
Cybercrime is on the rise, and understanding how to protect against it has now become a fundamental part of any business strategy. While setting up basic network security systems or implementing risk assessment protocols might seem difficult for those less familiar with technology, having the right resources, as well as knowledge about data protection, authentication systems and mitigating risks, means that organizations can reduce their vulnerability significantly and stay safe from malicious attacks. Thus, cyber security fundamentals are required!
In this blog, we will be looking at key fundamentals of cybersecurity so businesses can form strategies which defend them effectively from cyber threats.
What is Cyber Security?

In the digital age, cybersecurity refers to the practice of protecting computer systems, networks, and sensitive data from theft, damage, or unauthorized access. It’s an essential discipline for ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information in the face of evolving threats.
What is the importance of Cyber Security in the digital world?

Cybersecurity is crucial for protecting individuals, businesses, governments, and nations from a wide range of threats that can have financial, operational, and reputational consequences. As our reliance on digital technologies continues to grow, the importance of cybersecurity becomes even more significant. A few reasons indicating the need for cybersecurity in this digital era are as follows-
-
Protection of Sensitive Data
Cybersecurity helps safeguard sensitive information, such as personal and financial data, intellectual property, trade secrets, and government secrets. Breaches of this data can lead to financial loss, identity theft, and a range of other problems.
-
Privacy Preservation
It ensures the protection of individual privacy by preventing unauthorized access to personal information, communication, and online activities.
-
Business Continuity
Cybersecurity measures are essential for the uninterrupted operation of businesses and organizations. Cyberattacks, if successful, can disrupt operations, leading to financial losses and damage to reputation.
-
National Security
Cybersecurity is a critical component of national security. Governments rely on secure systems to protect critical infrastructure, military secrets, and other sensitive data. Cyberattacks on a nation’s infrastructure can have significant implications for its security.
-
Economic Impact
Cyberattacks can have a substantial economic impact on individuals, businesses, and entire nations. They can result in direct financial losses and damage a country’s economic stability.
-
Reputation Management
Data breaches and cyberattacks can harm an organization’s reputation. Customers, partners, and stakeholders lose trust in entities that fail to protect their information.
-
Legal and Regulatory Compliance
Many industries and regions have established laws and regulations related to data protection and cybersecurity. Non-compliance can lead to fines and legal consequences.
-
Intellectual Property Protection
For businesses, intellectual property is often their most valuable asset. Cybersecurity helps protect patents, trademarks, and copyrights from theft or unauthorized use.
-
Prevention of Cybercrime
Cybersecurity efforts help combat various forms of cybercrime, such as hacking, phishing, ransomware, and online fraud. This reduces the financial impact on individuals and organizations.
-
Data Integrity
Cybersecurity measures ensure the accuracy and reliability of data by protecting it from unauthorized tampering or alteration.
-
Safety and Public Health
In cases where cybersecurity is linked to critical infrastructure like power grids and healthcare systems, a breach could have life-threatening consequences. Ensuring the security of these systems is crucial for public safety.
-
International Relations
Cybersecurity also plays a role in international diplomacy and relations. Cyberattacks between nations can strain diplomatic ties and lead to retaliatory measures.
Understanding the Basic Cyber Security Fundamentals

The top basic cybersecurity fundamentals in this digital era are as follows-
Strong Passwords
Create complex and unique passwords for each online account or system. Consider using a password manager to keep track of them.
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
Enable MFA wherever possible to add an extra layer of security to your accounts.
Regular Updates and Patch Management
Keep your operating systems, software, and applications up to date to fix known vulnerabilities.
Firewalls
Implement firewalls, both at the network and device level, to control incoming and outgoing traffic.
Antivirus and Antimalware Software
Use reputable security software to protect against viruses, malware, and other threats.
Data Encryption
Encrypt sensitive data, both at rest and in transit, to prevent unauthorized access.
