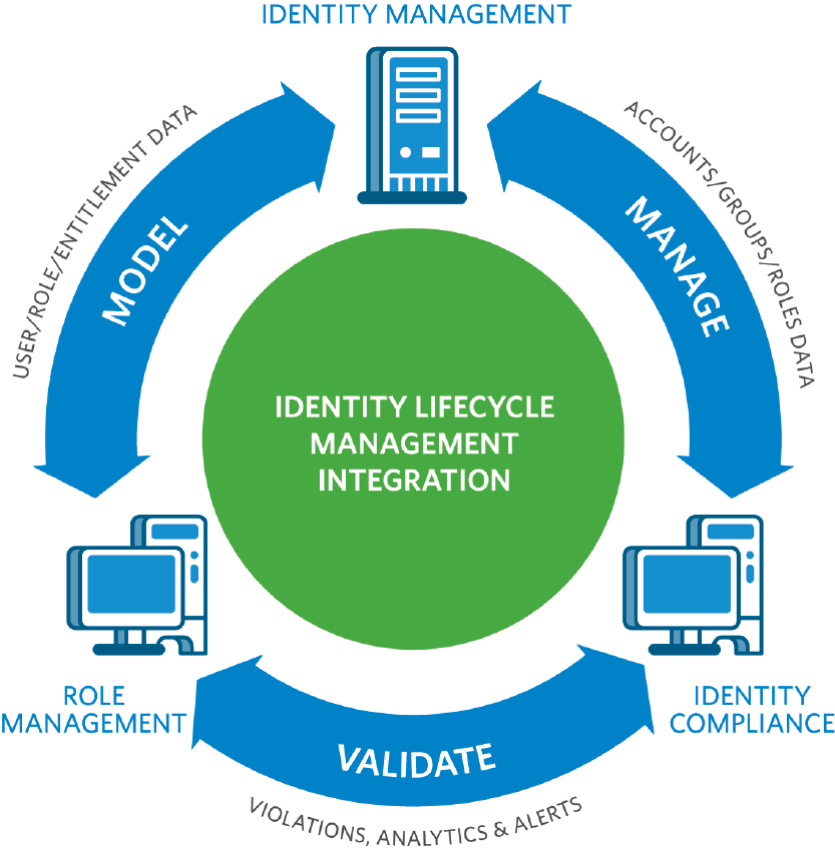
Cloud computing security needs strong risk mitigation strategies. Even if your data is stored securely, there are always risks associated with using the cloud services. So, it’s important to develop tactics for reducing these risks and keeping your information protected and private. One of the most crucial techniques in this regard is identity management. This helps you control who has access to what data within a system or network making sure individuals can only view relevant resources they need at any given time rather than having unrestricted access all over the place – boosting overall protection against malpractice significantly!
When it comes to using cloud services, proper identity management can go a long way. It limits what access users have and makes sure only the right people are allowed to view or alter your data – safeguarding against malicious actors who could potentially get their hands on sensitive information. What’s more, encryption is another important step in making sure you’re not left exposed when turning to the cloud. If we want our data stored safely, these two strategies must come hand-in-hand; after all, they both work towards keeping us safe from any potential risk associated with the use of cloud services. So why leave yourself at risk?
Encrypting your info while managing identities appropriately really is key!
Encrypting data before storing it in the cloud makes sure that if anyone were to get unauthorised access to your data, they wouldn’t be able to make sense of it due to its encrypted form. Plus, encryption ensures any attempts at altering your data will be spotted straight away as any shifts would cause a contrast between the received and anticipated files.
Finally, regular monitoring is important for ensuring the security of your cloud environment. By regularly keeping an eye on activity logs and conducting reviews on where exactly and how data is stored within a cloud system, unexpected patterns or oddities can swiftly be noticed and taken care of before becoming a problem. This helps keep track of who has looked into what information plus whatever changes were made across the system so possible breaches or other difficulties can be speedily identified and dealt with justly before any destruction happens.
Importance of Data Protection in Cloud Computing
Data protection in the cloud is of utmost importance for organisations to make sure their information and data stay safe from any malicious activities. With more and more cyber threats, breaches and hackers out there, it is becoming increasingly necessary for users of cloud computing to understand how exactly they can protect their precious info. There are a few ways you can ensure proper defence within this virtual environment: encryption; access control measures; and authentication protocols – just to name a few. But what does all that mean? How does each one work to keep your data secure?
Encryption is a key security measure used by many organisations to guard their data when it’s sent or stored somewhere else. This makes it much harder for those trying to gain access without permission as the encrypted bits will be unreadable. Access control measures are also hugely important in ensuring that only permitted personnel can get into certain parts of an organisation’s system.
Authentication protocols check who someone is before they’re allowed entry, meaning just those with authority have the potential to break through specific barriers. Creating this kind of protection helps keep delicate information safe and secure – after all, how would you feel if confidential information about your company was open knowledge?
