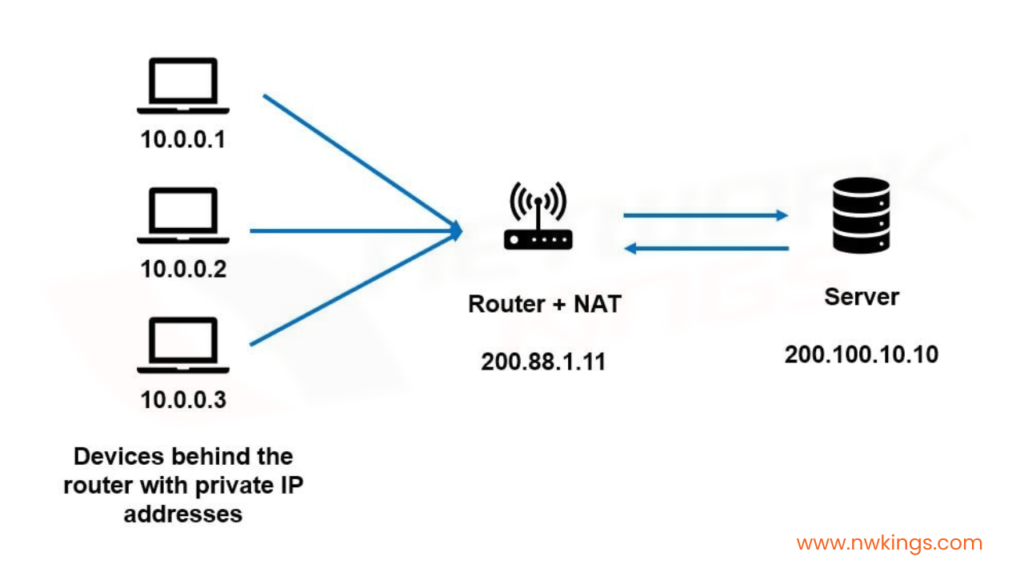
We all know that Private Addresses are not routable to the internet, but within a LAN network, we always use Private IP Addresses. Sounds contradictory?
How can a PC configured with a Private Address access the internet? To solve this purpose NAT got introduced.
What is Network Address Translation?
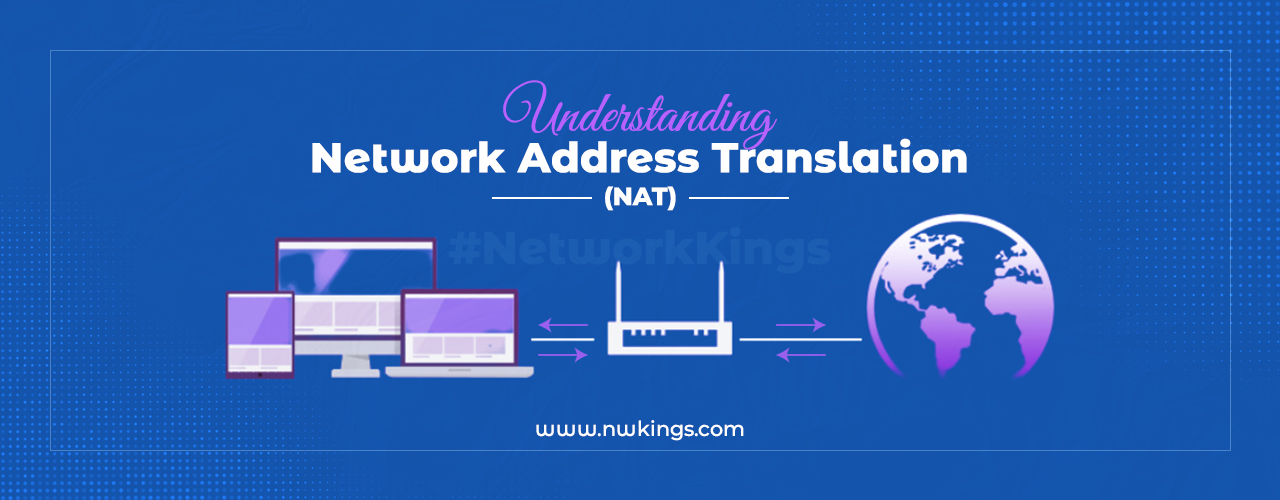
Network Address Translation (NAT) is a protocol used to translate Private IP Addresses to Public IP Addresses. NAT gets configured on the gateway router; hence, the gateway router performs the translation.