Regular Backups
Back up your data regularly to ensure you can recover it in case of a cyber incident.
Security Awareness Training
Educate yourself and your employees on cybersecurity best practices and the latest threats.
Email Security
Be cautious of phishing emails and suspicious attachments. Don’t click on links from unknown sources.
Access Control
Limit access to data and systems to only those who need it for their roles.
Network Segmentation
Divide your network into segments to prevent lateral movement by attackers.
Incident Response Plan
Develop a plan to respond to security incidents effectively and minimize damage.
Regular Security Audits and Scans
Conduct security audits and vulnerability assessments to identify and mitigate weaknesses.
Secure Web Browsing
Use secure and updated web browsers, avoid untrusted websites, and employ browser extensions for additional security.
Mobile Device Security
Secure mobile devices with PINs, biometrics, and remote wipe capabilities.
IoT Security
Secure Internet of Things (IoT) devices to prevent them from becoming entry points for attackers.
Secure Cloud Practices
Follow best practices for cloud security, including proper configuration, access control, and encryption.
Social Engineering Awareness
Be aware of social engineering tactics like pretexting, baiting, and tailgating.
Secure Development Practices
If you develop software, follow secure coding practices to minimize vulnerabilities.
Compliance with Regulations
Ensure compliance with industry-specific and regional cybersecurity regulations and standards.
What is the scope of cyber Security in digital advancements?
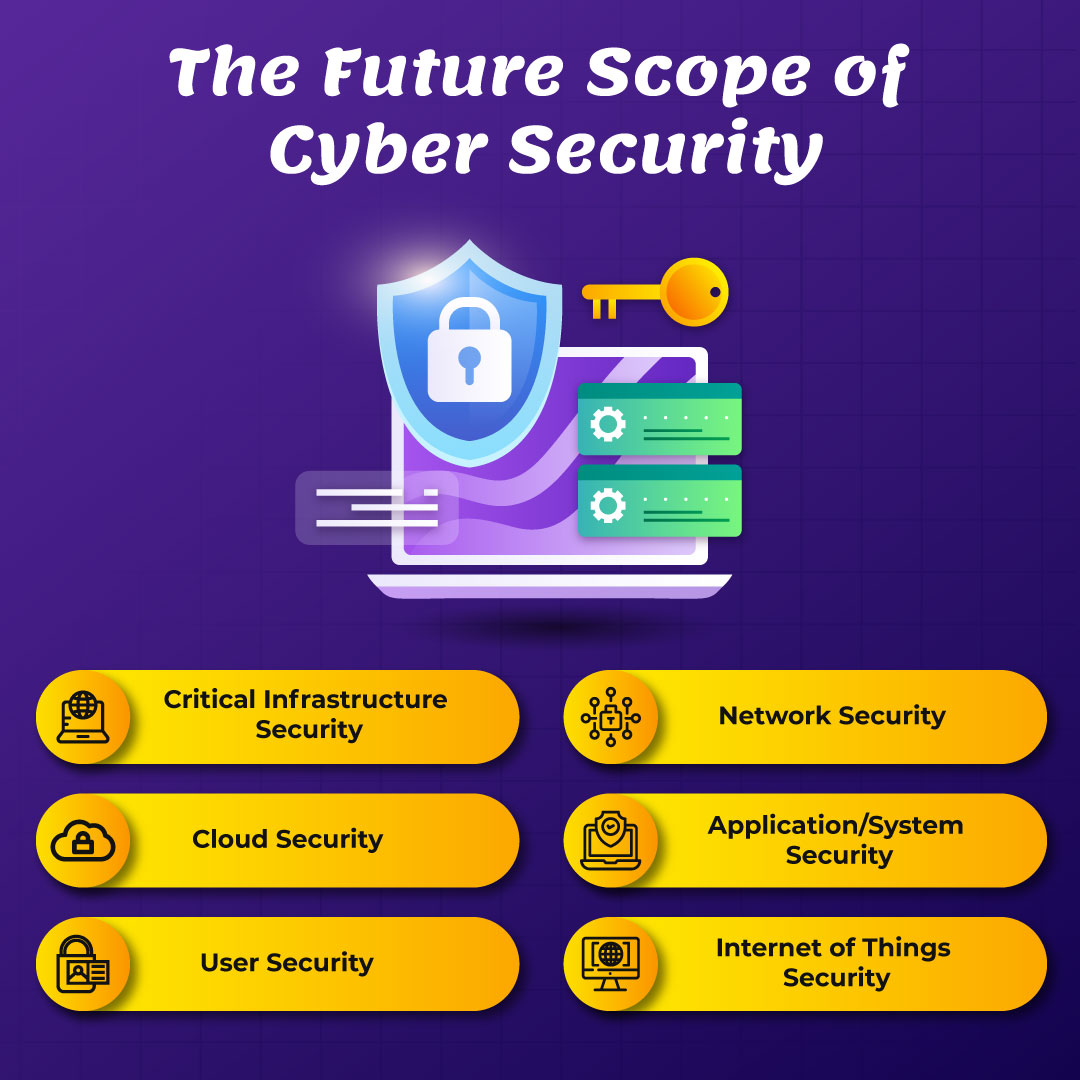
The scope of cybersecurity in digital advancements is expansive and critical. As technology continues to advance, the need for robust cybersecurity measures grows exponentially. With the increasing reliance on interconnected systems, cloud computing, IoT devices, and AI-driven applications, the attack surface for cyber threats expands. Cybersecurity professionals are in high demand to protect sensitive data, and infrastructure, and ensure the integrity of digital ecosystems.
As digital transformation accelerates across industries, cybersecurity experts will play a pivotal role in safeguarding against a multitude of threats, including ransomware, data breaches, and malicious hacking. This ever-evolving landscape offers vast opportunities for cybersecurity experts to innovate, adapt, and stay ahead of cyber adversaries, making it a dynamic and promising field for the foreseeable future.
