Have you come across SaaS in cloud computing? It is a way of providing software over the Internet, allowing businesses to access a variety of services via one network. With this type of system, companies can share resources such as applications and data without having to worry about installation or hardware.
Benefits include cost savings and increased flexibility for users; plus improved mobility, scalability and additional security and privacy with stored data – all reasons why more organisations both large and small are opting for SaaS solutions when it comes to accessing their files quickly.
In this blog post, we will delve into some further related topics associated with Cloud Saas: Security and Privacy; Data Storage and Sharing; and lastly Cloud Computing itself – what do these mean?
Overview of Cloud SaaS in cloud computing

Regarding cloud computing, Software as a Service (SaaS) is one of the most prevalent solutions. It involves providing software applications over the Internet and customers pay for this service on a subscription basis; they basically “rent” access to an application rather than buying it altogether. In some cases, SaaS can be referred to as either cloud-based or web-based software.
Generally speaking, when compared with traditional on-premises software programs and applications, SaaS tends to be more cost-effective since there isn’t any need for costs related to installation and maintenance – all of this being managed by the provider. A question arises here then: how does that work out in terms of meeting customer requirements?
It is a piece of cake for customers to access their software from any device, as long as they have an internet connection. And if that wasn’t already convenient enough, many SaaS platforms also offer mobile apps so users can stay up-to-date with the data on their phones or tablets whilst out and about. What’s more, another huge advantage comes in the form of providers doing all updates and maintenance automatically – meaning no need for hitting download buttons when newer versions come around!
This lessens IT duties significantly and spares organizations cash as far as time spent overseeing and observing their frameworks. What’s more, it guarantees that everybody approaches the most current form of the product, which urges joint effort while additionally ensuring everyone is taking a shot at state-of-the-art data consistently.
Lastly, given its adaptability and versatility, SaaS arrangements can without much of a stretch be adjusted for various kinds of businesses – regardless of whether you are running an independent venture or setting up a monster organization. In case your organization needs additional capacity space or client accounts, you can rapidly amplify your bundle without putting resources into new equipment or foundation improvement; making SaaS optimal for entrepreneurs who need quicker go-to-advertise systems just as operational nimbleness alongside diminished underlying speculations in innovation costs.
Understanding the role of SaaS in cloud computing
Cloud computing has been a popular subject within the tech industry for some time now and with good cause. As software-as-a-service (SaaS) takes up an expanding job in the world of cloud computing, it is important to comprehend how it all fits together. In this blog post, we will look at SaaS’s role in cloud computing as well as its implications and benefits.
Essentially, SaaS is simply a technique of delivering applications across cyberspace rather than having them installed on personal computers or gadgets. Can you imagine what life would be like if technology had always worked this way? It would have certainly made things more convenient!
With Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), users can access the same data and software from any gadget connected to the internet. This eliminates the need for pricey onsite hardware and software, making updates simpler since they are managed remotely by a provider instead of each computer or device. What does this mean? It means more efficient use of resources, cost savings, scalability and faster delivery time – all great news for businesses wanting to streamline their operations!
Although SaaS alone has its advantages, when combined with other cloud technologies such as Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) or Platforms as a Service (PaaS), it becomes even more powerful. IaaS provides fundamental storage and networking services, whereas PaaS gives developers access to all sorts of tools like databases, development environments, application servers etc., without the need to install any physical hardware nor need to manage them manually in any way.
With these services aided by SaaS companies can swiftly establish applications without having their very own IT foundation set up first. What’s great is that this entire process happens entirely online- no fussing around for setting up the infrastructure!
Aside from cost savings and quicker development times, there are further benefits to SaaS. It enables businesses to rapidly scale without needing to invest heavily in new hardware or increasing IT staff numbers; as well as facilitates easier remote collaboration than traditional methods – giving access not only for their employees but external partners too so that people located in different places can collaborate on projects more easily regardless of tech systems or language barriers. Furthermore, it reduces reliance on physical hardware which means less energy is used overall – helping organisations take steps towards becoming greener businesses.