History:
NAT was introduced to slow down the depletion rate of IP Addresses by translating all the Private IP Addresses in a LAN to a smaller number of Public IP Addresses. Initially, when the internet got introduced the number of devices was low. Therefore, it was possible to assign each device a unique IP Address. But as the internet became popular, devices increase, and IPv4 was not enough to provide each device with a unique IP Address simultaneously.
Case 1:
Private IP Addresses are non-routable and are used by hosts to communicate with each other but cannot be used to access the internet. LAN networks of multiple organizations can have the same Private IP Address simultaneously without any issue, which somewhat solves the problem of scarcity of IP Addresses.
Case 2:
Public IP Addresses are routable IP Addresses. If a host wants to route to the internet, it requires Public IP Address. Public IP Address is unique to a host and cannot get used by another host. ISP (Internet Service Provider) manages the task of providing a Public IP Address. Also, Public IP Addresses are not free. They get managed by an authority known as IANA (Internet Assigned Numbers Authority).
Since every host in a LAN has a Private IP Address, but to route to the internet, Public IP Address is required, a concept known as Network Address Translation gets used.
As shown in the figure, NAT will get configured on the gateway router (connected to ISP/Internet). In our home networks, the WIFI router is our home network gateway.
What is the concept of NAT?
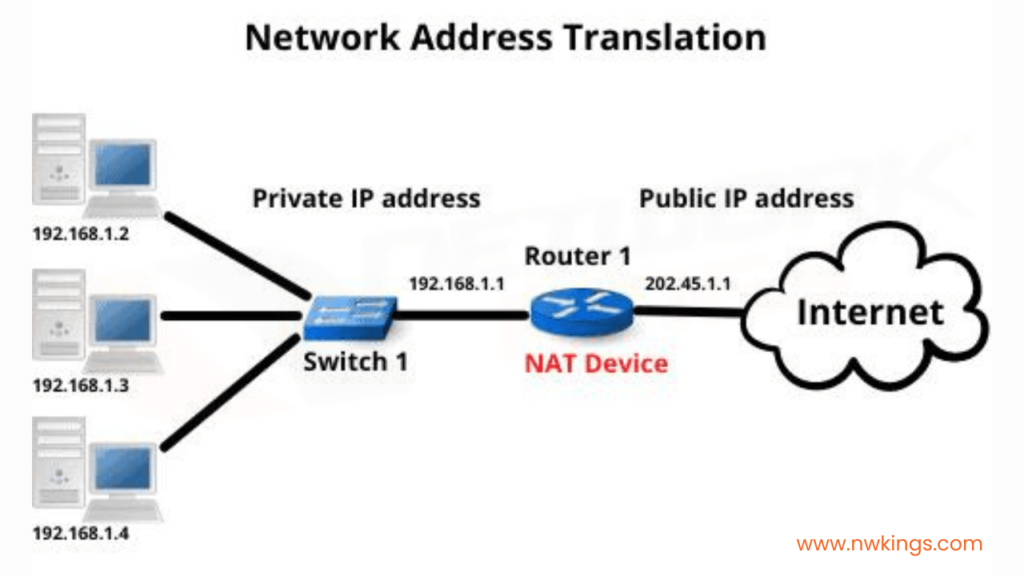
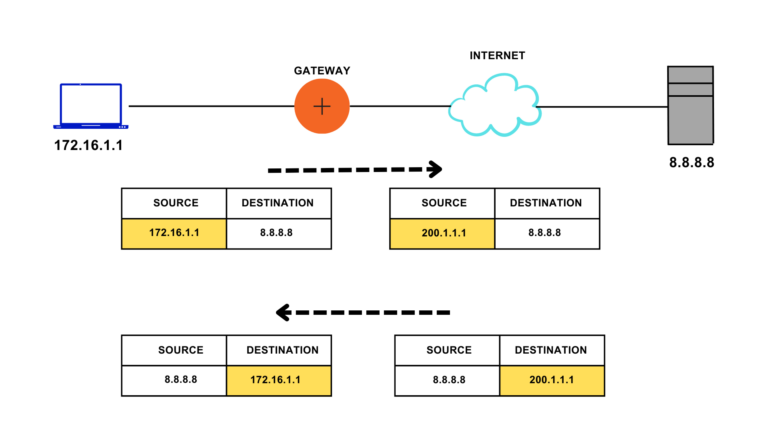
Network Address Translation converts the Private IP Address of the host, which is the non-routable address, to the Public IP Address. Let us see what changes occur in a packet. A router configured with NAT changes the source IP Address when the packet goes out to the internet and changes the destination address of the packet when it comes into a LAN Network.