What is the importance of data protection?

The importance of data protection in this digital era is as follows-
- Privacy: Data protection safeguards individuals’ personal information, ensuring their privacy and preventing unauthorized access, use, or disclosure.
- Legal Compliance: Many laws and regulations require organizations to protect sensitive data, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) in Europe and the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA) in the United States.
- Trust and Reputation: Effective data protection builds trust with customers and stakeholders. A data breach can severely damage an organization’s reputation and erode trust.
- Financial Consequences: Data breaches can lead to significant financial losses, including fines, legal expenses, and costs associated with mitigating the breach.
- Intellectual Property Protection: Data protection is essential for safeguarding proprietary information and intellectual property from theft or espionage.
- Business Continuity: Data protection measures ensure that critical data is available and intact, supporting business operations and preventing data loss due to disasters or cyberattacks.
- Competitive Advantage: Organizations that prioritize data protection may gain a competitive edge by demonstrating their commitment to security and privacy.
- Ethical Considerations: Respecting individuals’ rights to control their data aligns with ethical standards and promotes responsible data handling.
What are a few misconceptions regarding Cyber Security in IT?

A few common misconceptions regarding cybersecurity in IT are as follows-
“I’m not a target, so I don’t need cybersecurity.“
Demystification: Everyone is a potential target for cyberattacks. Attackers often target individuals or organizations with valuable information or vulnerabilities. Even if you don’t consider yourself a high-profile target, your personal or business data could still be valuable to cybercriminals. It’s essential to take precautions.
“Antivirus software is all I need to stay safe.“
Demystification: Antivirus software is essential, but it’s not a one-stop solution. It primarily detects known malware. To stay safe, you need a multi-layered security approach, including regular updates, strong passwords, user awareness, and more.
“My password is strong enough.“
Demystification: Strong passwords are crucial, but they are just one aspect of security. Using unique, long, and complex passwords is vital, but it’s also essential to enable multi-factor authentication (MFA) and change passwords periodically to enhance security.
