The difference between router and switch is what every network enthusiast must know. But how do a router and a switch work? Both the router and the switches enhance data communication.
Routing enables the whole network while switching connects a single network with individual computers. The role of routers and switches are similar, but router manages data communication on a larger scale.
This blog will focus on the difference between routing and switching in detail.
What is Routing?
Routing or Network Routing is the process of finding a path between one or more networks. Routing is available for any type of network, like telephones and public transportation. In packet-switching networking, the router chooses the path for IP packets to move to their destination. The routing decisions are in the hands of specialized network hardware called Routers.
What is the purpose of Routing?
The purpose of routing is to enclose data that helps to communicate beyond a network, to choose the paths that control traffic to final networks, to transform a URL name into an IP address, to supply safe Internet file transfer, and to advance traffic based on MAC addresses.
What are the main Routing protocols?
According to the network, a protocol is a method to format data in an easy language so that every computer can understand it. The role of a routing protocol is to identify or announce safe networking paths.
There are various protocols to find a way through data networks, and they are:
Internet Protocol or IP
The Internet Protocol identifies the origin and destination of each data packet. Routers inspect the IP headers of each packet and decide where to send them.
Broader Gateway Protocol or BGP
BGP checks which network will control which IP address. BGP comes under dynamic routing protocol. The sizeable networks that make this BGP announcement are called autonomous systems.
OSPF or Open Shortest Path First
OSPF selects the shortest path for sending network packets.
RIP or Routing Information Protocol
RIP searches for the shortest path using hop count to connect from one network to another. Hop count is the number of packets one must pass through on the way.
How does Routing work?
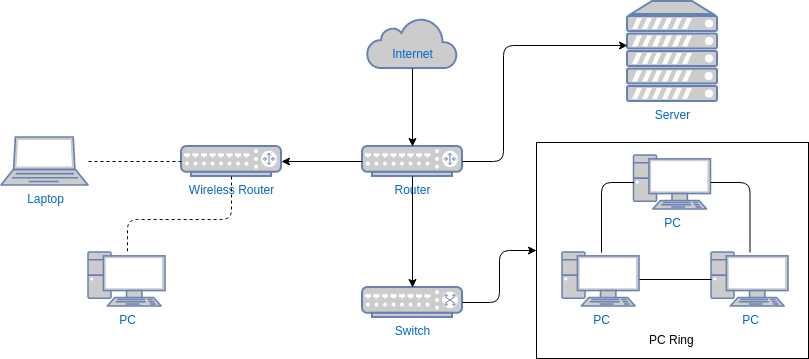
The router helps to connect internet-based devices like PCs, tablets, smartphones, thermostats, smart TVs, etc.. These devices can form a network where communication occurs through the same network. The router ensures fast and smooth network transfer. Different types of data use distinct bandwidths.
Here are the steps of working on a routing process:
- The router gets the packets and reads the headers of the packets.
- With the help of headers, it finds the destination of the packets.
- After searching the routing tables, it decides the destination of the packets.
- Numerous routers route a packet on their way to the final port of call.
- Two types of routers are there- dynamic and static.
- Static Router remains constant but the tables of the dynamic Router changes numerous routing protocols.
- For better enhancement, dynamic routers are more beneficial than static ones.
What are Switches?
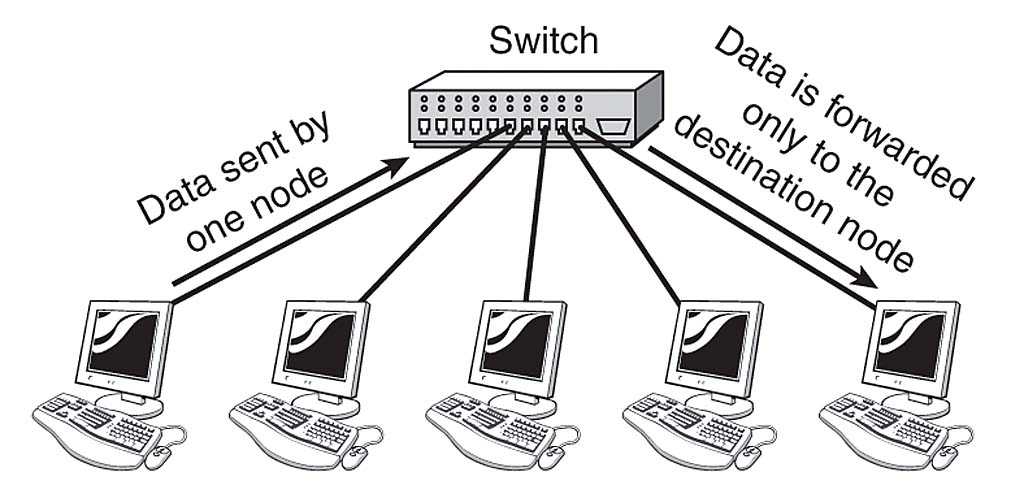
Switches allow networks to connect and exchange data packets to let them communicate. Switches can be in a hardware or software form. The operation of the switches occurs with the help of an OSI model. Switches check the Media access control or MAC address of each message and decide where to send the incoming message.