For instance: – In the given figure, the host sends out a packet with source address 172.16.1.1 and destination address 8.8.8.8. Notice that the router performing the NAT translates the source address from 172.16.1.1 to 200.1.1.1. So, for servers with IP Address 8.8.8.8, the source address is 200.1.1.1 and not 172.16.1.1. The server sends out a packet with the destination address 200.1.1.1. When this packet arrives at the gateway, it converts its destination address from 200.1.1.1 to 172.16.1.1.
What is an Inside Local Address?
A private IP Address assigned to the host is known as an Inside Local IP Address since the host with this IP Address is inside a local network. This IP Address is not routable and is used to communicate in a LAN network.
What is an Inside Global Address?
The Inside Global Address gets assigned to a local host by the gateway when it communicates with the outside world, i.e., the Internet. These are routable IP Addresses assigned by the internet service provider. This IP Address identifies devices from outside the private network.
NOTE: In the above example, 200.1.1.1 is the Inside Global IP Address.
What is an Outside Global Address?
Outside Global Address is the Public IP Address assigned to the host outside the private network. It is generally the IP Address of the destination to which the local host of the LAN wants to reach. This IP Address is not translated by NAT.
NOTE: In the above example, 8.8.8.8 is the Outside global IP Address.
What are the types of Network Address Translation?
The kinds of Network Address Translation (NAT) are as follows-
- Static NAT
- Dynamic NAT
- Port Address Translation or NAT Overload
What is Static NAT?
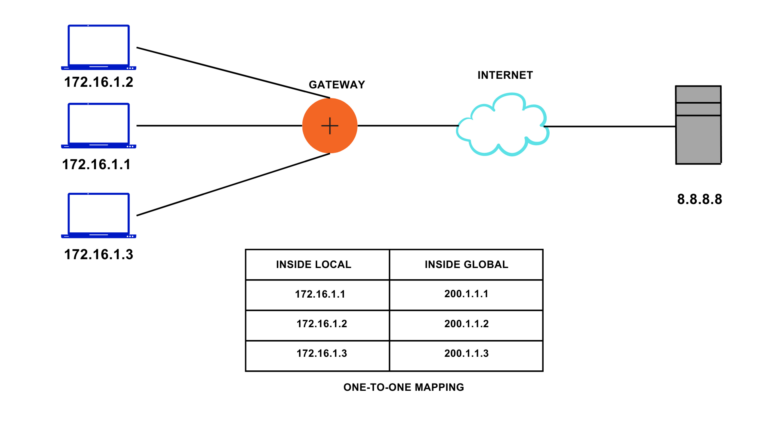
Static NAT gets used for a one-to-one mapping of local IP Addresses with Global IP Addresses, i.e., it maps the Private IP Address of a LAN to Public IP Address. In the case of static NAT, each private IP Address requires a unique public IP Address. If there are N devices in an organization, N number of Public IP Address are required, and each Private IP Address gets mapped to a unique Public IP Address. Hence it is not used in an organization where many devices are needed to route the internet. Static NAT is used for Web hosting to configure a server.