“Public Wi-Fi is safe for sensitive tasks.“
Demystification: Public Wi-Fi networks are often insecure and can be a hotspot for cyberattacks. Avoid sensitive transactions or use a virtual private network (VPN) when connected to public Wi-Fi to encrypt your data.
“Cyberattacks only come from foreign hackers.“
Demystification: Cyberattacks can originate from anywhere, including within your own country. Hackers can hide their origins, making it difficult to attribute attacks solely to foreign hackers.
“My Mac is immune to malware.“
Demystification: While Macs are generally less targeted than Windows PCs, they are not immune to malware. Cybercriminals are increasingly developing Mac-specific malware. Everyone should use security software on their Macs.
“Cyber Security is solely IT’s responsibility.“
Demystification: Cybersecurity is a shared responsibility. IT plays a crucial role, but every user must follow best practices and be vigilant. Employees should be aware of security risks and report them promptly.
“Incognito mode makes me anonymous.“
Demystification: Incognito mode only prevents your browsing history from being saved on your local device. It does not make you anonymous online. Your internet service provider and websites can still track your activity.
“Emails from trusted sources are always safe.“
Demystification: Trusting the source of an email is not foolproof. Cybercriminals can impersonate trusted sources and send phishing emails. Always verify the sender and be cautious with email attachments and links.
“I can spot phishing emails easily.“
Demystification: Phishing attacks are increasingly sophisticated and challenging to spot. Even tech-savvy individuals can fall victim to well-crafted phishing emails. Stay cautious and double-check before clicking or providing personal information.
“Firewalls protect against all threats.“
Demystification: Firewalls provide network security, but they can’t stop all threats. They are just one layer of protection. To protect against a broader range of threats, you need a combination of security measures.
“Cyber Security is too expensive for small businesses.“
Demystification: Small businesses can implement cost-effective cybersecurity measures, like free or low-cost security software and employee training. The cost of not investing in cyber Security could be much higher due to potential data breaches.
“Regular software updates are unnecessary.“
Demystification: Regular updates are critical. They often include security patches to fix vulnerabilities that hackers can exploit. Failing to update software can leave you vulnerable to known threats.
“Strong encryption prevents all data breaches.“
Demystification: Strong encryption is essential for data security, but it won’t prevent all data breaches. Other factors, like weak passwords or social engineering, can still lead to breaches.
“I don’t need a backup; my data is safe.“
Demystification: Data loss can occur due to various reasons, including hardware failure, accidents, or cyberattacks. Regular backups are crucial to ensure data recovery in case of unexpected events.
“Cyber Security tools slow down my computer.“
Demystification: Some security tools may have minimal impact on system performance. Modern security solutions are designed to be efficient and unobtrusive. Slowness may be due to other factors, such as hardware limitations.
“Multi-factor authentication is inconvenient.“
Demystification: MFA adds an extra layer of security but doesn’t have to be inconvenient. Many MFA methods are user-friendly, like receiving a text message or using a mobile app for authentication. The added security is worth the minor inconvenience.
“I can delete my data, and it’s gone forever.“
Demystification: Deleting data from your device doesn’t necessarily mean it’s gone forever. Data can often be recovered unless securely wiped. Secure data destruction methods are necessary to ensure data is irrecoverable.
“Cyber Security incidents won’t happen to me.“
Demystification: Cyber Security incidents can happen to anyone. Being prepared and following best practices is essential to reduce the risk and mitigate the impact if an incident does occur.
“The more security tools, the better.“
Demystification: Using too many security tools can lead to complexity and conflicts. It’s best to have a well-integrated and balanced security strategy that addresses your specific needs without overburdening your systems.
What are the future trends of cyber security in IT?