To sum up then: SaaS is an increasingly important part of cloud computing today with advantages including lower costs; speedier product cycles; scalability made simpler; increased potential for collaborations between various parties even across geographical borders and enhanced ecological sustainability. All these qualities make this technology such a sought-after proposition that looks set to be around long term!
Benefits of using Cloud SaaS in businesses
Software as a Service (SaaS) has been causing quite a stir in cloud computing for the last ten years or so. Businesses have found it incredibly useful, not just because of its ability to scale but also its cost-efficiency. With SaaS, businesses can pick from an array of software selections that are suitable for any application they may need. Furthermore, since this is cloud-based software companies don’t even require their computer systems – all you need is internet access and you are good to go! Who would have thought accessing data could be so comfortable?
The convenience of SaaS for businesses that are constantly on the move is outstanding. With this type of software, they don’t have to worry about being disconnected at any time. What’s more, it offers a great degree of scalability – something which can prove hugely beneficial in business as companies can easily scale up or down according to their requirements without incurring hefty upfront costs associated with gaining access to certain sorts of software licenses or making contractual commitments. This kind of flexibility means you’ll never find yourself overloaded (or underloaded) when having the right amount and type of support matters most!
Additionally, most cloud-based services come with the option of simple pay-as-you-go pricing models which make budgeting for them a lot easier than more traditional licensing models. This is great news for businesses as it allows better control over their finances and less uncertainty when forecasting budgets in the long term. What’s even better is that SaaS also offers an unparalleled level of flexibility when it comes to customising applications for specific roles within organisations. As such, companies can modify what they use according to their own employees’ requirements; this means no longer having to settle on generic solutions or waste time searching through options that won’t suit your business perfectly!
Take cloud SaaS, for instance. It can be tailored so that employees always have access to the right tools depending on their job function – marketing teams may require specific analytics tools while customer service staff need different types of customer feedback systems. And there are even more advantages; with its distributed nature, disaster recovery capabilities become a much simpler task since data gets stored across multiple servers all over the world.
This way no single point is vulnerable should any server fail or suffer outages and unplanned scenarios – many of these popular providers also include inbuilt redundancy features like automated backups which massively contribute to reliability and uptime availability when organisations depend heavily on digital resources for operations.
Overall, it is easy to see why businesses favour using SaaS: flexibility, scalability and most importantly…reliability! All three are fundamental elements today if you want efficient operations running smoothly day in and day out.
Exploring the key features of SaaS solutions

Examining the core attributes of SaaS systems has taken on a greater gravity in the present time of cloud computing and tech. Essentially, SaaS is an approach to software delivery and alludes to programs that are held up by the vendor’s frameworks – accessed through a web-driven interface for clients. In contrast with other kinds of cloud computing services like Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) or Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), this platform consolidates every component expected to support programming, including servers, capacity databases, networking and software. What’s more, do you need?
Bundling different services into a single package can be an efficient way for vendors to provide businesses with the IT tools they need. This not only offers organisations cost savings on buying and managing their hardware infrastructure but also provides users access to the latest software version – something that is automatically updated by the service provider. So you won’t ever have to worry about using out-of-date products!
What’s not to love about Software as a Service? Rather than buying licenses upfront, most vendors offer pay-as-you-go subscription packages which helps organisations better manage their cash flow. Plus with SaaS platforms, you can access applications from any location – great for when staff members need to work remotely! Setting up solutions is usually way quicker and easier since it requires far fewer technical configurations compared with typical onsite apps.
This in turn means employee training requirements are much lower too, no need for understanding hardware stuff here! So overall these advantages make the package an attractive option that could remarkably cut costs whilst helping businesses maximize efficiency and productivity across operations – now there’s something worth getting excited about.
Deep dive into Cloud Storage and its importance
Cloud Storage is getting more and more accepted as the need for cloud computing grows. This involves saving data on distant web servers linked to the internet, rather than storing it locally in physical hardware, allowing quick access from anywhere across the globe while at once preserving space in local physical devices. Various types of cloud storage are obtainable by companies – they range from public clouds to private ones or even hybrid solutions. What’s most befitting?
