What is SNMP?- We understood the concept of network management and its importance. Network management plays an important role in making a network work efficiently by preventing faults. But how do network managers manage a network?
It gets managed using a protocol called Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
What is Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)?
SNMP is a set of rules for managing network devices. It is an Application Layer Protocol used to monitor and manage network devices on Wide Area Network (WAN) or Local Area Network (LAN). SNMP works on a client-server model.
What is SNMP agent and SNMP manager?
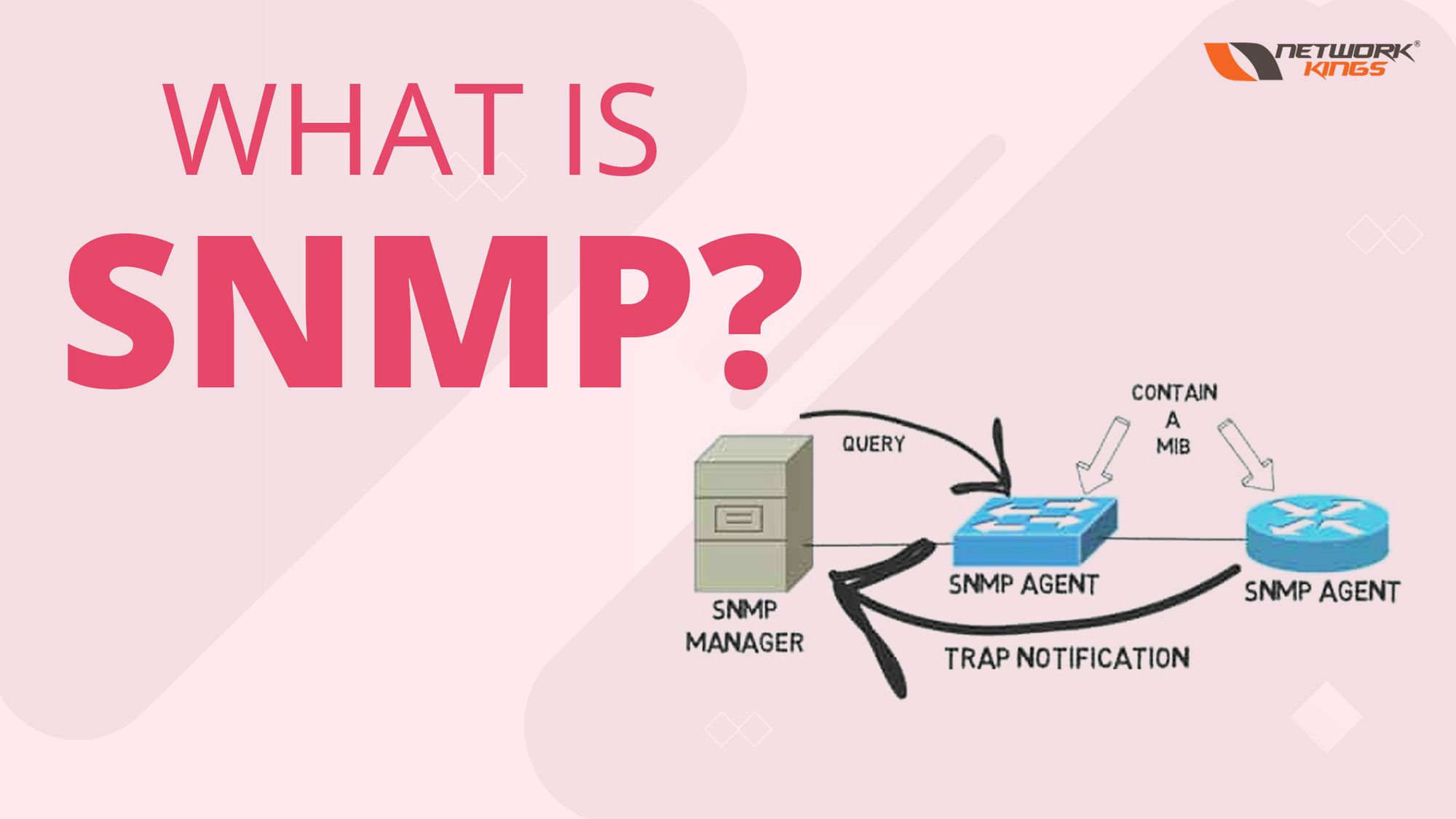
The management station which runs the SNMP client program is called the SNMP manager. The station managed by the manager is known as an agent.