The future trends of cybersecurity in IT are as follows-
AI and Machine Learning-Powered Security
AI and machine learning will be used to detect and respond to threats more efficiently by identifying patterns and anomalies in real-time data.
Zero Trust Architecture
The traditional perimeter-based security model is being replaced by a zero-trust approach, where trust is never assumed, and every user or device is continuously authenticated and authorized.
Cloud Security
With the increasing adoption of cloud services, securing cloud environments and data becomes a priority. Cloud security will evolve to address the unique challenges of this ecosystem.
IoT Security
As the Internet of Things (IoT) grows, there will be a greater focus on securing the vast number of IoT devices, many of which have limited security features.
Quantum Computing Threats and Solutions
The advent of quantum computers poses a threat to current encryption methods. Post-quantum cryptography and quantum-resistant algorithms will become essential.
5G Network Security
The rollout of 5G networks introduces new attack surfaces and potential vulnerabilities. Security measures will need to adapt to protect 5G infrastructure and connected devices.
Ransomware and Extortion Attacks
Ransomware attacks are evolving, and attackers are increasingly using extortion as a tactic. Organizations will need robust backup and recovery strategies.
Supply Chain Security
Securing the entire supply chain, including third-party vendors and partners, will be a top priority to prevent breaches that can originate from these sources.
Privacy Regulations
Privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA will continue to shape cybersecurity practices. Companies must ensure compliance and data protection.
User and Entity Behavior Analytics (UEBA)
UEBA tools will become more prevalent for monitoring user and entity activities and identifying suspicious behaviour.
Homomorphic Encryption
This emerging technology enables computation on encrypted data without decrypting it, offering enhanced privacy and security in data processing.
Biometric Authentication
Biometrics, such as facial recognition and fingerprint scanning, will become more common in user authentication, but also raise concerns about privacy and security.
Blockchain for Security
Blockchain technology is explored for applications in security, such as secure identity verification, supply chain tracking, and more.
Cyber Security Workforce Shortage
The shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals will continue to be a challenge, emphasizing the importance of automation and workforce development.