Delving deeper into cloud storage, it becomes clear to see its benefits and drawbacks. Perhaps the most notable advantage of this form of data storage is how accessible it can be. With digital solutions like Google Drive or iCloud, users can easily access their files from any device with an internet connection – whether that’s a smartphone, tablet or laptop! This makes sharing essential documents between customers or employees who are located remotely much simpler; turning around timeframes quickly and increasing efficiency across businesses as a whole.
Cloud storage gets rid of the need to buy pricey hardware, seeing as all data is virtually stored instead of taking up physical space – ideal for start-ups and small businesses who want to save money without compromising on high performance or security. No more having to find room in your office for cumbersome equipment; cloud storage can help you streamline operations while ensuring that sensitive information remains safe and secure.
Plus there is no hefty upfront cost associated with buying new technology, making it perfect for companies looking into cutting costs but still wanting top-notch service. Questions like ‘Will I have enough space?’ won’t even be an issue any longer!
Cloud storage is associated with several major benefits, the most prominent being improved scalability. When using platforms such as Amazon Web Services (AWS), businesses only shell out for what they use – their expenditure reflects precisely how much they have taken advantage of the service instead of paying an unchanging fee irrespective of usage levels all through time.
This makes it cost-effective and guarantees organisations do not get stuck with more storage than needed by investing in costly hardware or software that could be outdated speedily. The suppleness connected with these solutions also means companies can upgrade or downgrade their packages according to seasonal changes in demand – so if further capacity is required during peak periods but scarce at quieter times then this does not necessarily result in additional expense year-round for firms.
Generally speaking, one might easily observe plenty of advantages cloud storage provides which make it an appealing choice for entities around the globe who are aiming to streamline their workings while keeping bills low simultaneously – making it an invaluable tool within the continuously mutating domain of SaaS plus Cloud Computing. So why deprive yourself of reaping its rewards?
Unravelling the concept of Data Sharing in SaaS

Cloud computing, particularly Software as a Service (SaaS), has changed the way businesses work. It’s no surprise that it is becoming so popular and commonplace in various industries across the world. One of the main components of SaaS is data sharing – to comprehend this data sharing on SaaS we must look at what exactly it involves and how it can be used.
Essentially, with data sharing several users can access information from one source. Ask yourself if your business could benefit from such technology. Could you use multiple-user accessibility for shared resources?
This means that organisations can share crucial documents with other businesses without needing to use any extra software or hardware, which makes it simpler and better for their budget. With SaaS, you don’t need to worry about hosting your network infrastructure – everything is done through the cloud instead. This enables faster access times when speed matters most so companies can give speedy responses whenever customers want something from them. How great would it be if all business processes were this seamless?
Furthermore, data sharing not only provides more efficient solutions than traditional methods; it also ensures that confidential documents are safely shared between various members in an encrypted way. This is something which can’t be accomplished through old-fashioned document-sharing ways such as FTP or email attachments.
The encryption system makes sure that the authorised personnel are the only ones who can view and edit a particular file – hence reducing any possibility of leakage of private information or tampering with vital records. Would you feel safe if all your sensitive documents were securely stored?
Data sharing enables companies to collaborate on projects without needing to be gathered in one place, which is a massive advantage considering COVID-19 travel restrictions. With SaaS, teams can effortlessly communicate no matter their location through messaging channels such as Slack or Microsoft Teams and guarantee everyone has secure access to all documents via file-sharing services like Google Drive or Dropbox.
Ultimately, data sharing within SaaS platforms offers several advantages for businesses and makes working between various levels of staff extremely practical. For instance, sales teams may easily send marketing material and pricing lists straight from their CRM system – sparing them time searching elsewhere – whereas remote workers can swiftly get project briefs with no additional help from any IT personnel needed! The convenience provided by data-sharing together with its effectiveness renders it an exceptional tool for organisations wishing quick access to files anytime and anywhere!