In given figure, IP Address 172.16.1.1 , 172.16.1.2, 172.16.1.3 is one-to-one mapped with 200.1.1.1, 200.1.1.2, 200.1.1.3 respectively.
What is Dynamic NAT?
Dynamic NAT is like static NAT. It also provides a one-to-one mapping of Private IP Addresses to Public IP Addresses, but mapping inside local addresses to inside global addresses is done dynamically. Unlike Static NAT, mapping is not permanent.
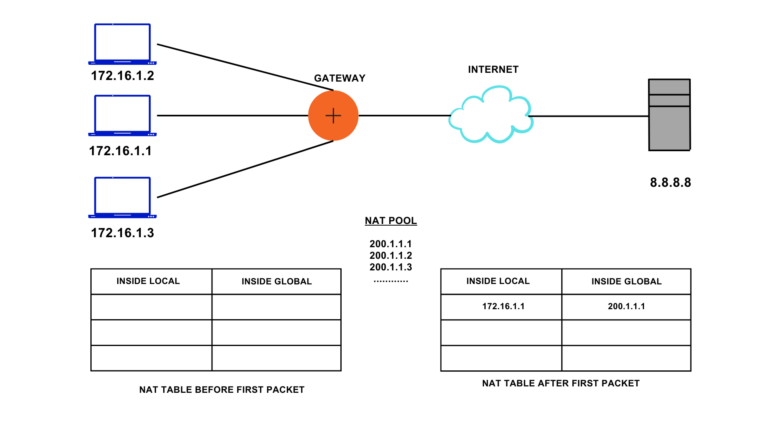
Suppose the Host with IP Address 172.16.1.1 sends a packet to 8.8.8.8. as the packet enters the gateway (i.e., a router in which NAT gets configured). Since the router gets configured to translate an inside local address to an inside global address, i.e., Private IP Address to Public IP Address, it will search for available inside global addresses from a pool of Global Addresses provided by the ISP. It adds an inside Local Address and inside Global Address to its entry and translates the source IP Address by forwarding the packet.
Entry remains in the table if traffic occasionally flows. Once the timeout value, i.e., how long a router should wait, is over, the entry gets removed from the table, and that particular Inside Global IP is free to use for some other Inside Local IP Address. If all the inside global IP gets utilized and a new packet with a different inside local source address comes to the gateway, the packet gets discarded, and the host must retry till the inside global IP Address is free.
In the given figure, initially, the NAT table is empty. Once the first packet arrives from the host, gateway looks for the available Inside Global IP Address from the pool of IP Address, and translates the inside local IP Address, i.e., 172.16.1.1 to 200.1.1.1. It also maintains an entry in its NAT table which also help to retranslate Inside Global IP Address to the Inside Local IP Address and reach the correct host. A similar process gets followed when another host sends out the packet.
What is Port Address Translation or NAT Overload?
Both Static NAT and Dynamic NAT have some limitations. To overcome them, NAT overload is introduced.
In most of the network, almost every host needs to reach the internet. For that purpose, NAT routers need a large pool of inside global IP Addresses.
Case 1:
In the case of Static NAT, each host requires a unique public registered global IP Address, which does not limit the number of Public IP Addresses required and is also very costly.
Case 2:
In the case of Dynamic NAT, whenever a host is not routing the internet, the Inside Global IP Address becomes free, reducing the need for Public IP Address, but still, an organization must have a large pool of Public IP Addresses. Again, it fails to reduce the number of Public IP Addresses.