It’s vitally important for companies to get their head around how their cloud service provider can assist them in getting stronger security by bringing extra barriers of protection against potential problems such as malware or ransomware attacks. A lot of providers offer solutions that involve threat detection, anti-virus cover, firewalls, intrusion recognition systems (IDS), identity direction frameworks (IMS) and a few other resources. Business owners need to make sure they utilize all the tools offered by their provider just so they can stretch out their level of security within the cloud environment. Are you taking full advantage? Have you taken sufficient measures to ensure your safety on clouds?
No one ever wants a data breach to occur, but businesses and organisations need to be prepared for such an event. An effective incident response plan is essential in the cloud environment as it outlines what needs to be done should there ever be a security compromise or attack on your network or system. It also provides strategies on how best you can manage any potential repercussions that come along with those incidents. Having this sort of plan in place helps minimize damage from these types of events and makes sure everything goes smoothly if they do happen – even though we all hope they never will!
Overview of the Authentication System in Cloud Computing
Ensuring cloud data is of utmost importance, and one way to do this successfully is authentication. In essence, authentication verifies that a user’s identity through passwords or biometric data such as fingerprinting. It plays an essential role in safeguarding cloud computing security by only allowing authorised people access to confidential information.
Authentication on the cloud begins with inputting details – whether it be username/password combinations or multi-factor validation steps etc. Cloud service providers are capable of setting up various safety protocols for authenticating users when they log into their accounts; making sure everything remains secure at all times!
When it comes to cloud computing, multiple authentication processes can be implemented to guarantee secure access. Two-step verification, single sign-on (SSO) and OAuth-based mechanisms all require users to go through an extra layer of security before being given access to any protected resources. This usually involves having the user verify their identity using biometrics or other methods such as hardware tokens or one-time passwords (OTP). These steps ensure only verified persons have permission the use cloud services – making sure your data is safe at all times!
Having an authentication system in place is essential for protecting against hackers, bots and any other attempt at unauthorised access – as well as preventing internal threats from privileged users who may try to misuse their rights. This helps guarantee that only authorised personnel can get hold of sensitive information, thus reducing the chances of data leakage or a social engineering attack occurring.
But even with all these measures taken into account, there’s no underestimating just how important it is to enforce proper safety procedures such as strong passwords and educating employees on how not to fall prey to phishing scams which could lead to identity theft or data loss. To ensure maximum effectiveness when deploying your system organisations must take notice of customer identity management policies alongside regular staff training sessions too!
Case Studies on Successful Cloud Security Implementation
Cloud computing has become a vital part of modern business operations. It supplies endless flexibility, scalability and efficiency to any organisation, while also permitting improved collaboration among teams. Even though the cloud is an incredible asset for businesses, it additionally carries notable security risks.
To shield their data from potential threats organisations must be aware of how exactly they ought to productively bring in cloud safety measures. One marvellous route to learning about putting into practice cloud security correctly is by looking through case studies that have brought success when doing so – this provides people with real-life examples which enables them to gain insight better than just reading facts off a page!
By taking a look at how other companies have put in place secure cloud solutions for their businesses, organisations can learn precious tips about the most effective ways of doing this. By studying case studies, firms can spot any potential issues they may face during set-up and come up with strategies to tackle them.
Moreover, these kinds of studies provide info on different security options available out there nowadays; thus giving more selection when it comes down to picking an option that suits its particular needs as well as budget limits. This way organizations don’t need to compromise between safety demands and cost constraints – they can get both!
A study conducted for a large financial company demonstrated that using multiple security layers was key to safeguarding sensitive customer info on the cloud platform. The organisation adopted encryption techniques such as tokenization and AWS CloudHSM, so access would only be allowed in line with regulatory compliance requirements. This strategy enabled them to store data across different servers without it being exposed – providing superior protection from cyber-attacks or insider threats.
By considering instances like this one, organisations can identify effective practices they should adopt when implementing cloud security measures of their own. These might include utilising encryption technology; multi-factor authentication opportunities; user permission protocols tighter monitoring of system updates and patches etc – all helpful in securing organisational data at any point while giving businesses confidence that their systems are defended against potential malicious habits or unauthorized accessors/disruptions associated with natural disasters or technical issues.
Challenges Faced in Implementing Cloud Security

When it comes to the benefits of cloud computing, there’s no denying that cost-efficiency, scalability and convenience are among the main advantages. But at what expense? Security and privacy issues remain largely unresolved when embracing this technology – something invaluable for businesses worldwide.
Cloud security includes protecting data stored in clouds; controlling secure access across different service providers; keeping malicious activities away from your system’s infrastructure etc., all of which require an efficient approach if you want to be on top of things regarding cyber safety. All these aspects pose a real challenge: how can we guarantee our customers’ total cybersecurity while taking full advantage of cloud technologies?