What is the purpose of Switches?
Switches maintain the transfer of information between distinct endpoints. This is the main purpose of the switches, but there are various other motives, too.
Here is a list of the aims of the network switches-
- Switches structure the network devices into modern data networks and transfer large traffic in the networks providing telecommunications.
- Network Switches offer binary communication, link network segments, enhance network performance, and use bandwidth effectively.
- Network switches offer wired connections to PCs, wireless APs, printers, industrial machinery, and IoT devices like card entry systems.
- Network switches work with power over Ethernet technology that supplies 100 watts of power to support network connectivity.
- Network switches can also collect data from IoT devices. Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning then utilize these data to improve smarter surroundings.
What are the types of switches?
There are almost seven types of networking switches. Here is a list of all seven:
Virtual Switches
They are the software-only switches embodied inside the VM hosting environment.
Routing Switches
Routing Switches link LAN. They perform MAC-based Layer 2 switching, functions at OSI Layer 3, and collect traffic based on the IP address in individual packets.
Managed Switches
It allows adjustment of each port on the switch that includes monitoring and configuration.
Unmanaged Switches
Unmanaged switches allow Ethernet devices to pass data using auto-negotiation that determines data rates. This is a dynamic configuration.
Smart Switches
Smart Switches ensure more control over data transmission. They are also called partially managed switches.
Stackable Switches
Stackable switches are dynamic switches. They are joined with each other via the backplane cable interface and structure into a single logical switch.
Modular Switches
Modular Switches are switch cards that are installed into sizable, and fixed-form factor chassis. Modular Switches ensure more flexibility and upgradeability.
How does a Network Switch work?
The major role of switches is to transform data to enhance data communication. But not every switch needs to use the same layout. Many layouts work with different arrays of hardware and software.
Here are the steps on how a network switch works:
- When a device gets attached to the network switch, it records its MAC or Media Access control address, which is present on the Network Interface Card [NIC] of the device.
- The NIC is connected to the Ethernet Cable, and the Cable is further connected to the switch.
- The network switch utilizes the MAC address to check which device outgoing packets are sent and decides the location of the incoming packets.
- The MAC address recognizes the physical device and keeps it constant, while layer 3 of the IP address can change.
- When the packet enters a switch, it examines the header to match it with the destination address.
- It sends these packets to their destination. Switches offer full-duplex functionality to avoid packet collision.
What is the difference between Router and Switch?
We have learned the role of routers and switches individually. Now, let us find the difference between routing and switching in detail-
- The router is a layer 3 device, and the switches are the layer 2 device on the OSI model.
- The router transfers data between 2+ computers, while the switches ensure resource sharing by connecting various devices on a single LAN.
- To determine the packet destination, the router surveys the IP address of the packet while the switches check the MAC address.
- Routers use data packets, and switches use data frames.
- To direct data across large networks, the routers use routing algorithms, but switches do not.
- Switches need wired connections to work, but routers can work with both wired and wireless connections.
- Routers give access to all ports to have their domain, but switches allow only one broadcast domain.
- Routers use full-duplex mode, and network switch uses both full and half-duplex modes.
- Routers can perform Network Address Translation or NAT and Port Address Translation or PAT, while Network switches perform neither NAT nor PAT.
- Routers do not need an internet connection, while network switches need internet connections.
