Monitoring, testing, and troubleshooting network devices to meet the requirement of an organization is known as Network Management.
With 100s and 1000s of devices in a network, it is hard to manage all of them, but SNMP is a protocol that can make our life easier.
What are the kinds of Network Management?
- Network Management can broadly get divided into five parts, namely-
- Configuration Management
- Fault Management
- Performance Management
- Security Management
- Accounting Management
What is Configuration Management?
Suppose a network has 100s of network devices with initial configurations connected physically or logically. The initial arrangements may change with time according to the change in requirements of the organization. There may be software updates, computer replacement to new devices, changes required in a PC to a new group or department, etc.
The configuration management system must be aware of all the changes and know the latest status of each device.
What are the kinds of configuration management?
Configuration Management is of two types-
- Reconfiguration:- Even the reconfiguration is of three types, namely-
- Hardware reconfiguration: Hardware reconfiguration covers all changes in the hardware. For example – System replacement, changes required in the router and network interface devices are part of hardware configuration. All such changes demand a trained person to manage and control them since they can not get automated.
- Software reconfiguration: Software changes like installing new software on a server or client, software updates, and operating system update fall under software reconfiguration.
- User-account reconfiguration: User-account reconfiguration includes adding new users or deleting old ones. The privileged users have only read permission, while others have both read and write permission.
- Documentation:- Documentation of the initial network configuration and each change must get recorded. Hardware documentation involves two sets of documents- Maps and Specifications. Maps include the position of each hardware and its connectivity to other devices. Specification includes hardware type, serial number, vendor warranty, etc.
Software documentation includes information, such as software and its types, versions, installation date, and license agreement.
What is Fault Management?
The network today comprises various network devices, and a fault in any of these devices can disturb the communication of the whole network. Hence handling and preventing such flaws is mandatory for the reliable working of communication systems.
What are the kinds of fault management?
Fault management is of two types-
1. Reactive Fault Management:- Detecting, isolating, correcting, and recording faults is knowns as reactive fault management. The first step is to detect the exact location or the device causing the defect. Once a fault is detected, the next step is to isolate the fault. If isolated on time, it may affect a few users. The next step includes its rectification which may require repairing or even replacing the devices.
Once the fault repairs, it should get documented with the correct location, the reason, and the steps and time taken to make the corrections.
2. Proactive Fault Management:- Proactive fault management prevents faults from occurring. It is the type of network monitoring that prevents defects before they occur. It is impossible to predict every defect. For example, If we see a flaw at the same location often, we can monitor it and reconfigure it to prevent further faults.
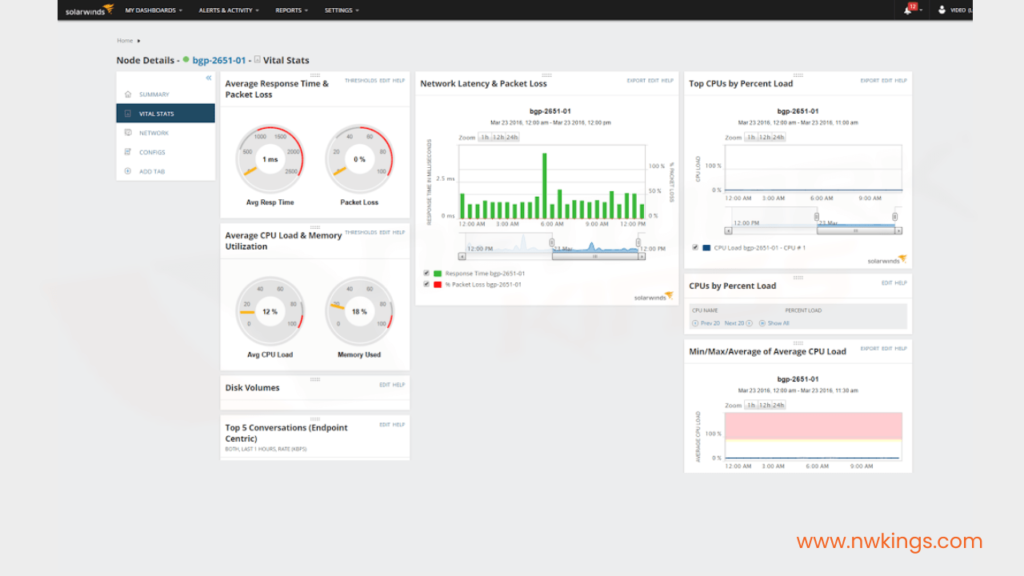
What is Performance Management?
In performance management, careful network monitoring ensures that it is running efficiently using some parameters to detect network efficiency, and those parameters are as follows-
- Capacity:- Capacity of each network is limited and is a crucial parameter which must get monitored. The performance management system ensures that a network does not get used above its capacity, or it can reduce the efficiency of a network. For example- LAN got designed for managing 100 devices with 20 Mbps. It will not operate efficiently if 200 devices get connected to it.
- Throughput:- Throughput of individual devices can get monitored. It is measured to ensure that it does not reduce to an unacceptable level.
- Traffic:- Traffic is of two types- internal and external. Internal traffic gets measured by packets travelling inside a network, while external traffic gets measured by packet exchanges outside the network. Blocking may occur when there is excessive traffic.
- Response Time:- The time receiver takes to respond to a request from the sender is called response time. Performance management measures response time and carefully examines it. Network capacity and traffic affect the response time. If response time increases, the network might operate at excessive capacity. Performance management monitors the average response time and peak hour response time. If there is a fluctuation in the response time, network congestion takes place.
What is Security Management?
As network devices of enterprises often work online, the risk of attack increases. Network Security Management is crucial to reduce the chances of attack. An enterprise network generates a steady stream of logs which the security management team analyzes to identify any possible threat fingerprints. It also leads to preventing unauthorized access.
What is Accounting and Utilization Management?
Utilization of data in an enterprise is also mandatory. If a user or department is consuming an excessive amount of bandwidth, it will add to the cost of an enterprise. The network bandwidth utilization gets monitored by the network accounting management team helping network managers to do short-term and long-term planning based on the demand for network use.
What are the benefits of network management?
Network Management has the following benefits:
- Reduces the risk of attacks
- Reduces cost
- Increases productivity and efficiency of a network
- Unplanned downtime can get predicted.
- Each change in the network hardware and software gets recorded, helping the network manager to stay updated and making it easier to make the changes if required.