Securing a cloud environment can be a tricky business. Not only are there complex architectures to consider, but also an overwhelming amount of data that needs handling. One major hurdle when it comes to ensuring cloud security is guaranteeing the authentication of each user interacting with the system – everyone must have their own identity which should always be exclusive worldwide to protect against any malicious activities from anyone or anything else.
Companies need to guarantee they put in place the right authentication processes like two-factor authentication, Single Sign On (SSO) and identity federation across different systems etc. This is to ensure secure access control over their cloud framework. A further challenge associated with creating safe storage protocols for data kept in cloud servers is encrypted backups.
It’s essential that companies using clouds backup their data regularly and then securely back them up on an external drive which can only be accessed by authorized personnel. But how do you guarantee this? How would you know your information won’t fall into the wrong hands if it isn’t correctly backed up? Questions without answers – yet!
Ensuring that data can be recovered from an offsite location is vital for businesses, in case any information stored on the server gets lost or corrupted due to unexpected events. To make sure this isn’t a problem they need to take measures and install robust Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) to prevent malicious behaviour before it even occurs – not just detect it afterwards!
It is also necessary that companies actively monitor their network system to Identify threats quickly; only then will organisations have suitable countermeasures readily available should anything happen. Doing these things will help protect against attackers targeting platforms or applications on them – something nobody wants happening but needs to prepare for nonetheless.
Future Trends in Cloud Computing Security

Cloud computing security has made significant progress since its inception. As technology progresses, the need for safety solutions is becoming increasingly important to maintain data and resources secure in companies. Cloud computing security will be enriched with more sophisticated technologies and techniques needed to ensure the protection of information stored on these systems. One noteworthy trend within this domain is making use of artificial intelligence (AI). AI can detect likely threats from criminal actors and aid organisations in taking quick action before any harm occurs.
Companies are now starting to realise the potential of AI-based solutions in helping them identify any looming security threats or vulnerabilities; enabling them to develop strategies for addressing those problems as soon as possible, so they can be mitigated before causing disruption. Taking this proactive approach is a great way of reducing risk and preventing damage from occurring.
Data encryption has become an incredibly important factor when it comes to protecting data within organisations – with greater awareness of how crucial it is for information not to fall into the wrong hands, many companies have started taking steps towards keeping their data secure using encrypting technologies. Questions remain surrounding questions around what level of privacy will be achievable but we are certainly making strides forward than ever before!
Encryption algorithms may vary greatly and understanding which would best suit an organisation’s needs is a must for maximising protection. Additionally, organisations are focusing more on data privacy regulations like GDPR or CCPA when using cloud services. Such rules require companies to take extra steps to protect customer information and be accountable for how it is used or shared; hence emphasising the need to have secure data privacy policies in place will become increasingly important moving forward.
At last, more companies are beginning to use multi-factor authentication when accessing cloud services to guarantee that only authorized people can access delicate data or apps. Using powerful authentications such as two-factor authorization ensures that no one else apart from the ones who should be allowed will enter their system.
To conclude, with cloud computing continuing its huge expansion businesses must remain current on the modern trends so they can maintain optimal levels of security while using this technology. From AI detection systems to stronger authentication measures – these trends will continue to be essential elements of successful cloud safety for many years ahead.
Wrapping Up!
In conclusion, cloud computing security provides a range of protocols to help protect data and mitigate risk. As organisations shift their data into the cloud, they must understand these measures to make sure information stays safe from potential threats. When used correctly, this type of security can provide an incredibly high level of protection while also helping companies manage any risks associated with transitioning to the cloud environment. What are some other ways businesses can use Cloud Computing Security? How have you seen effective implementation benefit organisations?
Are you ready to arm your organisation with the know-how and capability needed to successfully travel through this changing technology landscape? If so, sign up for our Cloud Architect Master Program and discover how to create secure, cost-effective cloud solutions that are flexible. With our thorough course content, you will gain an appreciation of architecture best practice principles when it comes to Amazon Web Services (AWS) as well as Microsoft Azure.
You will also delve into the basics of agile methodology in addition to its application within real-world situations. With a hands-on approach, earn mastery over constructing blocks which form any successful cloud system – from infrastructure development right down to automation orchestration!
Don’t wait around – start exploring today’s exciting sphere of computing clouds straight away! Ensure your team is equipped for whatever changes come their way by enrolling on our Cloud Architect Master Programme now – don’t miss out!
Are you looking to up your game in cloud architecture? Our Cloud Architect Master Program could be just what you are after. It offers a comprehensive package of course materials, practical project experience and individualised coaching from experienced mentors – giving you the skills required to become an accredited cloud architect. And if that wasn’t enough, signing up now means some special discounts are yours for the taking! So why wait around any longer? Make sure your place is booked today!
Happy Learning!


















)