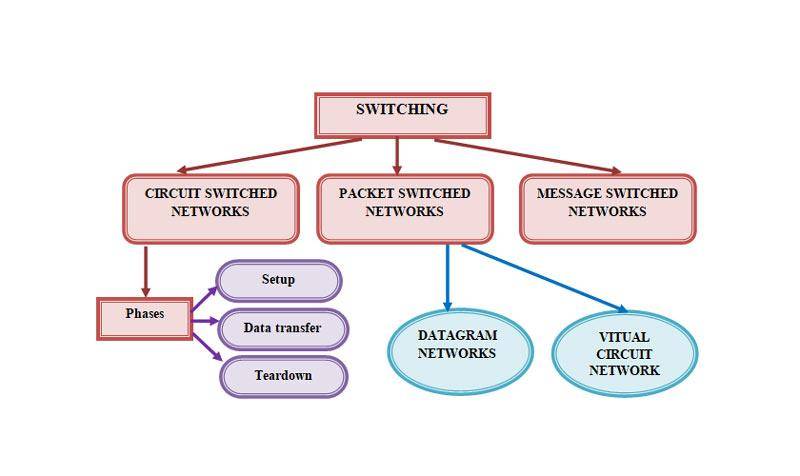
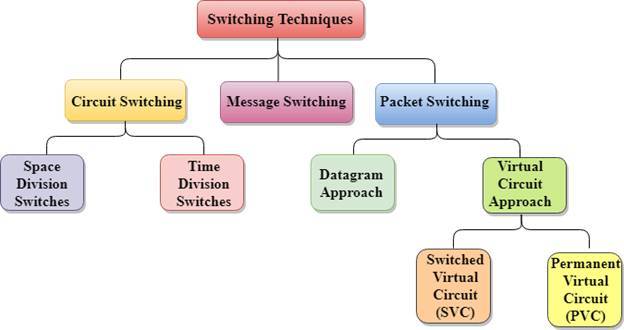
- There are two forms of routing- adaptive and non-adaptive while network switches are of three forms – circuit, packet, and message.
What are the similarities between Routing and Switching?
We have seen the difference between routing and switching, but they have a few similarities, too.
Here are the similarities between routing and switching:
- Routing and Switching come under computer networking. Both these processes are for connecting devices.
- Routing and Switching offer modern solutions network connectivity solutions.
- Routing and Switching are possible with home connections, like homes, small offices, etc.
- Routers and switches appear similar, and both are light in weight.
- The number of ports in routers and switches may vary, but both use ports.
How to get familiar with Routing and Switching Concept?
To get familiar with routing and switching concept, you must learn CCNA Routing and Switching. After learning CCNA Routing and Switching, you should clear the CCNA 200-301 exam to get certified. Let us get into more details about the CCNA routing and switching course. But before that, you should know the benefits of CCNA Routing and switching certification.
The IT industry is ever-growing and finding a job in IT with a networking degree is impossible. This is the first reason for pursuing the CCNA Routing and Switching certification course.
The student can learn deep IT knowledge, like fundamentals of networking, IP connectivity, such as components of the routing table, IPv4 and IPv6 static routing, different IP services (DHCP, DNS, SNMP, FTP, etc.), security fundamentals, and Automation and programmability.
A CCNA routing and switching certified student has a higher chance of getting a handsome salary than a student with an IT degree.
To pursue CCNA Routing and Switching courses from professionals, you must enroll with Network Kings. But why? Here are the reasons to pursue routing and switching courses with Network Kings-
- Network Kings offers CCNA Routing and switching courses from professionals.
- Network Kings has both recorded and live sessions to ease the learning process.
- Network Kings gives you the best career guidance along with the courses.
- The learner gets a completion certificate that adds value to the resume.
- With recorded lectures, the learners can enjoy flexible hours of learning time.
What skills will you learn in CCNA Routing and Switching course?
Following are the skills you will learn with the CCNA Routing and Switching course:
- LAN/WAN
- TCP/IP model
- Switches and routers
- Network utilities (ping, tracert, arp)
- IP addressing and subnetting
- VLANs and trunking
- Routing protocols such as OSPF
- WLAN
- NAT and ACLs
- Automation and programmability
What are the Job roles in the CCNA Routing and Switching?
- Technical Support Engineers
- Systems Engineers (Fresher)
- Systems Engineer
- Network Administrator
- Information Technology (IT) Manager
- Senior Network Engineer
- Network Security Specialist
What are the salary aspects of CCNA Routing and Switching job opportunities?
The salary aspects in CCNA Routing and Switching job profiles are:
- Technical Support Engineers- INR 3,00,000
- Systems Engineers (Fresher)- INR 2,50,000
- Systems Engineer- INR 4,40,000
- Network Administrator- INR 4,50,000
- Information Technology (IT) Manager- INR 9,00,000
- Senior Network Engineer- INR 7,00,000
- Network Security Specialist-INR 10,00,000
Conclusion
There are various advantages of routers and switches. Data communication is possible with routers and switches. An IT field is workable with safe and constant data communication. To enable such communication, one must possess the knowledge of routing and switching. Both routers and switchers enhance data communication but the pathways of both of these are different.
In short, there are differences between routers and switches. IT enthusiasts must know the difference between routers and switches. Both these routers and switches are beneficial in their own way. One must know how and when to use them.
I hope this blog has helped you know the difference between router and switch.
Thanks for reading!