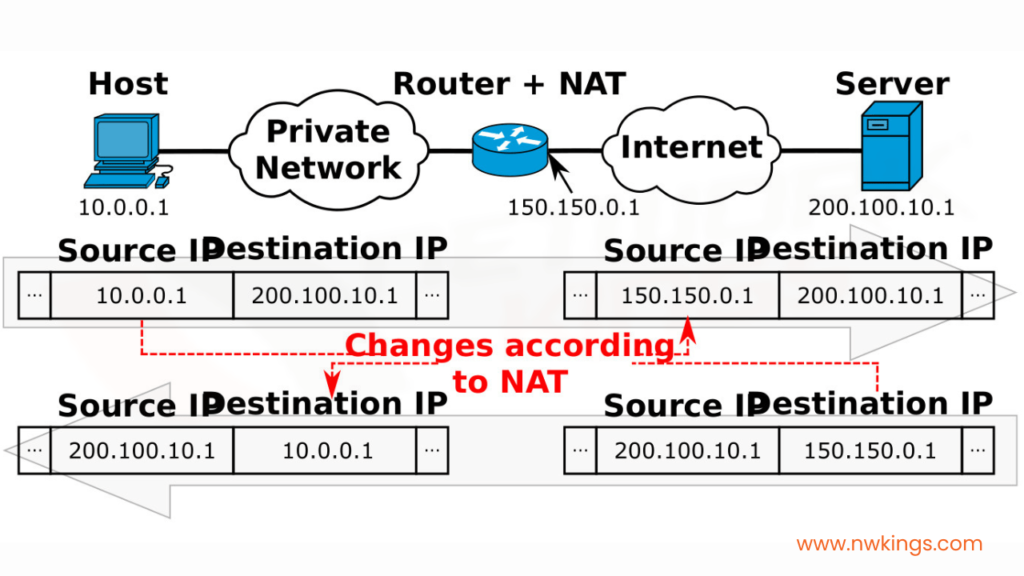
NAT Overload /PAT solves this problem allowing many hosts to use a limited number of Public IP Addresses. It uses the Transport layer protocols concept, i.e., TCP and UDP. It not only translates the IP Address but also assigns a unique port number to it, which makes the packet flow from different hosts look like a packet flow from a single host.
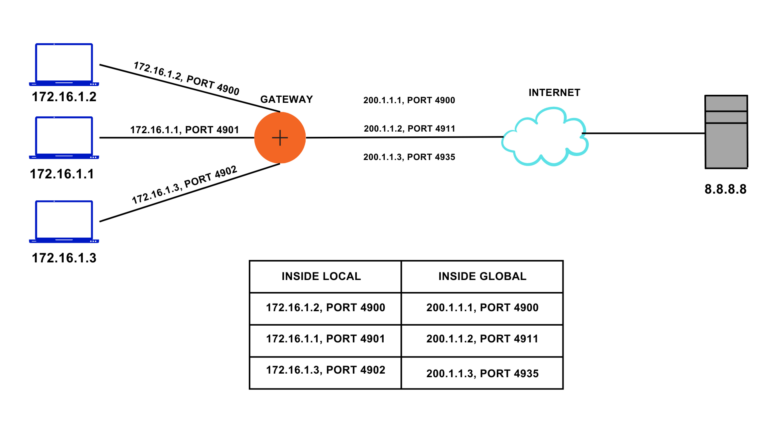
When Port Address Translation dynamically maps the IP Address, it also assigns a unique port to that IP Address. NAT table keeps every entry of inside local and inside global addresses along with the port number associated with it to identify the packet from each host. Since the Port number is 16bits, more than 65000 unique port numbers can be assigned, which drastically reduces the use of different Public IP Addresses. Each host can have the same Public IP Address.
NOTE: Gateway can distinguish between the packets of the host by using the port number since the port number is unique for each host.
In given figure, Port 4900, 4901,4902 are assigned to the Inside Local IP Address 172.16.1.2, 172.16.1.1,172.16.1.3, respectively. Ports assigned to the Inside Global IP Addresses may or may not be the same like the Inside Local IP Addresses. Gateway maintains the NAT table to translate incoming and outgoing packets properly.
Among all the three types of NAT, Port Address Translation is widely used because Static and Dynamic NAT both require one-one-mapping of IP Addresses, which fails to reduce the number of Public IP Addresses required. Since Port Address Translation assigns a port to IP Address, it drastically reduces the use of a Public IP Address.
NOTE: In small networks, even a single Public IP Address can fulfill the need.