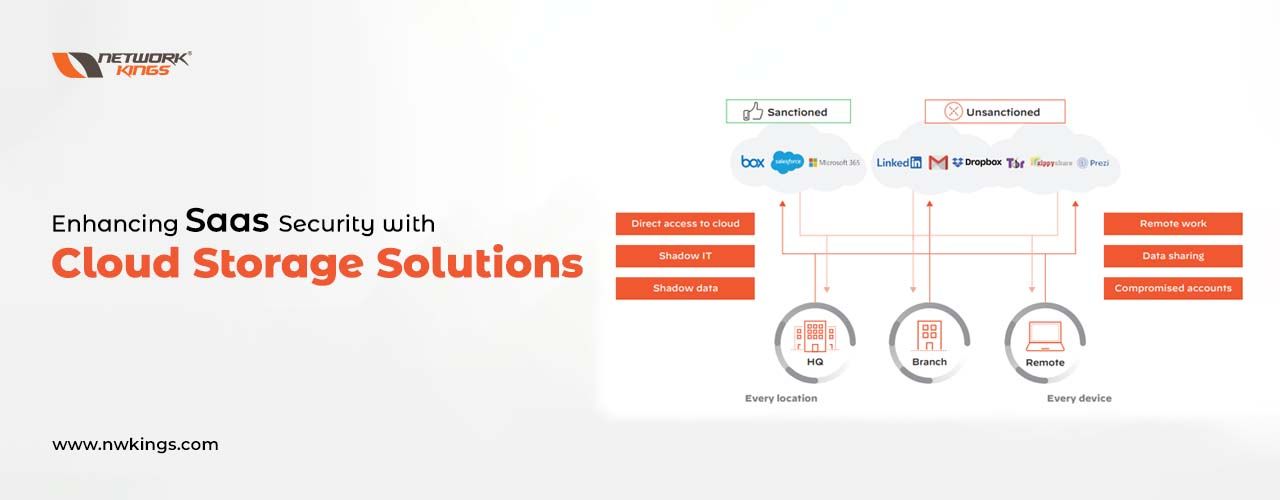
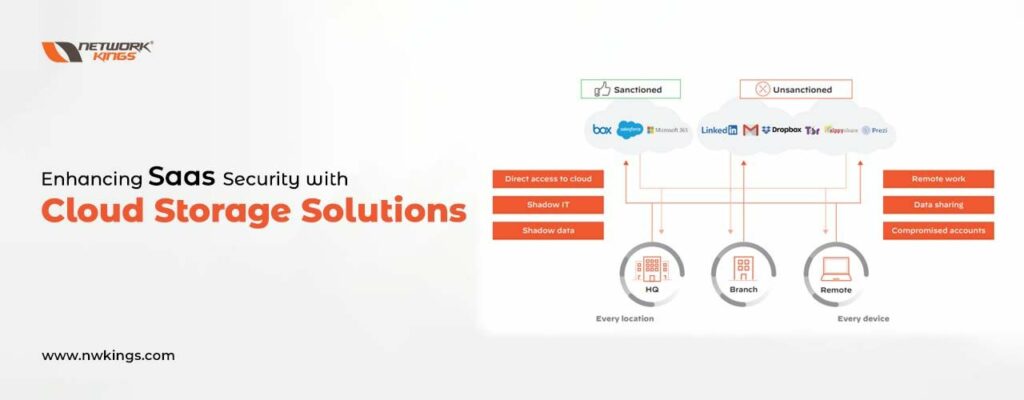
Analysing the criticality of SaaS Security in cloud computing

When discussing cloud computing, a key element of it is SaaS (Software as a Service). To put it simply, this form of technology involves the provision and use of software hosted on remote servers that can be accessed through the Internet. As with any type of techy stuff though, there are both benefits and drawbacks associated with SaaS. One huge plus point to note here is that users don’t need to install anything onto their own devices because all necessary functions have already been pre-installed on the server – how convenient!
When it comes to SaaS, one area where its value shines through is security. It is highly vulnerable to malicious actors who could access the sensitive data stored in databases, and that has serious consequences for both businesses and individuals alike. If someone can gain unauthorized access to confidential financial records or customer information then there are legal issues that could arise – fines may be handed out or even jail sentences depending on the severity of the breach. Not only would such a violation cause unwanted stress for everyone involved but also potentially put their livelihoods at risk too!