Cyber-Physical System Security
As operational technology (OT) and industrial control systems (ICS) become more connected, protecting critical infrastructure and cyber-physical systems will be paramount.
What are the challenges of cyber Security in the digital era?
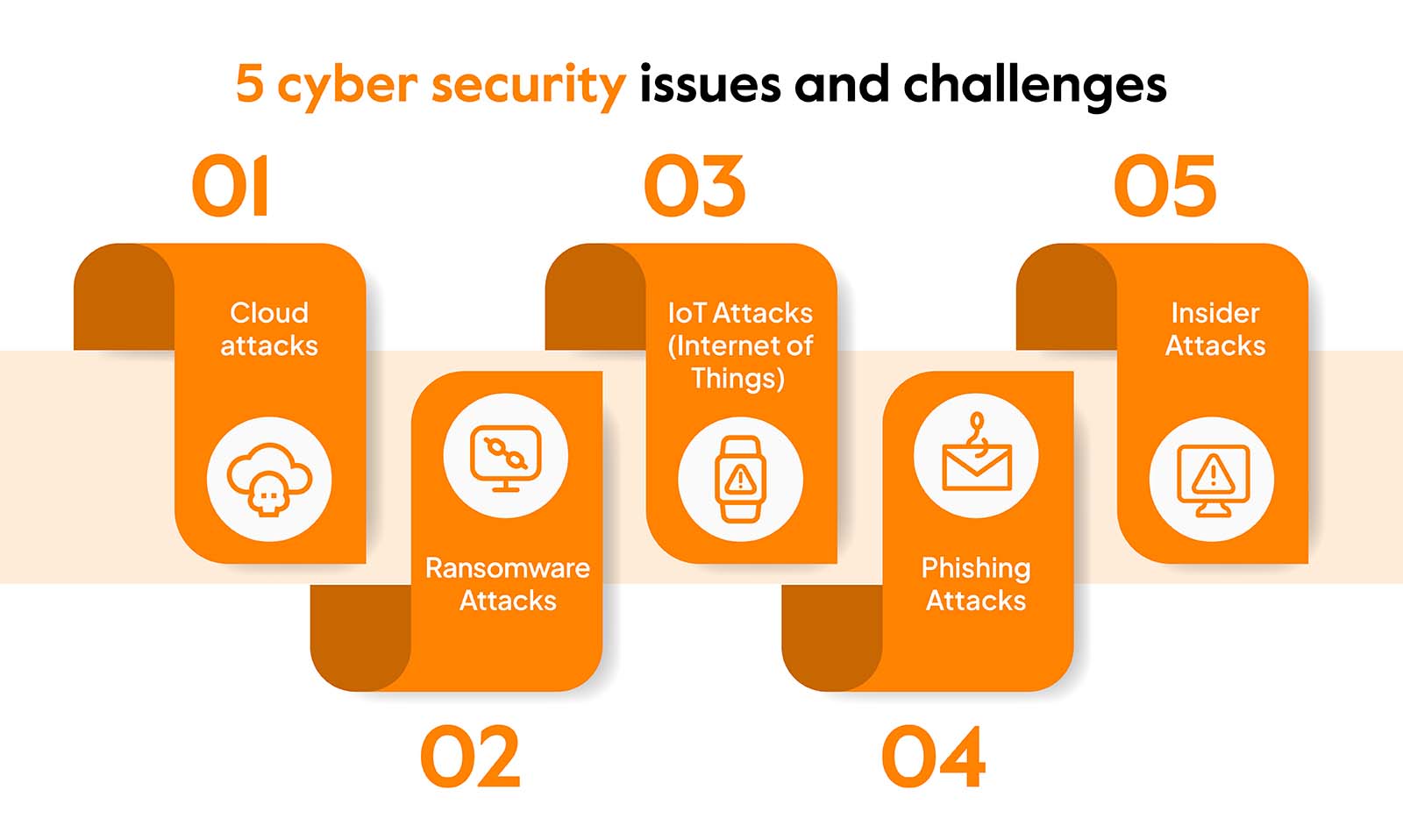
The challenges of cybersecurity in the digital era are as follows-
Sophisticated Cyber Threats
Cybercriminals are becoming more sophisticated, using advanced techniques and tools to breach systems and steal data.
Zero-Day Vulnerabilities
Discovering and patching vulnerabilities before they are exploited is challenging, as cybercriminals exploit “zero-day” vulnerabilities before they are known to the software or hardware provider.
Ransomware
Ransomware attacks continue to rise, causing significant financial and operational damage to organizations.
IoT Security
The proliferation of Internet of Things (IoT) devices introduces new attack vectors, as many of these devices lack robust security features.
Cloud Security
As more data and services move to the cloud, securing cloud environments and data becomes crucial.
Insider Threats
Malicious or negligent employees pose significant risks to organizations, making it challenging to protect against insider threats.
Regulatory Compliance
Compliance with data protection and privacy regulations, such as GDPR and CCPA, requires a significant commitment of resources and expertise.
Supply Chain Attacks
Attackers increasingly target the supply chain to compromise organizations, making it challenging to secure third-party vendors and partners.
AI and Machine Learning-Based Attacks
Hackers are using artificial intelligence and machine learning to create more effective and evasive attacks.
Lack of Cybersecurity Talent
There is a shortage of skilled cybersecurity professionals, making it difficult for organizations to find and retain the right talent.
Cybersecurity Awareness
People are often the weakest link in cybersecurity, and educating users and employees about best practices can be challenging.
Mobile Device Security
The increasing use of mobile devices for work and personal tasks expands the attack surface and requires robust security measures.
Big Data Security
Managing and securing vast amounts of data is complex, and ensuring its confidentiality, integrity, and availability is a challenge.
Identity and Access Management
Properly managing and securing user identities and their access to systems and data is essential but can be complicated.