The agent includes network devices like routers, printers, switches servers, etc. Management is done by the interaction between agent and manager, i.e. server and client.
The agent keeps performance data in its database while the manager can access and use it to make decisions about network usage congestions and faults.
For example – Router keeps a database of packets received and forwarded. The manager can fetch this data and decide if the router is congested by comparing it with the peak time data. If the router is congested or needs to reboot, the manager can send a packet including data to make the router reboot itself. Also, the agent contributes to the management process by sending a warning message called a trap, to the manager if it observes something unusual in its environment.
What are the components of SNMP?
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) has two components: –
- Structure of Management Information (SMI)
- Management Information Base (MIB)
What is the Structure of Management Information (SMI)?
Since we have a lot of network devices in the network, we need some rules regarding the naming of these devices. SMI is a collection of rules to name the object and list their types. The type of data stored in an object is defined using SMI. Along with that, it shows how to encode the data before transmitting it to the network.
What is the Management Information Base (MIB)?
MIB is an information database, a collection of all the objects that a manager can manage. Each agent has its database and Management Information Base.
It has eight groups, namely-
- sys:- This object defines general information about the device, such as the name, location, and lifetime.
- if:- This object is called interface and defines information about all the interfaces of the node, including interface number, physical address, and IP address.
- at:- This object is called address translation which defines the information about the ARP table.
- ip:- This object defines information related to the routing table and the IP address.
- Icmp:- This object defines information related to ICMP.
- TCP:- This object defines information related to TCP, such as the connection table, time-out value, number of ports, and number of packets sent and received.
- UDP:- This object defines information related to UDP, such as the number of ports and several packets sent and received.
- SNMP:- This object defines information related to SNMP itself.
What are the types of SNMP messages and commands?
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) has the following commands-
- SNMP GET REQUEST:- GET REQUEST is the message sent by the SNMP manager to the SNMP agent to retrieve the value of a managed object. The manager includes an Object Identifier of the desired object that helps agents to understand what information the agent is requesting. The agent then responds with the corresponding value of the object.
- SNMP GET NEXT REQUEST:- It is similar to the GET NEXT request but is used to retrieve the next managed object in the MIB. The manager specifies the OID and the agent replies with the closest next object to the OID that the manager has requested.
- SNMP GET RESPONSE:- It is the message sent by the agent to the manager in response to the GET NEXT REQUEST and GET REQUEST messages. It includes the requested value of the object requested by the manager.
- SNMP SET REQUEST:- It is the message sent by the SNMP manager to change the value of a particular object of the agent. The manager includes the OID and the new value of a particular object ID, and the agent applies the changes accordingly.
- SNMP TRAP:- SNMP TRAP is the message sent by the agent to the manager to make the manager aware of the unusual behaviour. It is the type of warning message to the manager. This message gets used for real-time monitoring and alerting purposes.
- SNMP INFORM REQUEST:- It is just like a trap message but includes an acknowledgement mechanism. It gets introduced in SNMP (v2). SNMP INFORM REQUEST is used to identify if the TRAP message is delivered to the manager. The agent is configured to send a TRAP message until it receives the INFORM REQUEST message. It adds the extra feature of acknowledgement to the TRAP message since TRAP messages are of high urgency.
What are the types of SNMP?
SNMP is of three types, namely-
- SNMP (v1):- It is the initial version of SNMP introduced in 1988. It provides the basic functionality of network management and monitoring. It uses community strings for authentication which are of 2 types: Read Only and Read-Write. It uses UDP.
- SNMP (v2): – It was introduced to fulfil some limitations of SNMPv1. It has some additional features like support for 64-bit counters and improved error handling. It can also use TCP along with UDP.
- SNMP (v3): – SNMPv3 includes strong security features like data encryption, data integrity check, and MD5 authentication. Inform message is introduced in SNMPv3 which allows reliable delivery of the message with acknowledgement.
Conclusion
SNMP is a very crucial protocol to make our network efficient and error-free. In the case of Network Management, this protocol is helpful. SNMP empowers network managers with real-time monitoring and efficient troubleshooting of network errors.