Analysing the criticality of SaaS security is an essential part of any cloud computing strategy. Malicious actors can try to gain access to confidential data stored on remotely hosted servers using different methods, such as SQL injection attacks and account hijacking. To counteract these risks organizations should establish secure authentication protocols that use two-factor verification at user logins, also making sure all transmitted data is encrypted with robust encryption algorithms before going online.
Additionally, companies must install monitoring systems which detect suspicious activities like sudden rises in login attempts from unknown IP addresses or strange network traffic coming from areas known for malicious cyber activity – taking extra measures like this will drastically reduce their chances of becoming targets while still providing access to important SaaS applications without risking too much security along the way.
Real-world applications and examples of Cloud SaaS
Cloud SaaS is one of the most sought-after applications when it comes to cloud computing. It is a software-as-a-service model, which lets users access different kinds of software over the internet. One huge advantage that Cloud SaaS brings us is being able to get our data and apps from any device or place – making life easier for businesses with multiple sites! But perhaps its greatest boon has got to be scalability; something we all appreciate in today’s world. Are there other benefits? Of course – just how many can you think of?!
Cloud Software as a Service (SaaS) offers businesses the convenience of being able to scale their operations up or down easily. Rather than having to purchase additional hardware and licences when needing more capacity, cloud SaaS gives companies much greater control and flexibility in how they choose to use it.
There are countless examples out there, from Salesforce for large enterprises right through to QuickBooks Online used by smaller firms – proving just how powerful this technology is in real-world applications. What’s more, you can make changes quickly without any costly investments! Regardless of the size or reach, these services are turning out to be progressively significant for organisations that need to remain competitive in today’s ever-changing commercial centre.
For example, a great deal of businesses presently use cloud-based CRM arrangements to monitor customer connections and smooth out deal forms. There are additionally various monetary administration instruments accessible that permit organizations to track expenses effectively and create nitty-gritty reports on their funds without requiring an entire bookkeeping office.
Another normal case of genuine utilization for cloud SaaS is content management systems (CMS). With such software, organisations can store data like images, videos etc., while simultaneously making them accessible across different platforms easily – how convenient would it be if you no longer worried about where your important files were stored!
These platforms allow organisations to quickly put together websites with a range of features without requiring extensive coding proficiency or exorbitantly priced web design firms. Even large media outlets such as The Washington Post have embraced WordPress as their CMS platform due to its convenience and comprehensive set of functions which make it perfect for web development projects big and small alike.
Finally, cloud SaaS has become an ideal solution for developers wanting to expeditiously deploy applications into production whilst still taking advantage of all security measures provided by their hosting provider through Infrastructure-as-a-Service (IaaS). Platforms like Google App Engine provide potent infrastructure services at merely a few clicks so that developers can cut straight into writing code instead of having to bother with server configuration tasks such as setting up firewalls or migrating databases from old hardware onto new machines – an intimidating prospect even for adept IT professionals! What’s more impressive is how effortless these processes have now become thanks to cutting-edge technology.
Challenges faced in deploying SaaS in cloud computing
Deploying SaaS (Software as a Service) in Cloud computing is gaining popularity due to its adaptability and on-demand scalability. But with these benefits come some difficulties that must be resolved for successful deployment of the software. The main challenge lies in keeping security while adhering to government regulations and industry standards.
Security vulnerabilities need to be minimised, so it’s essential to use encryption whenever doable along with strong authentication protocols such as passwords, 2FA (Two Factor Authentication), CAPTCHA or biometrics – all this just makes one think how vital are data security measures nowadays.
Moreover, businesses must make sure their data and applications are safeguarded properly and can’t be accessed by those not authorised to do so. To guarantee this, they need the correct hardware as well as software solutions in place along with robust regulations like encrypting data while it’s inactive or disk-level encryption which adds an extra layer of security. Additionally, there is a cost factor to consider; deploying SaaS may prove expensive due to licence fees plus other setup costs that come alongside it – making budgeting essential before implementation.