Global Nature of Cyber Threats
Cyber threats are borderless, and international cooperation is often required to track down and prosecute cybercriminals.
What are the top cyber security skills you need to learn?

The top cybersecurity skills one needs to learn are as follows-
Network Security
Understanding how to secure networks and protect against various threats, including intrusion detection and prevention.
Vulnerability Assessment and Management
Identifying and addressing vulnerabilities in systems and applications.
Penetration Testing (Ethical Hacking)
Simulating cyberattacks to find and fix security weaknesses.
Incident Response and Management
Developing plans and procedures to respond to security incidents effectively.
Security Architecture and Design
Creating secure network and system architectures.
Cryptography
Knowledge of encryption and decryption techniques to protect data.
Security Information and Event Management (SIEM)
Understanding and using SIEM tools to monitor and manage security events.
Cloud Security
Expertise in securing cloud-based environments like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud.
Web Application Security
Identifying and mitigating security risks in web applications, including OWASP Top Ten vulnerabilities.
Mobile Device Security
Protecting mobile devices and mobile apps against threats.
Security Assessment and Auditing
Conducting security assessments and audits to ensure compliance and security.
Secure Coding
Writing code with security in mind to prevent vulnerabilities.
IoT Security
Understanding the unique security challenges posed by the Internet of Things.
Security Policies and Procedures
Developing and enforcing security policies in organizations.
Security Awareness and Training
Educating users and employees about cybersecurity best practices.
Threat Intelligence
Staying informed about current threats and vulnerabilities.
Data Privacy and Protection
Complying with data protection regulations and securing sensitive data.
Endpoint Security
Protecting individual devices, such as computers and smartphones, from threats.
Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Controlling and securing access to systems and data.
Secure DevOps
Integrating security into the DevOps process to ensure a more secure development and deployment pipeline.
What cyber security courses can help me acquire top cyber security skills?
The top available cyber security courses in IT are as follows-
CEH (v12)
CEH is a certification that teaches ethical hacking skills. It equips professionals with knowledge to identify and counteract vulnerabilities and threats, enabling them to think like hackers and protect systems and networks from cyberattacks.
The exam details for the CEH (v12) course are as follows-
Exam Name | Certified Ethical Hacker (312-50) |
Exam Cost | USD 550 |
Exam Format | Multiple Choice |
Total Questions | 125 Questions |
Passing Score | 60% to 85% |
Exam Duration | 4 Hours |
Languages | English |
Testing Center | Pearson Vue |
CISSP Training
CISSP is a globally recognized certification for information security professionals. It covers a wide range of security topics, including access control, cryptography, and risk management, and validates expertise in designing, implementing, and managing security programs.
The exam details for the CISSP training course are as follows-
Exam Name | ISC2 Certified Information Systems Security Professional |
Exam Code | CISSP |
Exam Cost | USD 749 |
Exam Duration | 4 hours |
Number of Questions | 125-175 |
Exam Format | Multiple choice and advanced innovative questions |
Passing Marks | 700/1000 points |
Exam Language | English |
Testing Center | (ISC)^2 authorized PPC, PVTC Select Pearson VUE tests |
CompTIA PenTest+
CompTIA PenTest+ certifies skills in penetration testing and vulnerability assessment. It focuses on hands-on techniques for identifying and addressing security vulnerabilities, making it suitable for professionals who want to specialize in offensive security.
The exam details for the CompTIA PenTest+ course are as follows-
Exam Code | PT0-002 |
Number of Questions | Maximum of 85 questions |
Exam Cost | USD 392 |
Type of Questions | Performance-based and multiple choice |
Length of Test | 165 minutes |
Passing Score | 750 (on a scale of 100-900) |
Languages | English, Japanese, Portuguese and Thai |
Testing Provider | Pearson VUE |
CompTIA Security+
CompTIA Security+ is an entry-level certification covering essential security concepts and practices. It validates knowledge of network security, cryptography, and threat detection, making it a good choice for beginners and those pursuing IT security careers.