Companies must take into account the monetary effect of moving their existing workloads to SaaS before pledging as there could be obscure costs included, for example, extra capacity or continuous support necessities that should be taken into consideration in the general expenditure. Organizations also need to certify they can interconnect their current systems and procedures with the new SaaS provision without hindering activities or negatively influencing client experience which adds another layer of intricacy when it comes down to sending out.
It necessitates teams from different divisions such as IT, operations and customer service working together cooperatively so everyone can guarantee smooth integration across all frameworks engaged in deploying Software-as-a-Service (Saas) within a cloud computing environment – but this is no simple feat! How exactly would each department come together? What kind of steps do you have set up beforehand just for cases like this one?
Future trends in Cloud SaaS and cloud computing

The world of cloud computing is in a constant state of change. With the development and progress of technology, there are almost endless possibilities for Software as a Service (SaaS) companies and cloud computing to make use of. The phrase ‘cloud-native’ essentially describes applications and services which have been created with the intention that they will be run on various remote servers instead of being installed onto one system or contraption – this has major advantages for businesses who want to take advantage of all the mightiness offered by clouds but don’t necessarily have access to resources nor expertise necessary needed developing their solution.
Cloud SaaS, better known as “software as a service” is gaining more and more popularity among organisations seeking an economical way to make applications and data accessible from any part of the world. It gives firms the chance to shift their IT infrastructure requirements while providing customers with a safe and dependable platform where they can gain access to their apps and info.
Cloud SaaS could help companies cut back on expenses by getting rid of needing further hardware investments and diminishing labour costs which are connected to managing old-style server settings. So what does this mean? Well, it means that businesses have the possibility not only to save money but also expand efficiency without having to upgrade or maintain costly hardware infrastructures – sounds like good news all around!
Looking ahead, it is clear that SaaS and cloud computing are only going to become more interconnected. With the use of AI models set to revolutionize how companies process data, there will be a need for increased integration between different systems so they can feed into one another as efficiently as possible. This means we are likely to see greater automation both within services offered by providers and also across geographically distant areas too – making processes quicker and easier than ever before!
What’s more, applying artificial intelligence in this way could dramatically reduce costs associated with running certain operations; not least because fewer people or resources may be required for tasks to get done promptly. It will certainly make businesses far nimbler on their feet when changes arise suddenly or unexpected events occur!
AI can also be used to detect issues with existing software deployments at scale to pinpoint the areas that need more investment or development. In future, there will even be a bigger focus on security when it comes to SaaS deployment since more companies are increasingly reliant upon cloud-based services for their normal functioning. Thus, businesses have to ensure that they safeguard their data through rigorous authentication protocols along with end-to-end encryption systems so as not to let any unauthorised users or malicious elements access confidential information without permission.
Moreover, service providers must grant customers real-time access to their environment which allows them to monitor usage metrics and receive alerts if something strange occurs within those systems. All these advancements illustrate how far Cloud SaaS has come from its beginnings – but still, there’s much potential left unexploited within this flourishing technology sector!
Wrapping Up!
To sum up, Cloud Saas – which is also known as Software-as-a-Service – offers a fantastic cloud computing model that enables users to access applications remotely and securely with minimal initial expenditure. Businesses can take advantage of the additional storage options available, data-sharing capabilities and improved security measures without having to worry about maintaining large IT infrastructures. What’s more, this useful tool is highly scalable too so it won’t break the bank! All in all, if you’re an entrepreneur keen on making use of computer technology for increased effectiveness and scalability then there’s no doubt Cloud SaaS should be your first choice!
Are you keen to be a Cloud Architect? We have the perfect programme for anyone eager to get the skills and knowledge needed in this field. Our comprehensive training materials combined with experienced instruction, will help you understand cloud infrastructure design, implementation, security and optimisation.
And once completed our program should make sure you feel capable of taking on any opportunity that comes your way as a confident cloud architect – so join us now! Enrolling today means tapping into our wealth of expertise and starting on an exciting journey towards becoming a top-notch Cloud Architect professional. Don’t hesitate; sign up right away!
Happy Learning!