The exam details for the CompTIA Security+ course are as follows-
Exam Code | SY0-601 |
Number of Questions | Maximum of 90 questions |
Type of Questions | MCQs and performance-based |
Length of Test | 90 minutes |
Passing Score | 750 |
Exam Cost | USD 392 |
Testing Provider | Pearson VUE |
Languages | English, Japanese, Vietnamese, Thai, Portuguese |
CompTIA CySA+
CompTIA CySA+ is a mid-level certification emphasizing threat detection and analysis. It equips professionals with skills to monitor, analyze, and respond to security incidents effectively, making it valuable for security analysts and related roles.
The exam details for the CompTIA CySA+ course are as follows-
Exam Name | CompTIA CySA+ |
Exam Code | CS0-003 |
Exam Cost | USD 392 |
Exam Format | MCQs and performance-based questions |
Total Questions | 85 questions |
Passing Score | 750/900 |
Exam Duration | 165 minutes |
Languages | English, Japanese, Portuguese, and Spanish |
Testing Center | Pearson VUE |
Where to enroll for the best cybersecurity certifications?
To learn the top cybersecurity skills in IT, you can choose Network Kings. Being one of the best ed-tech platforms, you will get to enjoy the following perks-
- Learn directly from expert engineers
- 24*7 lab access
- Pre-recorded sessions
- Live doubt-clearance sessions
- Completion certificate
- Flexible learning hours
- And much more.
What are the job opportunities for a cybersecurity-certified in IT?
The top available job opportunities for a cybersecurity-certified in IT are as follows-
- Cybersecurity Analyst
- Information Security Officer
- Security Consultant
- Penetration Tester (Ethical Hacker)
- Security Administrator
- Incident Responder
- Security Architect
- Security Engineer
- Network Security Engineer
- Vulnerability Assessor
- Security Auditor
- Security Manager/Director
- Cybersecurity Trainer/Instructor
- Cybersecurity Researcher
- Malware Analyst
- Security Software Developer
- Identity and Access Management Specialist
- Data Security Analyst
- Cloud Security Architect
- IoT Security Specialist
What are the salary aspects for a cybersecurity-certified professional?
The salary aspects for a cybersecurity-certified professional in different countries are as follows-
- United States: USD 90,000 to USD 180,000 per year
- United Kingdom: GBP 45,000 to GBP 120,000 per year
- Canada: CAD 80,000 to CAD 150,000 per year
- Australia: AUD 80,000 and AUD 150,000 per year
- Germany: EUR 60,000 to EUR 120,000 per year
- France: EUR 45,000 to EUR 100,000 per year
- Singapore: SGD 60,000 and SGD 150,000 per year
- India: INR 600,000 to INR 2,500,000per year
- China: CNY 150,000 to CNY 400,000 per year
- Japan: JPY 5,000,000 to JPY 12,000,000 per year
- Brazil: BRL 80,000 to BRL 200,000 per year
- South Africa: ZAR 300,000 to ZAR 800,000 per year
- UAE (Dubai): AED 180,000 and AED 400,000 per year
- Saudi Arabia: SAR 120,000 to SAR 300,000 per year
- Russia: RUB 1,000,000 to RUB 2,500,000 per year
Wrapping Up!
In conclusion, cyber security is paramount in the IT landscape, given the rising cyber threats. This blog offered a thorough insight into its significance, spanning data protection, privacy, business continuity, and national security. We addressed common misconceptions and examined emerging trends like AI, zero-trust architecture, and IoT security. We also highlighted top cybersecurity skills and relevant courses for lucrative job prospects. Staying informed, adaptable, and vigilant is crucial as the digital age advances. Investment in knowledge and skills is key to safeguarding against evolving cyber threats in our interconnected world.
Happy Learning!


